Product Description
High quality For CZPT hilux front axle Factory direct sale CV axle drive shaft for CZPT hilux OEM 43430-0K571
HangZhou CZPT Auto Parts Co., Ltd.Our Factory Main Products with CZPT pickup trucks,hilux,vigo,revo,rocco,prado land cruiser ,nissan NAVARA CZPT D-MAX ,FORD RANGER Series full vehicle accessories.
HangZhou CZPT Auto Parts Co., Ltd. is a professional and leading company specialized in auto spare parts sales since 2571 in HangZhou of China.Our company specialized in products such as spark plug, ignition coil,brake padsoxygen sensor, handbrake cable,air conditioner filter,cylinder assy,suspension part,HID bulbs etc for Toyota, Honda, Nissan, MAZDA, MITSUBISHI, HYUNDAI, MERCEDES Benz, BMW, Volkswagen and so on. We always keep a stable and long term cooperation with many factories for meeting our customers various requirements.
Q: What’s your MOQ?
A: MOQ usually is 20 pieces. (depend on which products you need)
Q: What’s your Payment terms?
A: 30% deposit, 70% balance payment before shipment.
Q: What payment method you accept?
A: Bank Tranfer, T/T, Credit Card, PayPal. Western Union.
Q: How do you control your quality?
A: All products were produced in high standards, and has passed component tests, unfinished tests and 100% products testing before delivery.
Q: How do you ship goods?
A: if you have shipping agent in China, we can send goods to your agent warehouse. If don’t have agent, we will long cooperated shipping company, you can choose by DHL, Fedex, or UPS. or shipping by sea, we will give you several solutions to choose.
Q: Can we customized the length, size or with different materials?
A: Yes, we will try our best to meet most of your needs.
Q: Can you produce the same product as mine if I provide you a sample?
A: Yes, we are capable of producing the electric parts for the most products.
Q: Can you provide me free sample first?
A: It depends on the sample’s cost, normally we can, but client need to pay the shipping cost.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online Support |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | CE |
| Type: | Universal Joint |
| Application Brand: | Toyota |
| Samples: |
US$ 26.88/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can drivelines be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings?
Drivelines can indeed be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings. While there are some differences in the specific requirements and design considerations between these two applications, many fundamental principles and components of drivelines remain applicable to both sectors. Let’s explore how drivelines can be adapted for use in automotive and industrial settings:
1. Power Transmission:
In both automotive and industrial applications, drivelines serve the purpose of transmitting power from a source (such as an engine or motor) to various driven components. The driveline components, including transmissions, clutches, differentials, and shafts, can be adapted and optimized based on the specific power requirements and operating conditions of each application. While automotive drivelines typically focus on delivering power for propulsion, industrial drivelines may transmit power to various machinery and equipment.
2. Gearboxes and Transmissions:
Both automotive and industrial drivelines often incorporate gearboxes or transmissions to provide multiple gear ratios for efficient power transfer. However, the gear ratios and design considerations may differ based on the specific requirements of each application. Automotive drivelines are typically optimized for a wide range of operating conditions, including varying speeds and loads. Industrial drivelines, on the other hand, may be designed to meet specific torque and speed requirements of industrial machinery.
3. Shaft and Coupling Systems:
Shafts and coupling systems are essential components of drivelines in both automotive and industrial settings. They transmit power between different components and allow for misalignment compensation. While automotive drivelines often use driveshafts and universal joints to transmit power to the wheels, industrial drivelines may employ shafts, couplings, and flexible couplings to connect various machinery components such as motors, pumps, and generators.
4. Differentiated Requirements:
Automotive and industrial drivelines have different operating conditions, load requirements, and environmental considerations. Automotive drivelines need to accommodate various road conditions, vehicle dynamics, and driver comfort. Industrial drivelines, on the other hand, may operate in more controlled environments but are subjected to specific industry requirements, such as high torque, continuous operation, or exposure to harsh conditions. The driveline components and materials can be adapted accordingly to meet these different requirements.
5. Control and Monitoring Systems:
Both automotive and industrial drivelines can benefit from advanced control and monitoring systems. These systems can optimize power distribution, manage gear shifts, monitor component health, and improve overall driveline efficiency. In automotive applications, electronic control units (ECUs) play a significant role in controlling driveline functions, while industrial drivelines may incorporate programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or other specialized control systems.
6. Customization and Integration:
Drivelines can be customized and integrated into specific automotive and industrial applications. Automotive drivelines can be tailored to meet the requirements of different vehicle types, such as passenger cars, trucks, or sports vehicles. Industrial drivelines can be designed to integrate seamlessly with specific machinery and equipment, considering factors such as available space, power requirements, and maintenance accessibility.
7. Maintenance and Service:
While the specific maintenance requirements may vary, both automotive and industrial drivelines require regular inspection, lubrication, and component replacement to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper maintenance practices, as discussed earlier, are essential for prolonging the lifespan of driveline components in both settings.
In summary, drivelines can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings by considering the unique requirements and operating conditions of each application. While there are some differences in design considerations and component selection, the fundamental principles of power transmission and driveline functionality remain applicable in both sectors.

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with driveline systems?
While driveline systems offer numerous advantages in terms of power transmission and vehicle performance, there are also some limitations and disadvantages associated with their use. It’s important to consider these factors when designing, operating, and maintaining driveline systems. Let’s explore some of the limitations and disadvantages:
1. Complex Design and Integration:
Driveline systems can be complex in design, especially in modern vehicles with advanced technologies. They often consist of multiple components, such as transmissions, differentials, transfer cases, and drive shafts, which need to be properly integrated and synchronized. The complexity of the driveline system can increase manufacturing and assembly challenges, as well as the potential for compatibility issues or failures if not designed and integrated correctly.
2. Energy Losses:
Driveline systems can experience energy losses during power transmission. These losses occur due to factors such as friction, heat generation, mechanical inefficiencies, and fluid drag in components like gearboxes, differentials, and torque converters. The energy losses can negatively impact overall efficiency and result in reduced fuel economy or power output, especially in systems with multiple driveline components.
3. Limited Service Life and Maintenance Requirements:
Driveline components, like any mechanical system, have a limited service life and require regular maintenance. Components such as clutches, bearings, gears, and drive shafts are subject to wear and tear, and may need to be replaced or repaired over time. Regular maintenance, including lubrication, adjustments, and inspections, is necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failures. Failure to perform proper maintenance can lead to driveline malfunctions, increased downtime, and costly repairs.
4. Weight and Space Constraints:
Driveline systems add weight and occupy space within a vehicle. The additional weight affects fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Moreover, the space occupied by driveline components can limit design flexibility, particularly in compact or electric vehicles where space optimization is crucial. Manufacturers must strike a balance between driveline performance, vehicle weight, and available space to meet the requirements of each specific vehicle type.
5. Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH):
Driveline systems can generate noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) during operation. Factors such as gear meshing, unbalanced rotating components, or improper driveline alignment can contribute to unwanted vibrations or noise. NVH issues can affect driving comfort, passenger experience, and vehicle refinement. Manufacturers employ various techniques, including vibration dampening materials, isolators, and precision engineering, to minimize NVH levels, but achieving complete elimination can be challenging.
6. Limited Torque Handling Capability:
Driveline systems have limitations in terms of torque handling capability. Excessive torque beyond the rated capacity of driveline components can lead to failures, such as shearing of gears, clutch slippage, or drive shaft breakage. High-performance vehicles or heavy-duty applications may require specialized driveline components capable of handling higher torque loads, which can increase costs and complexity.
7. Traction Limitations:
Driveline systems, particularly in vehicles with two-wheel drive configurations, may experience traction limitations, especially in slippery or off-road conditions. Power is typically transmitted to only one or two wheels, which can result in reduced traction and potential wheel slippage. This limitation can be mitigated by utilizing technologies such as limited-slip differentials, electronic traction control, or implementing all-wheel drive systems.
While driveline systems provide crucial power transmission and vehicle control, they do have limitations and disadvantages that need to be considered. Manufacturers, designers, and operators should carefully assess these factors and implement appropriate design, maintenance, and operational practices to optimize driveline performance, reliability, and overall vehicle functionality.

What is a driveline and how does it function in vehicles and machinery?
A driveline, also known as a drivetrain, refers to the components and systems responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels or tracks in vehicles and machinery. It encompasses various elements such as the engine, transmission, drive shafts, differentials, axles, and wheels or tracks. The driveline plays a crucial role in converting the engine’s power into motion and enabling the vehicle or machinery to move. Here’s a detailed explanation of how the driveline functions in vehicles and machinery:
1. Power Generation: The driveline starts with the engine, which generates power by burning fuel or utilizing alternative energy sources. The engine produces rotational force, known as torque, which is transferred to the driveline for further transmission to the wheels or tracks.
2. Transmission: The transmission is a crucial component of the driveline that controls the distribution of power and torque from the engine to the wheels or tracks. It allows the driver or operator to select different gear ratios to optimize performance and efficiency based on the vehicle’s speed and load conditions. The transmission can be manual, automatic, or a combination of both, depending on the specific vehicle or machinery.
3. Drive Shaft: The drive shaft, also called a propeller shaft, is a rotating mechanical component that transmits torque from the transmission to the wheels or tracks. In vehicles with rear-wheel drive or four-wheel drive, the drive shaft transfers power to the rear axle or all four wheels. In machinery, the drive shaft may transfer power to the tracks or other driven components. The drive shaft is typically a tubular metal shaft with universal joints at each end to accommodate the movement and misalignment between the transmission and the wheels or tracks.
4. Differential: The differential is a device located in the driveline that enables the wheels or tracks to rotate at different speeds while still receiving power. It allows the vehicle or machinery to smoothly negotiate turns without wheel slippage or binding. The differential consists of a set of gears that distribute torque between the wheels or tracks based on their rotational requirements. In vehicles with multiple axles, there may be differentials on each axle to provide power distribution and torque balancing.
5. Axles: Axles are shafts that connect the differential to the wheels or tracks. They transmit torque from the differential to the individual wheels or tracks, allowing them to rotate and propel the vehicle or machinery. Axles are designed to withstand the loads and stresses associated with power transmission and wheel movement. They may be solid or independent, depending on the vehicle or machinery’s suspension and drivetrain configuration.
6. Wheels or Tracks: The driveline’s final components are the wheels or tracks, which directly contact the ground and provide traction and propulsion. In vehicles with wheels, the driveline transfers power from the engine to the wheels, allowing them to rotate and propel the vehicle forward or backward. In machinery with tracks, the driveline transfers power to the tracks, enabling the machinery to move over various terrains and surfaces.
7. Functioning: The driveline functions by transmitting power from the engine through the transmission, drive shaft, differential, axles, and finally to the wheels or tracks. As the engine generates torque, it is transferred through the transmission, which selects the appropriate gear ratio based on the vehicle’s speed and load. The drive shaft then transfers the torque to the differential, which distributes it between the wheels or tracks according to their rotational requirements. The axles transmit the torque from the differential to the individual wheels or tracks, allowing them to rotate and propel the vehicle or machinery.
8. Four-Wheel Drive and All-Wheel Drive: Some vehicles and machinery are equipped with four-wheel drive (4WD) or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, which provide power to all four wheels simultaneously. In these systems, the driveline includes additional components such as transfer cases and secondary differentials to distribute power to the front and rear axles. The driveline functions similarly in 4WD and AWD systems, but with enhanced traction and off-road capabilities.
In summary, the driveline is a vital component in vehicles and machinery, responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels or tracks. It involves the engine, transmission, drive shafts, differentials, axles, and wheels or tracks. By efficiently transferring torque and power, the driveline enables vehicles and machinery to move, providing traction, propulsion, and control. The specific configuration and components of the driveline may vary depending on the vehicle or machinery’s design, purpose, and drive system.


editor by CX 2024-03-26
China Custom Harvester Farm Harrow Tractor Pto Drive Shaft and Power Tiller Cardan Shaft for Agricultural Machinery Spare Parts Drive Line
Product Description
Harvester Farm Harrow Tractor Pto Drive Shaft and Power Tiller Cardan Shaft for Agricultural Machinery Spare Parts
Product Description
A Power Take-Off shaft (PTO shaft) is a mechanical device utilized to transmit power from a tractor or other power source to an attached implement, such as a mower, tiller, or baler. Typically situated at the rear of the tractor, the PTO shaft is driven by the tractor’s engine through the transmission.
The primary purpose of the PTO shaft is to supply a rotating power source to the implement, enabling it to carry out its intended function. To connect the implement to the PTO shaft, a universal joint is employed, allowing for movement between the tractor and the implement while maintaining a consistent power transfer.
Here is our advantages when compare to similar products from China:
1.Forged yokes make PTO shafts strong enough for usage and working;
2.Internal sizes standard to confirm installation smooth;
3.CE and ISO certificates to guarantee to quality of our goods;
4.Strong and professional package to confirm the good situation when you receive the goods.
Product Specifications
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
HangZhou Hanon Technology Co.,ltd is a modern enterprise specilizing in the development,production,sales and services of Agricultural Parts like PTO shaft and Gearboxes and Hydraulic parts like Cylinder , Valve ,Gearpump and motor etc..
We adhere to the principle of ” High Quality, Customers’Satisfaction”, using advanced technology and equipments to ensure all the technical standards of transmission .We follow the principle of people first , trying our best to set up a pleasant surroundings and platform of performance for each employee. So everyone can be self-consciously active to join Hanon Machinery.
FAQ
1.What’re your main products?
we currently product Agricultural Parts like PTO shaft and Gearboxes and Hydraulic parts like Cylinder , Valve ,Gear pump and motor.You can check the specifications for above product on our website and you can email us to recommend needed product per your specification too.
2.What’s the lead time for a regular order?
Generally speaking, our regular standard product will need 30-45days, a bit longer for customized products. But we are very flexible on the lead time, it will depend on the specific orders.
3.What’s your warranty terms?
One year.
4.Can you send me a price list?
For all of our product, they are customized based on different requirements like length, ratio,voltage,and power etc. The price also varies according to annual quantity. So it’s really difficult for us to provide a price list. If you can share your detailed requirements and annual quantity, we’ll see what offer we can provide.
5.What’s the payment term?
When we quote for you,we will confirm with you the way of transaction,FOB,CIFetc.<br> For mass production goods, you need to pay 30% deposit before producing and70% balance against copy of documents.The most common way is by T/T.
6.How to deliver the goods to us?
Usually we will ship the goods to you by sea.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Agricultural Spare Part, Agricultural Spare Part |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Agricultural Products Processing, Farmland Infrastructure, Tillage, Harvester, Planting and Fertilization, Grain Threshing, Cleaning and Drying, Agricultural Machinery,Farm Tractor, Agricultural Products Processing, Farmland Infrastructure, Tillage, Harvester, Planting and Fertilization, Grain Threshing, Cleaning and Drying, Agricultural Machinery, Farm Tractor |
| Material: | Carbon Steel, 45cr Steel, Carbon Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 20/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What maintenance practices are essential for prolonging the lifespan of driveline components?
Implementing proper maintenance practices is crucial for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of driveline components. Regular maintenance helps identify potential issues, prevent major failures, and prolong the lifespan of driveline components. Here are some essential maintenance practices for prolonging the lifespan of driveline components:
1. Regular Inspections:
Performing regular visual inspections of driveline components is essential for detecting any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the driveline components, including driveshafts, universal joints, CV joints, differentials, and transmission components, for any cracks, leaks, excessive play, or unusual noise. Identifying and addressing issues early can prevent further damage and potential driveline failure.
2. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication of driveline components is crucial for minimizing friction, reducing wear, and ensuring smooth operation. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and use the appropriate type and grade of lubricant. Regularly check and maintain the lubrication levels in components such as bearings, gears, and joints to prevent excessive heat buildup and premature wear.
3. Fluid Changes:
Fluids play a vital role in driveline component performance and longevity. Regularly change fluids, such as transmission fluid, differential oil, and transfer case fluid, according to the manufacturer’s recommended intervals. Over time, these fluids can become contaminated or break down, leading to compromised performance and increased wear. Fresh fluids help maintain proper lubrication, cooling, and protection of driveline components.
4. Alignment and Balancing:
Proper alignment and balancing of driveline components are essential for minimizing vibration, reducing stress, and preventing premature wear. Periodically check and adjust the alignment of driveshafts, ensuring they are properly aligned with the transmission and differential. Additionally, balance rotating components, such as driveshafts or flywheels, to minimize vibrations and prevent excessive stress on driveline components.
5. Torque Check:
Regularly check and ensure that all driveline components are properly torqued according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Over time, fasteners can loosen due to vibrations or thermal expansion and contraction. Loose fasteners can lead to misalignment, excessive play, or even component failure. Regular torque checks help maintain the integrity and performance of the driveline system.
6. Maintenance of Supporting Systems:
Driveline components rely on the proper functioning of supporting systems, such as cooling systems and electrical systems. Ensure that cooling systems are functioning correctly, as overheating can cause driveline components to degrade or fail. Additionally, regularly inspect electrical connections, wiring harnesses, and sensors to ensure proper communication and operation of driveline components.
7. Proper Driving Techniques:
The way a vehicle is driven can significantly impact the lifespan of driveline components. Avoid aggressive driving, sudden acceleration, and excessive braking, as these actions can put undue stress on the driveline components. Smooth and gradual acceleration, proper shifting techniques, and avoiding excessive load or towing capacities help minimize wear and prolong component life.
8. Service and Maintenance Records:
Maintain comprehensive service and maintenance records for the driveline components. Keep track of all maintenance tasks, repairs, fluid changes, and inspections performed. These records help ensure that maintenance tasks are performed on time, provide a history of component performance, and assist in diagnosing any recurring issues or patterns.
By following these maintenance practices, vehicle owners can prolong the lifespan of driveline components, minimize the risk of failures, and ensure optimal performance and reliability of the driveline system.

How do drivelines enhance the performance of different types of vehicles?
Drivelines significantly contribute to enhancing the performance of different types of vehicles by optimizing power delivery, improving traction, and tailoring the driving characteristics to suit specific needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drivelines enhance performance in various vehicle types:
1. Passenger Cars:
In passenger cars, driveline configurations, such as front-wheel drive (FWD), rear-wheel drive (RWD), and all-wheel drive (AWD), play a crucial role in performance. Here’s how drivelines enhance performance in passenger cars:
- FWD: Front-wheel drive systems provide better traction and stability, particularly in adverse weather conditions. FWD drivelines distribute weight more evenly over the front wheels, resulting in improved grip during acceleration and cornering.
- RWD: Rear-wheel drive drivelines offer better weight distribution, allowing for improved handling and balanced performance. RWD vehicles typically exhibit better acceleration and a more engaging driving experience, especially in performance-oriented cars.
- AWD: All-wheel drive drivelines deliver power to all four wheels, improving traction and stability in various driving conditions. AWD systems enhance performance by maximizing grip and providing optimal power distribution between the front and rear wheels.
2. Sports Cars and Performance Vehicles:
Driveline systems in sports cars and performance vehicles are designed to enhance acceleration, handling, and overall driving dynamics. Key features include:
- Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD): RWD drivelines are often favored in sports cars for their ability to deliver power to the rear wheels, resulting in better weight transfer during acceleration and improved handling characteristics.
- Performance-oriented AWD: Some high-performance vehicles employ advanced AWD systems that can variably distribute torque between the front and rear wheels. These systems enhance traction, stability, and cornering capabilities, allowing for superior performance on both dry and slippery surfaces.
- Torque Vectoring: Certain driveline systems incorporate torque vectoring technology, which actively varies the torque distribution between wheels. This enables precise control during cornering, reducing understeer and enhancing agility and stability.
3. Off-Road Vehicles:
Drivelines in off-road vehicles are designed to provide exceptional traction, durability, and maneuverability in challenging terrains. Key features include:
- Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) and All-Wheel Drive (AWD): 4WD and AWD drivelines are commonly used in off-road vehicles to improve traction on uneven surfaces. These drivelines distribute power to all wheels, allowing for better grip and enhanced off-road capability.
- Differential Locks: Off-road drivelines often incorporate differential locks that can be engaged to lock the wheels on an axle together. This feature ensures that power is evenly distributed to all wheels, maximizing traction and overcoming challenging obstacles.
- High Ground Clearance: Drivelines in off-road vehicles are designed to accommodate higher ground clearance, allowing for improved approach, departure, and breakover angles. This design feature enhances the vehicle’s ability to navigate over rough terrain without damaging the driveline components.
4. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Drivelines in trucks and commercial vehicles are engineered to provide high torque delivery, durability, and efficiency. Key features include:
- High Torque Handling: Drivelines in trucks and commercial vehicles are designed to handle high torque outputs from powerful engines, enabling efficient towing, hauling, and overall performance.
- Transmission Options: Drivelines in trucks often feature transmissions with multiple gear ratios, allowing drivers to select the appropriate gear for different load conditions. This enhances performance, fuel efficiency, and overall drivability.
- Efficient Power Transfer: Drivelines in commercial vehicles focus on maximizing power transfer efficiency, minimizing energy losses, and optimizing fuel economy. This is achieved through the use of efficient transmission designs, low-friction components, and advanced control systems.
5. Electric and Hybrid Vehicles:
Drivelines in electric and hybrid vehicles play a crucial role in delivering power from the electric motor(s) to the wheels. Key features include:
- Instant Torque: Electric drivelines offer instant torque delivery, providing quick acceleration andresponsive performance. This enhances the driving experience and allows for swift overtaking and merging.
- Regenerative Braking: Electric and hybrid drivelines can incorporate regenerative braking systems, which convert kinetic energy during braking into electrical energy. This improves overall efficiency and extends the vehicle’s range.
- Multi-Motor Systems: Some electric and hybrid drivelines utilize multiple motors to drive different axles or wheels independently. This enables advanced torque vectoring and enhances handling, stability, and traction control.
These are just a few examples of how drivelines enhance the performance of different types of vehicles. Driveline configurations, technologies, and engineering considerations are tailored to each vehicle type, optimizing power delivery, handling, traction, and other performance characteristics specific to their intended use and market segment.

Which industries and vehicles commonly use drivelines for power distribution?
Drivelines are widely used in various industries and vehicles for power distribution. They play a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine or power source to the driven components, enabling motion and torque transfer. Here’s a detailed explanation of the industries and vehicles that commonly utilize drivelines for power distribution:
1. Automotive Industry: The automotive industry extensively utilizes drivelines in passenger cars, commercial vehicles, and off-road vehicles. Drivelines are a fundamental component of vehicles, enabling power transmission from the engine to the wheels. They are found in a range of vehicle types, including sedans, SUVs, pickup trucks, vans, buses, and heavy-duty trucks. Drivelines in the automotive industry are designed to provide efficient power distribution, enhance vehicle performance, and ensure smooth acceleration and maneuverability.
2. Agricultural Industry: Drivelines are essential in the agricultural industry for various farming machinery and equipment. Tractors, combines, harvesters, and other agricultural machinery rely on drivelines to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks. Drivelines in agricultural equipment often incorporate power take-off (PTO) units, allowing the connection of implements such as plows, seeders, and balers. These drivelines are designed to handle high torque loads, provide traction in challenging field conditions, and facilitate efficient farming operations.
3. Construction and Mining Industries: Drivelines are extensively used in construction and mining equipment, where they enable power distribution and mobility in heavy-duty machinery. Excavators, bulldozers, wheel loaders, dump trucks, and other construction and mining vehicles rely on drivelines to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks. Drivelines in these industries are designed to withstand rigorous operating conditions, deliver high torque and traction, and provide the necessary power for excavation, hauling, and material handling tasks.
4. Industrial Equipment: Various industrial equipment and machinery utilize drivelines for power distribution. This includes material handling equipment such as forklifts and cranes, industrial trucks, conveyor systems, and industrial vehicles used in warehouses, factories, and distribution centers. Drivelines in industrial equipment are designed to provide efficient power transmission, precise control, and maneuverability in confined spaces, enabling smooth and reliable operation in industrial settings.
5. Off-Road and Recreational Vehicles: Drivelines are commonly employed in off-road and recreational vehicles, including all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), side-by-side vehicles (UTVs), dirt bikes, snowmobiles, and recreational boats. These vehicles require drivelines to transfer power from the engine to the wheels, tracks, or propellers, enabling off-road capability, traction, and water propulsion. Drivelines in off-road and recreational vehicles are designed for durability, performance, and enhanced control in challenging terrains and recreational environments.
6. Railway Industry: Drivelines are utilized in railway locomotives and trains for power distribution and propulsion. They are responsible for transmitting power from the locomotive’s engine to the wheels or driving systems, enabling the movement of trains on tracks. Drivelines in the railway industry are designed to handle high torque requirements, ensure efficient power transfer, and facilitate safe and reliable train operation.
7. Marine Industry: Drivelines are integral components in marine vessels, including boats, yachts, ships, and other watercraft. Marine drivelines are used for power transmission from the engine to the propellers or water jets, providing thrust and propulsion. They are designed to withstand the corrosive marine environment, handle high torque loads, and ensure efficient power transfer for marine propulsion.
These are some of the industries and vehicles that commonly rely on drivelines for power distribution. Drivelines are versatile components that enable efficient power transmission, mobility, and performance across a wide range of applications, contributing to the functionality and productivity of various industries and vehicles.


editor by CX 2024-03-26
China supplier CZPT CV Axle Left & Right Drive Shaft for CZPT CZPT Honda CZPT CZPT CZPT VW Mazda BMW Drive Line
Product Description
Warm Tips: Please Contact Us To Confirm Your Car Model
Product Description
1.We are manufacturer of cv drive shaft,cv axle, cv joint and cv boot, we have more than 20-years experience in producing and selling auto parts.
2.We have strict quality control, the quality of our products is very good.
3.We are professional in different market around the world.
4.The reviews our customers given us are very positive, we have confidence in our products.
5.OEM/ODM is available, meet your requirements well.
6.Large warehouse, huge stocks!!! friendly for those customers who want some quantity.
7.Ship products out very fastly, we have stock.
| Product Name | Drive shaft | Material | 42CrMo alloy steel |
| Car fitment | Toyota | Warranty | 12 months |
| Model | for CZPT CZPT Honda CZPT CZPT CZPT VW Mazda BMW | Place of origin | ZHangZhoug, China |
| Productive year | pls contact us for more details | MOQ | 4 PCS |
| OE number | factory standard | Delivery time | 1-7 days |
| OEM/ODM | Yes | Brand | GJF |
| Packing size | according to each model | Payment | L/C,T/T,western Union,Cash,PayPal |
| Sample service | Depends on the situation of stock | Weight | 7.9KG |
Detailed Photos
Customer Review
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 12 Months |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Axle Number: | 1 |
| Application: | Car |
| Certification: | ASTM, CE, DIN, ISO |
| Material: | Alloy |
| Samples: |
US$ 42.8/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do drivelines handle variations in load and torque during operation?
Drivelines are designed to handle variations in load and torque during operation by incorporating various components and mechanisms that optimize power transmission and mitigate the effects of these variations. Let’s delve into the ways drivelines handle load and torque variations:
1. Flexible Couplings:
Drivelines often utilize flexible couplings, such as universal joints or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate misalignment and angular variations between connected components. These couplings allow for smooth power transmission even when there are slight misalignments or changes in angles. They can compensate for variations in load and torque by flexing and adjusting their angles, thereby reducing stress on the driveline components.
2. Torque Converters:
In some driveline systems, such as those found in automatic transmissions, torque converters are employed. Torque converters use hydraulic principles to transmit power between the engine and the drivetrain. They provide a degree of slip, which allows for torque multiplication and smooth power delivery, especially during low-speed and high-load conditions. Torque converters help manage variations in torque by absorbing and dampening sudden changes, ensuring smoother operation.
3. Clutches:
Clutches play a critical role in drivelines, particularly in manual transmissions or systems that require torque control. Clutches engage and disengage the power flow between the engine and the drivetrain. By engaging or disengaging the clutch, the driveline can handle variations in load and torque. For instance, when starting a vehicle from a standstill, the clutch gradually engages to transmit power smoothly and prevent abrupt torque surges.
4. Gearboxes and Transmission Systems:
Drivelines often incorporate gearboxes and transmissions that provide multiple gear ratios. These systems allow for varying torque and speed outputs, enabling the driveline to adapt to different load conditions. By changing gears, the driveline can match the power requirements of the vehicle or machinery to the load and torque demands, optimizing power delivery and efficiency.
5. Differential Systems:
In drivelines for vehicles with multiple driven wheels, such as cars with rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive, differential systems are employed. Differentials distribute torque between the driven wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds, particularly during turns. This capability helps handle variations in load and torque between the wheels, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing tire wear.
6. Control Systems:
Modern drivelines often incorporate control systems that monitor and adjust power distribution based on various inputs, including load and torque conditions. These control systems, such as electronic control units (ECUs), can optimize power delivery, manage gear shifts, and adjust torque output to handle variations in load and torque. They may also incorporate sensors and feedback mechanisms to continuously monitor driveline performance and make real-time adjustments.
7. Overload Protection Mechanisms:
Some driveline systems include overload protection mechanisms to safeguard against excessive load or torque. These mechanisms can include torque limiters, shear pins, or safety clutches that disengage or slip when the load or torque exceeds a certain threshold. By providing a fail-safe mechanism, drivelines can protect the components from damage due to sudden or excessive variations in load and torque.
By incorporating these components and mechanisms, drivelines are capable of handling variations in load and torque during operation. They optimize power transmission, ensure smooth operation, and protect the driveline components from excessive stress or damage, ultimately enhancing the performance and longevity of the driveline system.

What safety precautions should be followed when working with driveline components?
Working with driveline components requires careful attention to safety to prevent accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. Driveline components, such as transmissions, drive shafts, and differentials, can involve rotating parts, high torque, and heavy machinery, making it essential to follow proper safety precautions. Here are some important safety measures to consider when working with driveline components:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential hazards such as flying debris, sharp edges, and contact with hot or moving parts. Use steel-toed safety boots to protect your feet from heavy objects or accidental impacts.
2. Lockout/Tagout:
Prior to working on driveline components, follow lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the equipment is properly shut down and isolated from its power source. Lockout/tagout involves disconnecting power, applying locks or tags to control switches, and verifying that the equipment is de-energized. This prevents accidental startup or release of stored energy that could cause serious injuries.
3. Vehicle/Equipment Stability:
Ensure that the vehicle or equipment is stable and securely supported before working on driveline components. Use appropriate jack stands or hoists to provide a stable and reliable support structure. Never rely solely on hydraulic jacks or unstable supports, as they can lead to accidents or equipment damage.
4. Proper Lifting Techniques:
When handling heavy driveline components, use proper lifting techniques to prevent strains or injuries. Lift with your legs, not your back, and get assistance when dealing with heavy or bulky components. Use mechanical lifting aids, such as hoists or cranes, when necessary to avoid overexertion or dropping components.
5. Component Inspection:
Prior to installation or maintenance, carefully inspect driveline components for any signs of damage, wear, or corrosion. Replace any worn or damaged parts to ensure safe and reliable operation. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and specifications for component inspection, maintenance, and replacement intervals.
6. Proper Tools and Equipment:
Use the correct tools and equipment for the job. Improper tools or makeshift solutions can lead to accidents, damaged components, or stripped fasteners. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for specialized tools or equipment needed for specific driveline components.
7. Follow Service Manuals and Procedures:
Refer to the relevant service manuals and follow proper procedures when working on driveline components. Service manuals provide step-by-step instructions, torque specifications, and safety precautions specific to the vehicle or equipment you are working on. Adhering to these guidelines ensures proper disassembly, installation, and adjustment of driveline components.
8. Proper Disposal of Fluids and Waste:
Dispose of fluids, such as oil or coolant, and waste materials in accordance with local regulations. Spilled fluids can create slip hazards, and improper disposal can harm the environment. Use appropriate containers and disposal methods as prescribed by local laws and regulations.
9. Training and Knowledge:
Ensure that individuals working with driveline components have received proper training and possess the necessary knowledge and skills. Inadequate training or lack of knowledge can lead to errors, accidents, or improper installation, compromising safety and performance.
10. Follow Workplace Safety Regulations:
Adhere to workplace safety regulations and guidelines established by relevant authorities. These regulations may include specific requirements for working with driveline components, such as safety standards, training requirements, and equipment certifications. Stay updated on safety regulations and ensure compliance to maintain a safe working environment.
By following these safety precautions, individuals can minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, and equipment damage when working with driveline components. Safety should always be a top priority to promote a secure and productive work environment.

Can you explain the components of a typical driveline and their specific roles?
A typical driveline consists of several components that work together to transmit power from the engine or power source to the driven components, enabling motion and providing torque. Each component plays a specific role in the driveline system. Here’s an explanation of the key components of a typical driveline and their specific roles:
1. Engine: The engine is the power source of the driveline system. It converts fuel energy (such as gasoline or diesel) into mechanical power by the process of combustion. The engine generates rotational power, which is transferred to the driveline to initiate power transmission.
2. Transmission: The transmission is responsible for selecting the appropriate gear ratio and transmitting power from the engine to the driven components. It allows the driver or operator to control the speed and torque output of the driveline. In manual transmissions, the driver manually selects the gears, while in automatic transmissions, the gear shifts are controlled by the vehicle’s computer system.
3. Drive Shaft: The drive shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or prop shaft, is a tubular component that transmits rotational power from the transmission to the differential or the driven components. It typically consists of a hollow metal tube with universal joints at both ends to accommodate variations in driveline angles and allow for smooth power transfer.
4. Differential: The differential is a gearbox-like component that distributes power from the drive shaft to the wheels or driven axles while allowing them to rotate at different speeds, particularly during turns. It compensates for the difference in rotational speed between the inner and outer wheels in a turn, ensuring smooth and controlled operation of the driveline system.
5. Axles: Axles are shafts that connect the differential to the wheels. They transmit power from the differential to the wheels, allowing them to rotate and generate motion. In vehicles with independent suspension, each wheel typically has its own axle, while in solid axle configurations, a single axle connects both wheels on an axle assembly.
6. Clutch: In manual transmission systems, a clutch is employed to engage or disengage the engine’s power from the driveline. It allows the driver to smoothly engage the engine’s power to the transmission when shifting gears or coming to a stop. By disengaging the clutch, power transmission to the driveline is temporarily interrupted, enabling gear changes or vehicle stationary positions.
7. Torque Converter: Torque converters are used in automatic transmissions to transfer power from the engine to the transmission. They provide a fluid coupling between the engine and transmission, allowing for smooth power transmission and torque multiplication. The torque converter also provides a torque amplification effect, which helps in vehicle acceleration.
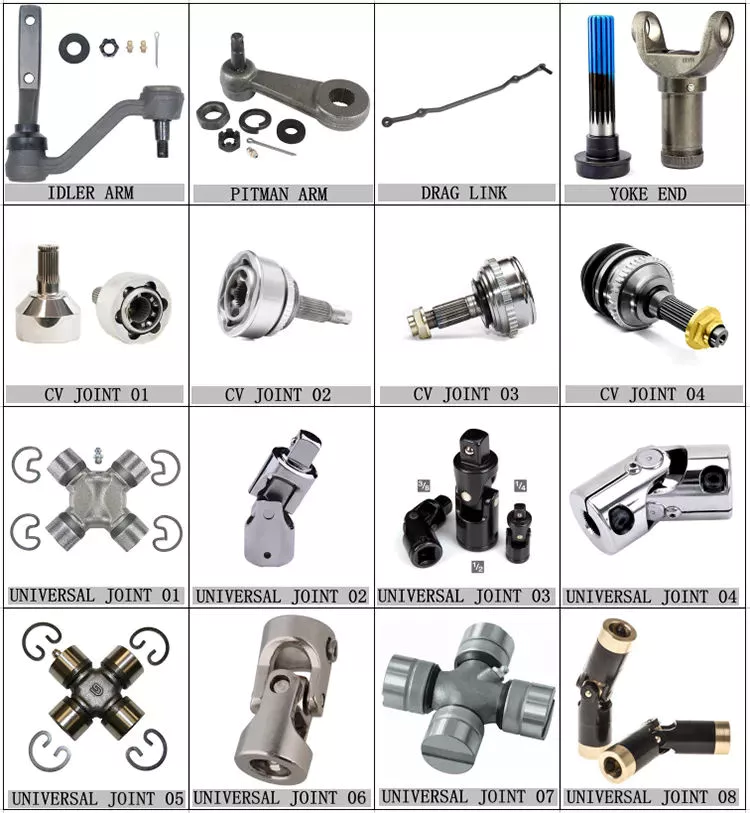
8. Universal Joints: Universal joints, also known as U-joints, are flexible couplings used in the driveline to accommodate variations in angles and misalignments between the components. They allow for the smooth transmission of power between the drive shaft and other components, compensating for changes in driveline angles during vehicle operation or suspension movement.
9. Constant Velocity Joints (CV Joints): CV joints are specialized joints used in some drivelines, particularly in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles. They enable smooth power transmission while accommodating variations in angles and allowing the wheels to turn at different speeds. CV joints maintain a constant velocity during rotation, minimizing vibrations and power losses.
10. Transfer Case: A transfer case is a component found in four-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive systems. It transfers power from the transmission to both the front and rear axles, allowing all wheels to receive power. The transfer case usually includes additional components such as a multi-speed gearbox and differential mechanisms to distribute power effectively to the axles.
These are the key components of a typical driveline and their specific roles. Each component is crucial in transferring power, enabling motion, and ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of vehicles and equipment.


editor by CX 2024-03-26
China wholesaler China Manufacturer of Drive Shaft, High Precision Drive Line
Product Description
|
Gear Types |
spur gear, helical gear, internal spur gear, ring gear, straight/spiral bevel gear, hypoid gear, CZPT wheel & pinion, gear shaft, worm gear & worm shaft, spline shaft & bushing, etc. |
|||
|
Gear Material |
Steel: C45, 40Cr, 42CrMo, 20CrMnTi, 20CrNiMo, etc.; Aluminum Alloy: 2571, 7075, etc.; Brass, Bronze, Aluminum Brone, etc.; POM Plastic, MC901 Nylon, etc.; |
|||
|
Processing |
blank turning; tooth hobbing, broaching, milling, shaping, etc.; bore honing; tooth shaving, tooth grinding |
|||
|
Heat Treating
|
tooth induction quenching, vacuum quenching, etc. for 45-50HRC; carburizing for 56-62 HRC; nitriding, carbon-nitriding for gears required abrision resistan; |
|||
|
Application |
Automotive, Agricultural, Electronic, industrial, Medical, Defense, Off-highway, etc. |
|||
Quality control system:Our company carries out quality control in each link, the raw material needs to have the trace element assay report, the forging blank size inspection and the density inspection, each production process has the inspection worker to inspect, the metallographic organization after the heat treatment and the hardness inspection and so on.
FAQ:
1. Q: What information should we provide before placing an order?
A: a) Ditailed drawings if possible. b) Samples without Drawings. c) Purchase quantity. d) Other special requirements.
2. Q: Are you a factory or a trading company?
A: We are a professional group company with more than 20 years of experience.
3. Q: Can you customize according to our requirements?
A: Yes, we can design non-standard products according to customers’ special requirements.
4. Q: How long is the delivery date?
A: 30 – 45 business days, according to quantity.
5. Q: What are your payment terms?
A: 30% prepayment, 70% paid before shipment.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Type: | 1 |
| Application Brand: | 2 |
| Samples: |
US$ 80/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What maintenance practices are essential for prolonging the lifespan of driveline components?
Implementing proper maintenance practices is crucial for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of driveline components. Regular maintenance helps identify potential issues, prevent major failures, and prolong the lifespan of driveline components. Here are some essential maintenance practices for prolonging the lifespan of driveline components:
1. Regular Inspections:
Performing regular visual inspections of driveline components is essential for detecting any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the driveline components, including driveshafts, universal joints, CV joints, differentials, and transmission components, for any cracks, leaks, excessive play, or unusual noise. Identifying and addressing issues early can prevent further damage and potential driveline failure.
2. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication of driveline components is crucial for minimizing friction, reducing wear, and ensuring smooth operation. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and use the appropriate type and grade of lubricant. Regularly check and maintain the lubrication levels in components such as bearings, gears, and joints to prevent excessive heat buildup and premature wear.
3. Fluid Changes:
Fluids play a vital role in driveline component performance and longevity. Regularly change fluids, such as transmission fluid, differential oil, and transfer case fluid, according to the manufacturer’s recommended intervals. Over time, these fluids can become contaminated or break down, leading to compromised performance and increased wear. Fresh fluids help maintain proper lubrication, cooling, and protection of driveline components.
4. Alignment and Balancing:
Proper alignment and balancing of driveline components are essential for minimizing vibration, reducing stress, and preventing premature wear. Periodically check and adjust the alignment of driveshafts, ensuring they are properly aligned with the transmission and differential. Additionally, balance rotating components, such as driveshafts or flywheels, to minimize vibrations and prevent excessive stress on driveline components.
5. Torque Check:
Regularly check and ensure that all driveline components are properly torqued according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Over time, fasteners can loosen due to vibrations or thermal expansion and contraction. Loose fasteners can lead to misalignment, excessive play, or even component failure. Regular torque checks help maintain the integrity and performance of the driveline system.
6. Maintenance of Supporting Systems:
Driveline components rely on the proper functioning of supporting systems, such as cooling systems and electrical systems. Ensure that cooling systems are functioning correctly, as overheating can cause driveline components to degrade or fail. Additionally, regularly inspect electrical connections, wiring harnesses, and sensors to ensure proper communication and operation of driveline components.
7. Proper Driving Techniques:
The way a vehicle is driven can significantly impact the lifespan of driveline components. Avoid aggressive driving, sudden acceleration, and excessive braking, as these actions can put undue stress on the driveline components. Smooth and gradual acceleration, proper shifting techniques, and avoiding excessive load or towing capacities help minimize wear and prolong component life.
8. Service and Maintenance Records:
Maintain comprehensive service and maintenance records for the driveline components. Keep track of all maintenance tasks, repairs, fluid changes, and inspections performed. These records help ensure that maintenance tasks are performed on time, provide a history of component performance, and assist in diagnosing any recurring issues or patterns.
By following these maintenance practices, vehicle owners can prolong the lifespan of driveline components, minimize the risk of failures, and ensure optimal performance and reliability of the driveline system.

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with driveline systems?
While driveline systems offer numerous advantages in terms of power transmission and vehicle performance, there are also some limitations and disadvantages associated with their use. It’s important to consider these factors when designing, operating, and maintaining driveline systems. Let’s explore some of the limitations and disadvantages:
1. Complex Design and Integration:
Driveline systems can be complex in design, especially in modern vehicles with advanced technologies. They often consist of multiple components, such as transmissions, differentials, transfer cases, and drive shafts, which need to be properly integrated and synchronized. The complexity of the driveline system can increase manufacturing and assembly challenges, as well as the potential for compatibility issues or failures if not designed and integrated correctly.
2. Energy Losses:
Driveline systems can experience energy losses during power transmission. These losses occur due to factors such as friction, heat generation, mechanical inefficiencies, and fluid drag in components like gearboxes, differentials, and torque converters. The energy losses can negatively impact overall efficiency and result in reduced fuel economy or power output, especially in systems with multiple driveline components.
3. Limited Service Life and Maintenance Requirements:
Driveline components, like any mechanical system, have a limited service life and require regular maintenance. Components such as clutches, bearings, gears, and drive shafts are subject to wear and tear, and may need to be replaced or repaired over time. Regular maintenance, including lubrication, adjustments, and inspections, is necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failures. Failure to perform proper maintenance can lead to driveline malfunctions, increased downtime, and costly repairs.
4. Weight and Space Constraints:
Driveline systems add weight and occupy space within a vehicle. The additional weight affects fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Moreover, the space occupied by driveline components can limit design flexibility, particularly in compact or electric vehicles where space optimization is crucial. Manufacturers must strike a balance between driveline performance, vehicle weight, and available space to meet the requirements of each specific vehicle type.
5. Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH):
Driveline systems can generate noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) during operation. Factors such as gear meshing, unbalanced rotating components, or improper driveline alignment can contribute to unwanted vibrations or noise. NVH issues can affect driving comfort, passenger experience, and vehicle refinement. Manufacturers employ various techniques, including vibration dampening materials, isolators, and precision engineering, to minimize NVH levels, but achieving complete elimination can be challenging.
6. Limited Torque Handling Capability:
Driveline systems have limitations in terms of torque handling capability. Excessive torque beyond the rated capacity of driveline components can lead to failures, such as shearing of gears, clutch slippage, or drive shaft breakage. High-performance vehicles or heavy-duty applications may require specialized driveline components capable of handling higher torque loads, which can increase costs and complexity.
7. Traction Limitations:
Driveline systems, particularly in vehicles with two-wheel drive configurations, may experience traction limitations, especially in slippery or off-road conditions. Power is typically transmitted to only one or two wheels, which can result in reduced traction and potential wheel slippage. This limitation can be mitigated by utilizing technologies such as limited-slip differentials, electronic traction control, or implementing all-wheel drive systems.
While driveline systems provide crucial power transmission and vehicle control, they do have limitations and disadvantages that need to be considered. Manufacturers, designers, and operators should carefully assess these factors and implement appropriate design, maintenance, and operational practices to optimize driveline performance, reliability, and overall vehicle functionality.

What benefits do drivelines offer for different types of vehicles and equipment?
Drivelines offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment across various industries. They play a critical role in power transmission, mobility, efficiency, and overall performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of the benefits drivelines offer for different types of vehicles and equipment:
1. Power Transmission: Drivelines are designed to efficiently transmit power from the engine or power source to the driven components, such as wheels, tracks, implements, or machinery. They ensure the smooth transfer of torque, allowing vehicles and equipment to generate the necessary power for propulsion, lifting, hauling, or other tasks. By effectively transmitting power, drivelines maximize the performance and productivity of vehicles and equipment.
2. Mobility and Maneuverability: Drivelines enable vehicles and equipment to achieve mobility and maneuverability across various terrains and working conditions. By transmitting power to the wheels or tracks, drivelines provide the necessary traction and control to overcome obstacles, navigate uneven surfaces, and operate in challenging environments. They contribute to the overall stability, handling, and agility of vehicles and equipment, allowing them to move efficiently and safely.
3. Versatility and Adaptability: Drivelines offer versatility and adaptability for different types of vehicles and equipment. They can be designed and configured to meet specific requirements, such as front-wheel drive, rear-wheel drive, four-wheel drive, or all-wheel drive systems. This flexibility allows vehicles and equipment to adapt to various operating conditions, including normal roads, off-road terrains, agricultural fields, construction sites, or industrial facilities. Drivelines also accommodate different power sources, such as internal combustion engines, electric motors, or hybrid systems, enhancing the adaptability of vehicles and equipment.
4. Efficiency and Fuel Economy: Drivelines contribute to efficiency and fuel economy in vehicles and equipment. They optimize power transmission by utilizing appropriate gear ratios, minimizing energy losses, and improving overall system efficiency. Drivelines with advanced technologies, such as continuously variable transmissions (CVTs) or automated manual transmissions (AMTs), can further enhance efficiency by continuously adjusting gear ratios based on load and speed conditions. Efficient driveline systems help reduce fuel consumption, lower emissions, and maximize the operational range of vehicles and equipment.
5. Load Carrying Capacity: Drivelines are designed to handle and transmit high torque and power, enabling vehicles and equipment to carry heavy loads. They incorporate robust components, such as heavy-duty axles, reinforced drive shafts, and durable differentials, to withstand the demands of load-bearing applications. Drivelines ensure the reliable transmission of power, allowing vehicles and equipment to transport materials, tow trailers, or carry payloads efficiently and safely.
6. Safety and Control: Drivelines contribute to safety and control in vehicles and equipment. They enable precise control over acceleration, deceleration, and speed, enhancing driver or operator confidence and maneuverability. Drivelines with features like traction control systems, limited-slip differentials, or electronic stability control provide additional safety measures by improving traction, stability, and handling in challenging road or operating conditions. By ensuring optimal power distribution and control, drivelines enhance the overall safety and stability of vehicles and equipment.
7. Durability and Reliability: Drivelines are built to withstand harsh operating conditions and provide long-term durability and reliability. They are engineered with high-quality materials, precise manufacturing processes, and advanced technologies to ensure the driveline components can endure the stresses of power transmission. Well-designed drivelines require minimal maintenance, reducing downtime and enhancing the overall reliability of vehicles and equipment.
8. Specialized Functionality: Drivelines offer specialized functionality for specific types of vehicles and equipment. For example, in off-road vehicles or heavy-duty construction equipment, drivelines with features like differential locks, torque vectoring, or adjustable suspension systems provide enhanced traction, stability, and control. In agricultural machinery, drivelines with power take-off (PTO) units enable the connection of various implements for specific tasks like plowing, seeding, or harvesting. Such specialized driveline features enhance the performance and versatility of vehicles and equipment in their respective applications.
In summary, drivelines provide numerous benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They ensure efficient power transmission, facilitate mobility and maneuverability, offer versatility and adaptability, contribute to efficiency and fuel economy, handle heavy loads, enhance safety and control, provide durability and reliability, and offer specialized functionality. By incorporating well-designed drivelines, manufacturers can optimize the performance, productivity, and overall functionality of vehicles and equipment across various industries.


editor by CX 2024-03-20
China OEM Customized High Precision Spare Parts Auto/Truck/Drive/Gear/Spline/Propeller/Half/Sleeve/Machinery/Sliding/Transmission Axle Shaft 42CrMo 20crmoti
Product Description
Customized High Precision Spare Parts Auto/Truck/Drive/Gear/Spline/Propeller/Half/Sleeve/Machinery/Sliding/Transmission Axle Shaft 42CrMo 20CrMoTi
(1) Accessory products of the truck, the product quality is stable and reliable.
(2) Forged with 42CrMo material and heat treated and tempered for 32 degrees, so that the half shaft has stronger toughness and is not easy to break and bend.
(3) Processed in the machining center, ensure that the products have rigorous dimensional coordinates to ensure 100% qualified rate of products.
(4) Products are inspected 1 by 1 and delivered out of the warehouse, with unified laser identification to ensure product traceability.
(5) Various sizes of axle shafts can be customized to meet customer needs.
(6) The unified brand carton, inner bag and integral foam packaging, which is strong and beautiful.
Factory Show
More Products
| Truck Model | Sinotruk, Shacman, CZPT Auman, CZPT Xihu (West Lake) Dis., Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng, Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng Liuqi Balong, North BENZ( BEIBEN), C&C, JAC, etc. | |
| Product catalogue | Axle | Wheel Assembly |
| Differential Assembly | ||
| Main Reducer Assembly | ||
| Inner Ring Gear& Bracket | ||
| Basin Angle Gear/ Bevel Gear | ||
| Axle Shaft/ Half Shaft & Through Shaft | ||
| Axle Housing& Axle Assembly | ||
| Steering knuckle & Front Axle | ||
| Gear | ||
| Brake Drum& Wheel Hub | ||
| Flange | ||
| Bearing | ||
| Main Reducer Housing | ||
| Oil Seal Seat | ||
| Nut& Shim Series | ||
| Brake Backing Plate | ||
| Chassis Support Products | Leaf Spring Bracket | |
| Drop Arm Series | ||
| Bracket Series | ||
| Leaf Spring Shackle Series | ||
| Balanced Suspension Series | Balance Shaft Assembly | |
| Balance Shaft Housing | ||
| Axle Spring Seat | ||
| Thrust Rod | ||
| Balance Shaft Parts | ||
| Shock Absorber Series | Shock Absorber | |
| Shock Absorbing Airbag | ||
| Steering System | Power Steering Pump | |
| Power Steering Gear | ||
| Rubber Products | Oil Seal | |
| Rubber Support | ||
| Thrust Rod Rubber Core | ||
| Truck Belt | ||
| Engine support | ||
| Other | ||
| Clutch Series | Clutch Pressure Plate | |
| Clutch Disc | ||
| Flywheel Assembly | ||
| Flywheel Ring Gear | ||
| Adjusting Arm Series | ||
Function
Heavy trucks usually have double rear axles. If they are driven separately, they need to use 2 transmission shafts or add a transfer case at the output of the gearbox, which is heavy and cumbersome. Now a through shaft is designed in the middle axle to solve this problem. Only 1 transmission shaft is needed to drive 2 rear axles at the same time.
Packaging & Shipping
Exhibition
FAQ
Q1. Are you a factory or trading company?
We are a factory integrating research, development, production and sales.
Q2. What are the advantages of your products?
We support product customization to meet customer needs for special products. We can strictly control the products from raw materials to production, processing, product quality inspection, delivery, packaging, etc., and provide customers with high-end products and the most advantageous prices.
Q3. How about products price?
We are a factory, all products are direct sale at factory price. For the same price, we will provide the best quality; for the same quality, we have the most advantageous price.
Q4. What is your terms of packing?
We have branded packaging and neutral packaging, and we can also do what you want with authorization. This is flexible.
Q5. How to guarantee your after-sales service?
Strict inspection during production, Strictly check the products before shipment to ensure our packaging in good condition. Track and receive feedback from customer regularly. Our products warranty is 365 days.
Each product provides quality assurance service. If there is a problem with the product within the warranty period, the customer can negotiate with us in detail about the related claims, and we will do our best to satisfy the customer.
Certifications
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | 45#Steel, 42CrMo, 20crmoti |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | High Precision |
| Samples: |
US$ 29/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What maintenance practices are crucial for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts?
To prolong the lifespan of drive shafts and ensure their optimal performance, several maintenance practices are crucial. Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate, reduces wear and tear, and ensures the drive shaft operates smoothly and efficiently. Here are some essential maintenance practices for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts:
1. Regular Inspection:
Performing regular inspections is vital for detecting any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the drive shaft visually, looking for cracks, dents, or any signs of excessive wear on the shaft itself and its associated components such as joints, yokes, and splines. Check for any signs of lubrication leaks or contamination. Additionally, inspect the fasteners and mounting points to ensure they are secure. Early detection of any issues allows for timely repairs or replacements, preventing further damage to the drive shaft.
2. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of drive shafts. Lubricate the joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity joints, as recommended by the manufacturer. Lubrication reduces friction, minimizes wear, and helps dissipate heat generated during operation. Use the appropriate lubricant specified for the specific drive shaft and application, considering factors such as temperature, load, and operating conditions. Regularly check the lubrication levels and replenish as necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failure.
3. Balancing and Alignment:
Maintaining proper balancing and alignment is crucial for the lifespan of drive shafts. Imbalances or misalignments can lead to vibrations, accelerated wear, and potential failure. If vibrations or unusual noises are detected during operation, it is important to address them promptly. Perform balancing procedures as necessary, including dynamic balancing, to ensure even weight distribution along the drive shaft. Additionally, verify that the drive shaft is correctly aligned with the engine or power source and the driven components. Misalignment can cause excessive stress on the drive shaft, leading to premature failure.
4. Protective Coatings:
Applying protective coatings can help prolong the lifespan of drive shafts, particularly in applications exposed to harsh environments or corrosive substances. Consider using coatings such as zinc plating, powder coating, or specialized corrosion-resistant coatings to enhance the drive shaft’s resistance to corrosion, rust, and chemical damage. Regularly inspect the coating for any signs of degradation or damage, and reapply or repair as necessary to maintain the protective barrier.
5. Torque and Fastener Checks:
Ensure that the drive shaft’s fasteners, such as bolts, nuts, or clamps, are properly torqued and secured according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Loose or improperly tightened fasteners can lead to excessive vibrations, misalignment, or even detachment of the drive shaft. Periodically check and retighten the fasteners as recommended or after any maintenance or repair procedures. Additionally, monitor the torque levels during operation to ensure they remain within the specified range, as excessive torque can strain the drive shaft and lead to premature failure.
6. Environmental Protection:
Protecting the drive shaft from environmental factors can significantly extend its lifespan. In applications exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or abrasive substances, take appropriate measures to shield the drive shaft. This may include using protective covers, seals, or guards to prevent contaminants from entering and causing damage. Regular cleaning of the drive shaft, especially in dirty or corrosive environments, can also help remove debris and prevent buildup that could compromise its performance and longevity.
7. Manufacturer Guidelines:
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance practices specific to the drive shaft model and application. The manufacturer’s instructions may include specific intervals for inspections, lubrication, balancing, or other maintenance tasks. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that the drive shaft is properly maintained and serviced, maximizing its lifespan and minimizing the risk of unexpected failures.
By implementing these maintenance practices, drive shafts can operate reliably, maintain efficient power transmission, and have an extended service life, ultimately reducing downtime and ensuring optimal performance in various applications.

Can drive shafts be customized for specific vehicle or equipment requirements?
Yes, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements. Customization allows manufacturers to tailor the design, dimensions, materials, and other parameters of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility and optimal performance within a particular vehicle or equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts can be customized:
1. Dimensional Customization:
Drive shafts can be customized to match the dimensional requirements of the vehicle or equipment. This includes adjusting the overall length, diameter, and spline configuration to ensure proper fitment and clearances within the specific application. By customizing the dimensions, the drive shaft can be seamlessly integrated into the driveline system without any interference or limitations.
2. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for drive shafts can be customized based on the specific requirements of the vehicle or equipment. Different materials, such as steel alloys, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, can be selected to optimize strength, weight, and durability. The material selection can be tailored to meet the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the application, ensuring the drive shaft’s reliability and longevity.
3. Joint Configuration:
Drive shafts can be customized with different joint configurations to accommodate specific vehicle or equipment requirements. For example, universal joints (U-joints) may be suitable for applications with lower operating angles and moderate torque demands, while constant velocity (CV) joints are often used in applications requiring higher operating angles and smoother power transmission. The choice of joint configuration depends on factors such as operating angle, torque capacity, and desired performance characteristics.
4. Torque and Power Capacity:
Customization allows drive shafts to be designed with the appropriate torque and power capacity for the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers can analyze the torque requirements, operating conditions, and safety margins of the application to determine the optimal torque rating and power capacity of the drive shaft. This ensures that the drive shaft can handle the required loads without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
5. Balancing and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can be customized with precision balancing and vibration control measures. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, increased wear, and potential driveline issues. By employing dynamic balancing techniques during the manufacturing process, manufacturers can minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation. Additionally, vibration dampers or isolation systems can be integrated into the drive shaft design to further mitigate vibrations and enhance overall system performance.
6. Integration and Mounting Considerations:
Customization of drive shafts takes into account the integration and mounting requirements of the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers work closely with the vehicle or equipment designers to ensure that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the driveline system. This includes adapting the mounting points, interfaces, and clearances to ensure proper alignment and installation of the drive shaft within the vehicle or equipment.
7. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate with vehicle manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft customization process. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can address specific needs, optimize performance, and ensure compatibility with the vehicle or equipment. This collaborative approach enhances the customization process and results in drive shafts that meet the exact requirements of the application.
8. Compliance with Standards:
Customized drive shafts can be designed to comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, ensures that the customized drive shafts meet quality, safety, and performance requirements. Adhering to these standards provides assurance that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into the specific vehicle or equipment.
In summary, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements through dimensional customization, material selection, joint configuration, torque and power capacity optimization, balancing and vibration control, integration and mounting considerations, collaboration with stakeholders, and compliance with industry standards. Customization allows drive shafts to be precisely tailored to the needs of the application, ensuring compatibility, reliability, and optimal performance.

Are there variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery?
Yes, there are variations in drive shaft designs to cater to the specific requirements of different types of machinery. The design of a drive shaft is influenced by factors such as the application, power transmission needs, space limitations, operating conditions, and the type of driven components. Here’s an explanation of how drive shaft designs can vary for different types of machinery:
1. Automotive Applications:
In the automotive industry, drive shaft designs can vary depending on the vehicle’s configuration. Rear-wheel-drive vehicles typically use a single-piece or two-piece drive shaft, which connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential. Front-wheel-drive vehicles often use a different design, employing a drive shaft that combines with the constant velocity (CV) joints to transmit power to the front wheels. All-wheel-drive vehicles may have multiple drive shafts to distribute power to all wheels. The length, diameter, material, and joint types can differ based on the vehicle’s layout and torque requirements.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Drive shaft designs for industrial machinery depend on the specific application and power transmission requirements. In manufacturing machinery, such as conveyors, presses, and rotating equipment, drive shafts are designed to transfer power efficiently within the machine. They may incorporate flexible joints or use a splined or keyed connection to accommodate misalignment or allow for easy disassembly. The dimensions, materials, and reinforcement of the drive shaft are selected based on the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the machinery.
3. Agriculture and Farming:
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters, often requires drive shafts that can handle high torque loads and varying operating angles. These drive shafts are designed to transmit power from the engine to attachments and implements, such as mowers, balers, tillers, and harvesters. They may incorporate telescopic sections to accommodate adjustable lengths, flexible joints to compensate for misalignment during operation, and protective shielding to prevent entanglement with crops or debris.
4. Construction and Heavy Equipment:
Construction and heavy equipment, including excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes, require robust drive shaft designs capable of transmitting power in demanding conditions. These drive shafts often have larger diameters and thicker walls to handle high torque loads. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to accommodate operating angles and absorb shocks and vibrations. Drive shafts in this category may also have additional reinforcements to withstand the harsh environments and heavy-duty applications associated with construction and excavation.
5. Marine and Maritime Applications:
Drive shaft designs for marine applications are specifically engineered to withstand the corrosive effects of seawater and the high torque loads encountered in marine propulsion systems. Marine drive shafts are typically made from stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials. They may incorporate flexible couplings or dampening devices to reduce vibration and mitigate the effects of misalignment. The design of marine drive shafts also considers factors such as shaft length, diameter, and support bearings to ensure reliable power transmission in marine vessels.
6. Mining and Extraction Equipment:
In the mining industry, drive shafts are used in heavy machinery and equipment such as mining trucks, excavators, and drilling rigs. These drive shafts need to withstand extremely high torque loads and harsh operating conditions. Drive shaft designs for mining applications often feature larger diameters, thicker walls, and specialized materials such as alloy steel or composite materials. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to handle operating angles, and they are designed to be resistant to abrasion and wear.
These examples highlight the variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery. The design considerations take into account factors such as power requirements, operating conditions, space constraints, alignment needs, and the specific demands of the machinery or industry. By tailoring the drive shaft design to the unique requirements of each application, optimal power transmission efficiency and reliability can be achieved.


editor by CX 2024-03-19
China Good quality for Land Rover Discovery Range Rover Front Driveshaft Drive Line
Product Description
Product Description
As a professional manufacturer for propeller shaft, we have +1000 item s for all kinds of car. At present, our products are mainly sold in North America, Europe, Australia, South Korea, the Middle East and Southeast Asia and other regions, applicable models are European ca rs, American cars, Japanese and Korean cars, etc.
Our advantage:
1. Full range of products
2. MOQ qty: 1pcs/items
3. Delivery on time
4: Warranty: 1 YEAR
| OE NUMBER | FRC8386;TVB100610 |
| TYPE | LAND ROVER – DISCOVERY |
| MATERIAL | STEEL |
| BALANCE STHangZhouRD | G16 3200RPM |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1years |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Can drivelines be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings?
Drivelines can indeed be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings. While there are some differences in the specific requirements and design considerations between these two applications, many fundamental principles and components of drivelines remain applicable to both sectors. Let’s explore how drivelines can be adapted for use in automotive and industrial settings:
1. Power Transmission:
In both automotive and industrial applications, drivelines serve the purpose of transmitting power from a source (such as an engine or motor) to various driven components. The driveline components, including transmissions, clutches, differentials, and shafts, can be adapted and optimized based on the specific power requirements and operating conditions of each application. While automotive drivelines typically focus on delivering power for propulsion, industrial drivelines may transmit power to various machinery and equipment.
2. Gearboxes and Transmissions:
Both automotive and industrial drivelines often incorporate gearboxes or transmissions to provide multiple gear ratios for efficient power transfer. However, the gear ratios and design considerations may differ based on the specific requirements of each application. Automotive drivelines are typically optimized for a wide range of operating conditions, including varying speeds and loads. Industrial drivelines, on the other hand, may be designed to meet specific torque and speed requirements of industrial machinery.
3. Shaft and Coupling Systems:
Shafts and coupling systems are essential components of drivelines in both automotive and industrial settings. They transmit power between different components and allow for misalignment compensation. While automotive drivelines often use driveshafts and universal joints to transmit power to the wheels, industrial drivelines may employ shafts, couplings, and flexible couplings to connect various machinery components such as motors, pumps, and generators.
4. Differentiated Requirements:
Automotive and industrial drivelines have different operating conditions, load requirements, and environmental considerations. Automotive drivelines need to accommodate various road conditions, vehicle dynamics, and driver comfort. Industrial drivelines, on the other hand, may operate in more controlled environments but are subjected to specific industry requirements, such as high torque, continuous operation, or exposure to harsh conditions. The driveline components and materials can be adapted accordingly to meet these different requirements.
5. Control and Monitoring Systems:
Both automotive and industrial drivelines can benefit from advanced control and monitoring systems. These systems can optimize power distribution, manage gear shifts, monitor component health, and improve overall driveline efficiency. In automotive applications, electronic control units (ECUs) play a significant role in controlling driveline functions, while industrial drivelines may incorporate programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or other specialized control systems.
6. Customization and Integration:
Drivelines can be customized and integrated into specific automotive and industrial applications. Automotive drivelines can be tailored to meet the requirements of different vehicle types, such as passenger cars, trucks, or sports vehicles. Industrial drivelines can be designed to integrate seamlessly with specific machinery and equipment, considering factors such as available space, power requirements, and maintenance accessibility.
7. Maintenance and Service:
While the specific maintenance requirements may vary, both automotive and industrial drivelines require regular inspection, lubrication, and component replacement to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper maintenance practices, as discussed earlier, are essential for prolonging the lifespan of driveline components in both settings.
In summary, drivelines can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings by considering the unique requirements and operating conditions of each application. While there are some differences in design considerations and component selection, the fundamental principles of power transmission and driveline functionality remain applicable in both sectors.

How do drivelines enhance the performance of different types of vehicles?
Drivelines significantly contribute to enhancing the performance of different types of vehicles by optimizing power delivery, improving traction, and tailoring the driving characteristics to suit specific needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drivelines enhance performance in various vehicle types:
1. Passenger Cars:
In passenger cars, driveline configurations, such as front-wheel drive (FWD), rear-wheel drive (RWD), and all-wheel drive (AWD), play a crucial role in performance. Here’s how drivelines enhance performance in passenger cars:
- FWD: Front-wheel drive systems provide better traction and stability, particularly in adverse weather conditions. FWD drivelines distribute weight more evenly over the front wheels, resulting in improved grip during acceleration and cornering.
- RWD: Rear-wheel drive drivelines offer better weight distribution, allowing for improved handling and balanced performance. RWD vehicles typically exhibit better acceleration and a more engaging driving experience, especially in performance-oriented cars.
- AWD: All-wheel drive drivelines deliver power to all four wheels, improving traction and stability in various driving conditions. AWD systems enhance performance by maximizing grip and providing optimal power distribution between the front and rear wheels.
2. Sports Cars and Performance Vehicles:
Driveline systems in sports cars and performance vehicles are designed to enhance acceleration, handling, and overall driving dynamics. Key features include:
- Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD): RWD drivelines are often favored in sports cars for their ability to deliver power to the rear wheels, resulting in better weight transfer during acceleration and improved handling characteristics.
- Performance-oriented AWD: Some high-performance vehicles employ advanced AWD systems that can variably distribute torque between the front and rear wheels. These systems enhance traction, stability, and cornering capabilities, allowing for superior performance on both dry and slippery surfaces.
- Torque Vectoring: Certain driveline systems incorporate torque vectoring technology, which actively varies the torque distribution between wheels. This enables precise control during cornering, reducing understeer and enhancing agility and stability.
3. Off-Road Vehicles:
Drivelines in off-road vehicles are designed to provide exceptional traction, durability, and maneuverability in challenging terrains. Key features include:
- Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) and All-Wheel Drive (AWD): 4WD and AWD drivelines are commonly used in off-road vehicles to improve traction on uneven surfaces. These drivelines distribute power to all wheels, allowing for better grip and enhanced off-road capability.
- Differential Locks: Off-road drivelines often incorporate differential locks that can be engaged to lock the wheels on an axle together. This feature ensures that power is evenly distributed to all wheels, maximizing traction and overcoming challenging obstacles.
- High Ground Clearance: Drivelines in off-road vehicles are designed to accommodate higher ground clearance, allowing for improved approach, departure, and breakover angles. This design feature enhances the vehicle’s ability to navigate over rough terrain without damaging the driveline components.
4. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Drivelines in trucks and commercial vehicles are engineered to provide high torque delivery, durability, and efficiency. Key features include:
- High Torque Handling: Drivelines in trucks and commercial vehicles are designed to handle high torque outputs from powerful engines, enabling efficient towing, hauling, and overall performance.
- Transmission Options: Drivelines in trucks often feature transmissions with multiple gear ratios, allowing drivers to select the appropriate gear for different load conditions. This enhances performance, fuel efficiency, and overall drivability.
- Efficient Power Transfer: Drivelines in commercial vehicles focus on maximizing power transfer efficiency, minimizing energy losses, and optimizing fuel economy. This is achieved through the use of efficient transmission designs, low-friction components, and advanced control systems.
5. Electric and Hybrid Vehicles:
Drivelines in electric and hybrid vehicles play a crucial role in delivering power from the electric motor(s) to the wheels. Key features include:
- Instant Torque: Electric drivelines offer instant torque delivery, providing quick acceleration andresponsive performance. This enhances the driving experience and allows for swift overtaking and merging.
- Regenerative Braking: Electric and hybrid drivelines can incorporate regenerative braking systems, which convert kinetic energy during braking into electrical energy. This improves overall efficiency and extends the vehicle’s range.
- Multi-Motor Systems: Some electric and hybrid drivelines utilize multiple motors to drive different axles or wheels independently. This enables advanced torque vectoring and enhances handling, stability, and traction control.
These are just a few examples of how drivelines enhance the performance of different types of vehicles. Driveline configurations, technologies, and engineering considerations are tailored to each vehicle type, optimizing power delivery, handling, traction, and other performance characteristics specific to their intended use and market segment.

Can you explain the components of a typical driveline and their specific roles?
A typical driveline consists of several components that work together to transmit power from the engine or power source to the driven components, enabling motion and providing torque. Each component plays a specific role in the driveline system. Here’s an explanation of the key components of a typical driveline and their specific roles:
1. Engine: The engine is the power source of the driveline system. It converts fuel energy (such as gasoline or diesel) into mechanical power by the process of combustion. The engine generates rotational power, which is transferred to the driveline to initiate power transmission.
2. Transmission: The transmission is responsible for selecting the appropriate gear ratio and transmitting power from the engine to the driven components. It allows the driver or operator to control the speed and torque output of the driveline. In manual transmissions, the driver manually selects the gears, while in automatic transmissions, the gear shifts are controlled by the vehicle’s computer system.
3. Drive Shaft: The drive shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or prop shaft, is a tubular component that transmits rotational power from the transmission to the differential or the driven components. It typically consists of a hollow metal tube with universal joints at both ends to accommodate variations in driveline angles and allow for smooth power transfer.
4. Differential: The differential is a gearbox-like component that distributes power from the drive shaft to the wheels or driven axles while allowing them to rotate at different speeds, particularly during turns. It compensates for the difference in rotational speed between the inner and outer wheels in a turn, ensuring smooth and controlled operation of the driveline system.
5. Axles: Axles are shafts that connect the differential to the wheels. They transmit power from the differential to the wheels, allowing them to rotate and generate motion. In vehicles with independent suspension, each wheel typically has its own axle, while in solid axle configurations, a single axle connects both wheels on an axle assembly.
6. Clutch: In manual transmission systems, a clutch is employed to engage or disengage the engine’s power from the driveline. It allows the driver to smoothly engage the engine’s power to the transmission when shifting gears or coming to a stop. By disengaging the clutch, power transmission to the driveline is temporarily interrupted, enabling gear changes or vehicle stationary positions.
7. Torque Converter: Torque converters are used in automatic transmissions to transfer power from the engine to the transmission. They provide a fluid coupling between the engine and transmission, allowing for smooth power transmission and torque multiplication. The torque converter also provides a torque amplification effect, which helps in vehicle acceleration.
8. Universal Joints: Universal joints, also known as U-joints, are flexible couplings used in the driveline to accommodate variations in angles and misalignments between the components. They allow for the smooth transmission of power between the drive shaft and other components, compensating for changes in driveline angles during vehicle operation or suspension movement.
9. Constant Velocity Joints (CV Joints): CV joints are specialized joints used in some drivelines, particularly in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles. They enable smooth power transmission while accommodating variations in angles and allowing the wheels to turn at different speeds. CV joints maintain a constant velocity during rotation, minimizing vibrations and power losses.
10. Transfer Case: A transfer case is a component found in four-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive systems. It transfers power from the transmission to both the front and rear axles, allowing all wheels to receive power. The transfer case usually includes additional components such as a multi-speed gearbox and differential mechanisms to distribute power effectively to the axles.
These are the key components of a typical driveline and their specific roles. Each component is crucial in transferring power, enabling motion, and ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of vehicles and equipment.


editor by CX 2024-03-19
China high quality CHINAMFG Axle Shaft Front Left Right CV Axle Drive Shaft for CHINAMFG Corolla Camry Mazda Suzuki CHINAMFG Pajero CHINAMFG
Product Description
Warm Tips: Please Contact Us To Confirm Your Car Model
Product Description
1.We are manufacturer of cv drive shaft,cv axle, cv joint and cv boot, we have more than 20-years experience in producing and selling auto parts.
2.We have strict quality control, the quality of our products is very good.
3.We are professional in different market around the world.
4.The reviews our customers given us are very positive, we have confidence in our products.
5.OEM/ODM is available, meet your requirements well.
6.Large warehouse, huge stocks!!! friendly for those customers who want some quantity.
7.Ship products out very fastly, we have stock.
| Product Name | Drive shaft | Material | 42CrMo alloy steel |
| Car fitment | Toyota | Warranty | 12 months |
| Model | for CZPT CZPT Honda CZPT CZPT CZPT VW Mazda BMW | Place of origin | ZHangZhoug, China |
| Productive year | pls contact us for more details | MOQ | 4 PCS |
| OE number | factory standard | Delivery time | 1-7 days |
| OEM/ODM | Yes | Brand | GJF |
| Packing size | according to each model | Payment | L/C,T/T,western Union,Cash,PayPal |
| Sample service | Depends on the situation of stock | Weight | 7.9KG |
Detailed Photos
Customer Review
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 12 Months |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Axle Number: | 1 |
| Samples: |
US$ 32.8/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
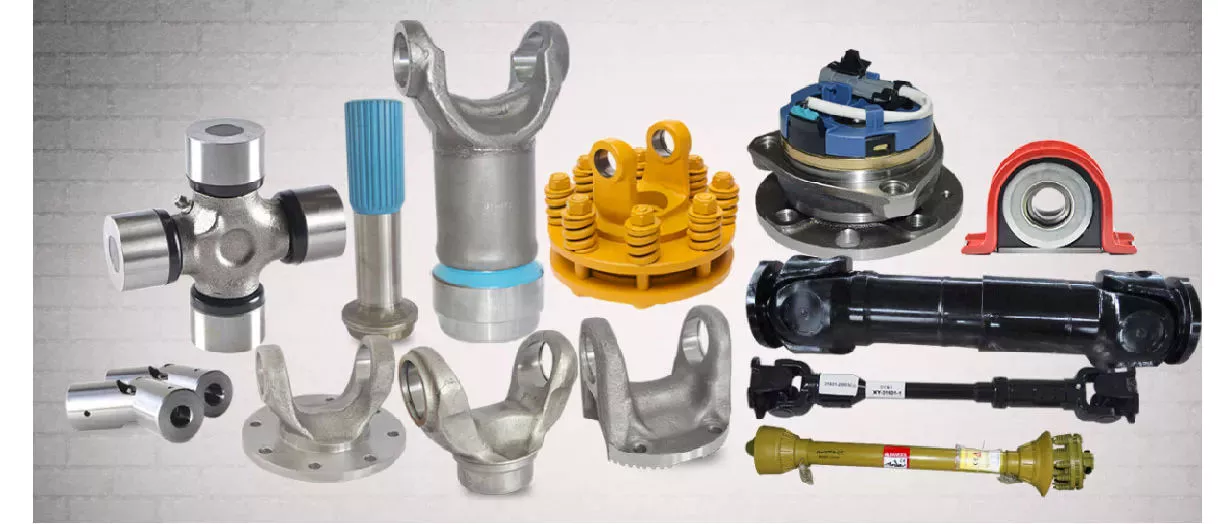

What factors should be considered when selecting the right drive shaft for an application?
When selecting the right drive shaft for an application, several factors need to be considered. The choice of drive shaft plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient and reliable power transmission. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Power and Torque Requirements:
The power and torque requirements of the application are essential considerations. It is crucial to determine the maximum torque that the drive shaft will need to transmit without failure or excessive deflection. This includes evaluating the power output of the engine or power source, as well as the torque demands of the driven components. Selecting a drive shaft with the appropriate diameter, material strength, and design is essential to ensure it can handle the expected torque levels without compromising performance or safety.
2. Operating Speed:
The operating speed of the drive shaft is another critical factor. The rotational speed affects the dynamic behavior of the drive shaft, including the potential for vibration, resonance, and critical speed limitations. It is important to choose a drive shaft that can operate within the desired speed range without encountering excessive vibrations or compromising the structural integrity. Factors such as the material properties, balance, and critical speed analysis should be considered to ensure the drive shaft can handle the required operating speed effectively.
3. Length and Alignment:
The length and alignment requirements of the application must be considered when selecting a drive shaft. The distance between the engine or power source and the driven components determines the required length of the drive shaft. In situations where there are significant variations in length or operating angles, telescopic drive shafts or multiple drive shafts with appropriate couplings or universal joints may be necessary. Proper alignment of the drive shaft is crucial to minimize vibrations, reduce wear and tear, and ensure efficient power transmission.
4. Space Limitations:
The available space within the application is an important factor to consider. The drive shaft must fit within the allocated space without interfering with other components or structures. It is essential to consider the overall dimensions of the drive shaft, including length, diameter, and any additional components such as joints or couplings. In some cases, custom or compact drive shaft designs may be required to accommodate space limitations while maintaining adequate power transmission capabilities.
5. Environmental Conditions:
The environmental conditions in which the drive shaft will operate should be evaluated. Factors such as temperature, humidity, corrosive agents, and exposure to contaminants can impact the performance and lifespan of the drive shaft. It is important to select materials and coatings that can withstand the specific environmental conditions to prevent corrosion, degradation, or premature failure of the drive shaft. Special considerations may be necessary for applications exposed to extreme temperatures, water, chemicals, or abrasive substances.
6. Application Type and Industry:
The specific application type and industry requirements play a significant role in drive shaft selection. Different industries, such as automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, agriculture, or marine, have unique demands that need to be addressed. Understanding the specific needs and operating conditions of the application is crucial in determining the appropriate drive shaft design, materials, and performance characteristics. Compliance with industry standards and regulations may also be a consideration in certain applications.
7. Maintenance and Serviceability:
The ease of maintenance and serviceability should be taken into account. Some drive shaft designs may require periodic inspection, lubrication, or replacement of components. Considering the accessibility of the drive shaft and associated maintenance requirements can help minimize downtime and ensure long-term reliability. Easy disassembly and reassembly of the drive shaft can also be beneficial for repair or component replacement.
By carefully considering these factors, one can select the right drive shaft for an application that meets the power transmission needs, operating conditions, and durability requirements, ultimately ensuring optimal performance and reliability.

Can you provide real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that use drive shafts?
Drive shafts are widely used in various vehicles and machinery to transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here are some real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that utilize drive shafts:
1. Automobiles:
Drive shafts are commonly found in automobiles, especially those with rear-wheel drive or four-wheel drive systems. In these vehicles, the drive shaft transfers power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or front differential, respectively. This allows the engine’s power to be distributed to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward.
2. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Drive shafts are essential components in trucks and commercial vehicles. They are used to transfer power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear axle or multiple axles in the case of heavy-duty trucks. Drive shafts in commercial vehicles are designed to handle higher torque loads and are often larger and more robust than those used in passenger cars.
3. Construction and Earthmoving Equipment:
Various types of construction and earthmoving equipment, such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and graders, rely on drive shafts for power transmission. These machines typically have complex drivetrain systems that use drive shafts to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks, enabling them to perform heavy-duty tasks on construction sites or in mining operations.
4. Agricultural Machinery:
Agricultural machinery, including tractors, combines, and harvesters, utilize drive shafts to transmit power from the engine to the wheels or driven components. Drive shafts in agricultural machinery are often subjected to demanding conditions and may have additional features such as telescopic sections to accommodate variable distances between components.
5. Industrial Machinery:
Industrial machinery, such as manufacturing equipment, generators, pumps, and compressors, often incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. These drive shafts transfer power from electric motors, engines, or other power sources to various driven components, enabling the machinery to perform specific tasks in industrial settings.
6. Marine Vessels:
In marine applications, drive shafts are commonly used to transmit power from the engine to the propeller in boats, ships, and other watercraft. Marine drive shafts are typically longer and designed to withstand the unique challenges posed by water environments, including corrosion resistance and appropriate sealing mechanisms.
7. Recreational Vehicles (RVs) and Motorhomes:
RVs and motorhomes often employ drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These drive shafts transfer power from the transmission to the rear axle, allowing the vehicle to move and providing propulsion. Drive shafts in RVs may have additional features such as dampers or vibration-reducing components to enhance comfort during travel.
8. Off-Road and Racing Vehicles:
Off-road vehicles, such as SUVs, trucks, and all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), as well as racing vehicles, frequently utilize drive shafts. These drive shafts are designed to withstand the rigors of off-road conditions or high-performance racing, transmitting power efficiently to the wheels and ensuring optimal traction and performance.
9. Railway Rolling Stock:
In railway systems, drive shafts are employed in locomotives and some types of rolling stock. They transfer power from the locomotive’s engine to the wheels or propulsion system, enabling the train to move along the tracks. Railway drive shafts are typically much longer and may have additional features to accommodate the articulated or flexible nature of some train configurations.
10. Wind Turbines:
Large-scale wind turbines used for generating electricity incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. The drive shafts transfer rotational energy from the turbine’s blades to the generator, where it is converted into electrical power. Drive shafts in wind turbines are designed to handle the significant torque and rotational forces generated by the wind.
These examples demonstrate the broad range of vehicles and machinery that rely on drive shafts for efficient power transmission and propulsion. Drive shafts are essential components in various industries, enabling the transfer of power from the source to the driven components, ultimately facilitating movement, operation, or the performance of specific tasks.

What benefits do drive shafts offer for different types of vehicles and equipment?
Drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They play a crucial role in power transmission and contribute to the overall performance, efficiency, and functionality of various systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the benefits that drive shafts provide:
1. Efficient Power Transmission:
Drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By connecting the engine or motor to the driven system, drive shafts efficiently transfer rotational power, allowing vehicles and equipment to perform their intended functions. This efficient power transmission ensures that the power generated by the engine is effectively utilized, optimizing the overall performance and productivity of the system.
2. Versatility:
Drive shafts offer versatility in their applications. They are used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and off-road vehicles. Additionally, drive shafts are employed in a wide range of equipment and machinery, such as agricultural machinery, construction equipment, industrial machinery, and marine vessels. The ability to adapt to different types of vehicles and equipment makes drive shafts a versatile component for power transmission.
3. Torque Handling:
Drive shafts are designed to handle high levels of torque. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source. Drive shafts are engineered to efficiently transmit this torque without excessive twisting or bending. By effectively handling torque, drive shafts ensure that the power generated by the engine is reliably transferred to the wheels or driven components, enabling vehicles and equipment to overcome resistance, such as heavy loads or challenging terrains.
4. Flexibility and Compensation:
Drive shafts provide flexibility and compensation for angular movement and misalignment. In vehicles, drive shafts accommodate the movement of the suspension system, allowing the wheels to move up and down independently. This flexibility ensures a constant power transfer even when the vehicle encounters uneven terrain. Similarly, in machinery, drive shafts compensate for misalignment between the engine or motor and the driven components, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing excessive stress on the drivetrain.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts contribute to weight reduction in vehicles and equipment. Compared to other forms of power transmission, such as belt drives or chain drives, drive shafts are typically lighter in weight. This reduction in weight helps improve fuel efficiency in vehicles and reduces the overall weight of equipment, leading to enhanced maneuverability and increased payload capacity. Additionally, lighter drive shafts contribute to a better power-to-weight ratio, resulting in improved performance and acceleration.
6. Durability and Longevity:
Drive shafts are designed to be durable and long-lasting. They are constructed using materials such as steel or aluminum, which offer high strength and resistance to wear and fatigue. Drive shafts undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure their reliability and longevity. Proper maintenance, including lubrication and regular inspections, further enhances their durability. The robust construction and long lifespan of drive shafts contribute to the overall reliability and cost-effectiveness of vehicles and equipment.
7. Safety:
Drive shafts incorporate safety features to protect operators and bystanders. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing, preventing contact with moving parts and reducing the risk of injury in the event of a failure. Similarly, in machinery, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts to minimize the potential hazards associated with rotating components. These safety measures ensure the well-being of individuals operating or working in proximity to vehicles and equipment.
In summary, drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They enable efficient power transmission, provide versatility in various applications, handle torque effectively, offer flexibility and compensation, contribute to weight reduction, ensure durability and longevity, and incorporate safety features. By providing these advantages, drive shafts enhance the performance, efficiency, reliability, and safety of vehicles and equipment across a wide range of industries.


editor by CX 2024-03-18
China Professional Gjf Brand One Stop Service Front and Rear CV Axle CV Joint Driveshaft for CZPT Corolla Zze12 Altis Wish 1.8 2001- C-To054A-8h Drive Line
Product Description
Product Description
Our Advantages:
1.We are manufacturer of drive shaft,cv joint and cv boot, we have more than 20-years experience in producing and selling auto parts.
2.We have strict quality control, the quality of our products is very good.
3.We are professional in different market around the world.
4.The reviews our customers given us are very positive, we have confidence in our products.
5.OEM/ODM is available, meet your requirements well.
6.Large warehouse, huge stocks!!! friendly for those customers who want some quantity.
7.Ship products out very fastly, we have stock.
→→More detail pictures of our products,
Pls contact us!!
| Product Name | One stop purchase of drive shaft and cv joint | Material | 42CrMo alloy steel |
| Car fitment | Toyota | Warranty | 12 months |
| Model | for CZPT Corolla ZZE12 ALTIS WISH 1.8 2001- C-TO054A-8H | Place of origin | ZHangZhoug, China |
| Productive year | pls contact us for more details | MOQ | 4 PCS |
| OE number | factory standard | Delivery time | 1-7 days |
| OEM/ODM | Yes | Brand | GJF |
| Packing size | according to each model | Payment | L/C,T/T,western Union,Cash,PayPal |
| Sample service | Depends on the situation of stock | Weight | 7.9KG |
Detailed Photos
Customer Review
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 12 Months Warranty |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Samples: |
US$ 1.15/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do manufacturers ensure the compatibility of driveline components with different vehicles?
Manufacturers employ various measures to ensure the compatibility of driveline components with different vehicles. These measures involve careful design, engineering, testing, and standardization processes to meet the specific requirements of each vehicle type. Let’s explore how manufacturers ensure compatibility:
1. Vehicle-Specific Design:
Manufacturers design driveline components with specific vehicle types in mind. Each vehicle type, such as passenger cars, trucks, SUVs, or commercial vehicles, has unique requirements in terms of power output, torque capacity, weight distribution, space constraints, and intended usage. Manufacturers consider these factors during the component design phase to ensure that the driveline components are optimized for compatibility with the intended vehicle type.
2. Engineering and Simulation:
Manufacturers employ advanced engineering techniques and simulation tools to evaluate the performance and compatibility of driveline components. They use computer-aided design (CAD) software and finite element analysis (FEA) simulations to model and analyze the behavior of the components under various operating conditions. This allows them to identify any potential compatibility issues, such as excessive stress, misalignment, or interference, and make necessary design adjustments before moving to the production stage.
3. Prototyping and Testing:
Manufacturers create prototypes of driveline components and subject them to rigorous testing to ensure compatibility. These tests include bench testing, dynamometer testing, and vehicle-level testing. By simulating real-world operating conditions, manufacturers can evaluate the performance, durability, and compatibility of the components. They assess factors such as power transmission efficiency, torque capacity, heat dissipation, noise and vibration levels, and overall drivability to ensure that the components meet the requirements and are compatible with the intended vehicle.
4. Standardization:
Manufacturers adhere to industry standards and specifications to ensure compatibility and interchangeability of driveline components. These standards cover various aspects such as dimensions, material properties, spline profiles, shaft diameters, and mounting interfaces. By following established standards, manufacturers can ensure that their driveline components can be seamlessly integrated into different vehicles from various manufacturers, promoting compatibility and ease of replacement or upgrade.
5. Collaborative Development:
Manufacturers often collaborate closely with vehicle manufacturers during the development process to ensure compatibility. This collaboration involves sharing specifications, design requirements, and performance targets. By working together, driveline manufacturers can align their component designs with the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications, ensuring that the driveline components fit within the vehicle’s space constraints, mating interfaces, and intended usage. This collaborative approach helps optimize compatibility and integration between the driveline components and the vehicle’s overall system.
6. Continuous Improvement:
Manufacturers continuously improve their driveline components based on feedback, field data, and advancements in technology. They gather information from vehicle manufacturers, end-users, and warranty claims to identify any compatibility issues or performance shortcomings. This feedback loop helps drive refinements and enhancements in the design, manufacturing processes, and material selection of the driveline components, ensuring better compatibility and performance in future iterations.
Overall, manufacturers employ a combination of vehicle-specific design, engineering and simulation, prototyping and testing, standardization, collaborative development, and continuous improvement to ensure the compatibility of driveline components with different vehicles. These efforts help optimize power transmission, reliability, and performance, while ensuring a seamless integration of the driveline components into the diverse range of vehicles present in the market.

How do drivelines handle variations in speed and direction during operation?
Drivelines are designed to handle variations in speed and direction during operation, enabling the efficient transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. They employ various components and mechanisms to accommodate these variations and ensure smooth and reliable power transmission. Let’s explore how drivelines handle speed and direction variations:
1. Transmissions:
Transmissions play a crucial role in managing speed variations in drivelines. They allow for the selection of different gear ratios to match the engine’s torque and speed with the desired vehicle speed. By shifting gears, the transmission adjusts the rotational speed and torque delivered to the driveline, enabling the vehicle to operate effectively at various speeds. Transmissions can be manual, automatic, or continuously variable, each with its own mechanism for achieving speed variation control.
2. Clutches:
Clutches are used in drivelines to engage or disengage power transmission between the engine and the driveline components. They allow for smooth engagement during startup and shifting gears, as well as for disconnecting the driveline when the vehicle is stationary or the engine is idling. Clutches facilitate the control of speed variations by providing a means to temporarily interrupt power flow and smoothly transfer torque between rotating components.
3. Differential:
The differential is a key component in drivelines, particularly in vehicles with multiple driven wheels. It allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds while maintaining power transfer. When a vehicle turns, the inside and outside wheels travel different distances and need to rotate at different speeds. The differential allows for this speed variation by distributing torque between the wheels, ensuring smooth operation and preventing tire scrubbing or driveline binding.
4. Universal Joints and CV Joints:
Universal joints and constant velocity (CV) joints are used in drivelines to accommodate variations in direction. Universal joints are typically employed in drivelines with a driveshaft, allowing for the transmission of rotational motion even when there is an angular misalignment between the driving and driven components. CV joints, on the other hand, are used in drivelines that require constant velocity and smooth power transfer at varying angles, such as front-wheel drive vehicles. These joints allow for a consistent transfer of torque while accommodating changes in direction.
5. Transfer Cases:
In drivelines with multiple axles or drivetrains, transfer cases are used to distribute power and torque to different wheels or axles. Transfer cases are commonly found in four-wheel drive or all-wheel drive systems. They allow for variations in speed and direction by proportionally distributing torque between the front and rear wheels, or between different axles, based on the traction requirements of the vehicle.
6. Electronic Control Systems:
Modern drivelines often incorporate electronic control systems to further enhance speed and direction control. These systems utilize sensors, actuators, and computer algorithms to monitor and adjust power distribution, shift points, and torque delivery based on various inputs, such as vehicle speed, throttle position, wheel slip, and road conditions. Electronic control systems enable precise and dynamic management of speed and direction variations, improving traction, fuel efficiency, and overall driveline performance.
By integrating transmissions, clutches, differentials, universal joints, CV joints, transfer cases, and electronic control systems, drivelines effectively handle variations in speed and direction during operation. These components and mechanisms work together to ensure smooth power transmission, optimized performance, and enhanced vehicle control in a wide range of driving conditions and applications.

Which industries and vehicles commonly use drivelines for power distribution?
Drivelines are widely used in various industries and vehicles for power distribution. They play a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine or power source to the driven components, enabling motion and torque transfer. Here’s a detailed explanation of the industries and vehicles that commonly utilize drivelines for power distribution:
1. Automotive Industry: The automotive industry extensively utilizes drivelines in passenger cars, commercial vehicles, and off-road vehicles. Drivelines are a fundamental component of vehicles, enabling power transmission from the engine to the wheels. They are found in a range of vehicle types, including sedans, SUVs, pickup trucks, vans, buses, and heavy-duty trucks. Drivelines in the automotive industry are designed to provide efficient power distribution, enhance vehicle performance, and ensure smooth acceleration and maneuverability.
2. Agricultural Industry: Drivelines are essential in the agricultural industry for various farming machinery and equipment. Tractors, combines, harvesters, and other agricultural machinery rely on drivelines to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks. Drivelines in agricultural equipment often incorporate power take-off (PTO) units, allowing the connection of implements such as plows, seeders, and balers. These drivelines are designed to handle high torque loads, provide traction in challenging field conditions, and facilitate efficient farming operations.
3. Construction and Mining Industries: Drivelines are extensively used in construction and mining equipment, where they enable power distribution and mobility in heavy-duty machinery. Excavators, bulldozers, wheel loaders, dump trucks, and other construction and mining vehicles rely on drivelines to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks. Drivelines in these industries are designed to withstand rigorous operating conditions, deliver high torque and traction, and provide the necessary power for excavation, hauling, and material handling tasks.
4. Industrial Equipment: Various industrial equipment and machinery utilize drivelines for power distribution. This includes material handling equipment such as forklifts and cranes, industrial trucks, conveyor systems, and industrial vehicles used in warehouses, factories, and distribution centers. Drivelines in industrial equipment are designed to provide efficient power transmission, precise control, and maneuverability in confined spaces, enabling smooth and reliable operation in industrial settings.
5. Off-Road and Recreational Vehicles: Drivelines are commonly employed in off-road and recreational vehicles, including all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), side-by-side vehicles (UTVs), dirt bikes, snowmobiles, and recreational boats. These vehicles require drivelines to transfer power from the engine to the wheels, tracks, or propellers, enabling off-road capability, traction, and water propulsion. Drivelines in off-road and recreational vehicles are designed for durability, performance, and enhanced control in challenging terrains and recreational environments.
6. Railway Industry: Drivelines are utilized in railway locomotives and trains for power distribution and propulsion. They are responsible for transmitting power from the locomotive’s engine to the wheels or driving systems, enabling the movement of trains on tracks. Drivelines in the railway industry are designed to handle high torque requirements, ensure efficient power transfer, and facilitate safe and reliable train operation.
7. Marine Industry: Drivelines are integral components in marine vessels, including boats, yachts, ships, and other watercraft. Marine drivelines are used for power transmission from the engine to the propellers or water jets, providing thrust and propulsion. They are designed to withstand the corrosive marine environment, handle high torque loads, and ensure efficient power transfer for marine propulsion.
These are some of the industries and vehicles that commonly rely on drivelines for power distribution. Drivelines are versatile components that enable efficient power transmission, mobility, and performance across a wide range of applications, contributing to the functionality and productivity of various industries and vehicles.


editor by CX 2024-03-18
China Best Sales Car Auto Parts Axle Shaft Front Left Right CV Axle Drive Shaft for CHINAMFG Corolla Camry CHINAMFG Mazda Suzuki CHINAMFG Pajero CHINAMFG
Product Description
As a professional manufacturer for propeller shaft, we have +800 items for all kinds of car, main suitable
for AMERICA & EUROPE market.
Our advantage:
1. Full range of products
2. MOQ qty: 5pcs/items
3. Delivery on time
4: Warranty: 1 YEAR
5. Develope new items: FREE
|
Brand Name |
KOWA DRIVE SHAFT |
|
Item name |
OEM |
|
Car maker |
For all japanese/korean/european/american car |
|
Moq |
5pcs |
|
Guarantee |
12 months |
|
sample |
Available if have stock |
|
Price |
Send inquiry to get lastest price |
|
BOX/QTY |
1PCS/Bag 4PCS /CTNS |
For some items, we have stock, small order (+3000USD) is welcome.
The following items are some of drive shafts, If you need more information, pls contact us for ASAP.
| For Japanese Car | |||
| for TOYOTA | for TOYOTA | ||
| 43420-57170 | 43420-57180 | 43410-0W081 | 43420-0W080 |
| 43410-57120 | 43420-57190 | 43410-0W091 | 43420-0W090 |
| 43410-57130 | 43420-57120 | 43410-0W100 | 43420-0W110 |
| 43410-57150 | 43420-02B10 | 43410-0W110 | 43420-0W160 |
| 43410-06221 | 43420-02B11 | 43410-0W140 | 43420-32161 |
| 43410-06231 | 43420-02B60 | 43410-0W150 | 43420-33250 |
| 43410-06460 | 43420-02B61 | 43410-0W180 | 43420-33280 |
| 43410-06570 | 43420-02B62 | 43410-12410 | 43420-48090 |
| 43410-06580 | 43420-06221 | 43410-33280 | 43420-48091 |
| 43410-066-90 | 43420-06231 | 43410-33290 | 43430OK571 |
| 43410-06750 | 43420-06460 | 43410-33330 | 66-5245 |
| 43410-06780 | 43420-06490 | 43410-48070 | 66-5247 |
| 43410-06A40 | 43420-06500 | 43410-48071 | 43420-57150 |
| 43410-06A50 | 43420- 0571 0 | 43410-0W061 | 43420-0W061 |
| 43410-07070 | 43420-06610 | 43410-0W071 | 43420-0W071 |
| for Acura | for LEXUS | ||
| 44305STKA00 | 66-4198 | 43410-06200 | 43410-06480 |
| 44305STKA01 | 66-4261 | 43410-06450 | 43410-06560 |
| 44305SZPA00 | 66-4262 | 66-5265 | |
| 44306STKA00 | 66-4270 | for MITSUBISHI | |
| 44306STKA01 | 66-4271 | 3815A309 | 3815A310 |
| 44306SZPA00 | |||
| for Honda | for MAZDA | ||
| 44571S1571 | 44306S3VA61 | 5L8Z3A428AB | GG052550XD |
| 44011S1571 | 44306S3VA62 | 5L8Z3A428DA | GG052560XE |
| 44305S2HN50 | 44306S9VA51 | 66-2090 | GG362550XA |
| 44305SCVA50 | 44306S9VA71 | 6L8Z3A428A | YL8Z3A427AA |
| 44305SCVA51 | 44306SCVA50 | 9L8Z3A427B | YL8Z3A427BA |
| 44305SCVA90 | 44306SCVA51 | GG032550XD | YL8Z3A428AA |
| 44305SCVA91 | 44306SCVA90 | GG042550XD | YL8Z3A428BA |
| 44305STXA02 | 44306SCVA91 | GG042560XG | ZC32550XA |
| 44305SZAA01 | 44306STXA02 | ||
| 44306S2H951 | 44306SZAA01 | ||
| 44306SZAA11 | 44306SZAA01RM | ||
| 44306SZAA12 | 66-4213 | ||
| 66-4214 | |||
| for Europe Car | |||
| for VOLKSWAGEN | for VOLKSWAGEN | ||
| 4885712AD | 7B0407271B | 7E0407271G | 7LA407272C |
| 4885713AF | 7B0407272 | 7E0407271P | 7LA4 0571 2CX |
| 4881214AE | 7B0407272E | 7LA407271E | |
| 7B0407271A | |||
| for America Car | |||
| for CHRYSLER | for MERCURY | ||
| 4593447AA | 557180AD | 4F1Z3B437AA | GG322560X |
| 4641855AA | 52114390AB | 5L8Z3A428DB | GG362560XA |
| 4641855AC | 5273546AC | 66-2249 | YL8Z3A427CA |
| 4641856AA | 66-3108 | 9L8Z3A427C | YL8Z3A427DA |
| 4641856AC | 66-3109 | 9L8Z3A427D | YL8Z3A427EA |
| 4882517 | 66-3130 | GG062550XD | YL8Z3A427FA |
| 4882518 | 66-3131 | GG062560XE | YL8Z3A428CA |
| 4882519 | 66-3234 | GG312560X | ZZDA2560X |
| 4882520 | 66-3518 | ZZDA2560XC | ZZDA2560XA |
| 557130AB | 66-3520 | for RAM | |
| 66-3552 | 66-3522 | 4885713AD | 55719AB |
| 66-3553 | 66-3551 | 4881214AD | 66-3404 |
| 66-3554 | 66-3639 | 55719AA | 66-3740 |
| 68193908AB | 66-3641 | 68571398AA | |
| for FORD | for DODGE | ||
| 1F0571400 | E6DZ3V428AARM | 4593449AA | 7B0407272A |
| 1F0571410 | E8DZ3V427AARM | 4641855AE | 7B0407272B |
| 1F2Z3B436AA | E8DZ3V428AARM | 4641855EE | 7B0407272C |
| 2F1Z3A428CA | E90Y3V427AARM | 4641856AD | R4881214AE |
| 2M5Z3B437CA | E90Y3V428AARM | 4641856AF | RL189279AA |
| 4F1Z3B437BA | F0DZ3V427AARM | 4885710AC | 557180AG |
| 5M6Z3A428AA | F0DZ3V428AARM | 4885710AE | 5170822AA |
| 5S4Z3B437AA | F21Z3B437A | 4885710AF | 52114390AA |
| 66-2005 | F21Z3B437B | 4885710AG | 5273546AD |
| 66-2008 | F2DZ3B436A | 4885711AC | 5273546AE |
| 66-2571 | F2DZ3B436B | 4885711AD | 5273546AF |
| 66-2084 | F2DZ3B437A | 4885712AC | 5273558AB |
| 66-2086 | F2DZ3B437B | 4885712AE | 5273558AD |
| 66-2095 | F4DZ3B437A | 4885712AG | 5273558AE |
| 66-2101 | F57Z3B436BA | 4885712AH | 5273558AF |
| 66-2143 | F57Z3B437BA | 4885713AC | 4881214AC |
| 6S4Z3B437BA | F5DZ3A427BA | 4885713AG | 4881214AF |
| 8S4Z3B437A | F5DZ3A428AS | 4885713AI | 4881214AG |
| 9L8Z3A427A | F5DZ3B426D | 4885713AJ | 557130AA |
| E6DZ3V427AARM | F5DZ3B436D | 5273558AG | 557180AE |
| YF1Z3A428RS | F5DZ3B437B | 66-3382 | 557180AF |
| YL8Z3A428DA | F5TZ3B436A | 66-3511 | 66-3514 |
| YS4Z3B437BB | GG032560XG | 66-3759 | 66-3564 |
| YS4Z3B437CB | GG362550X | ||
| YF1Z3A427L | |||
| for CHEVROLET | for JEEP | ||
| 257191 | 26062613 | 4578885AA | 5215710AA |
| 22791460 | 4578885AB | 5215711AB | |
| 26011961 | 4578885AC | 5215711AB | |
| 26571730 | 2657189 | 4720380 | 5273438AC |
| 2657165 | 66-1401 | 4720381 | 5273438AD |
| 26058932 | 66-1438 | 5012456AB | 5273438AE |
| 26065719 | 88982496 | 5012457AB | 5273438AG |
| for HUMMER | 5066571AA | 66-3220 | |
| 1571204 | 595716 | 557120AB | 66-3221 |
| 15886012 | 66-1417 | 557120AC | 66-3298 |
| for CADILLAC | 557120AD | 66-3352 | |
| 88957151 | 66-1416 | 557120AE | 66-3417 |
| 66-1009 | 66-1430 | 5189278AA | 66-3418 |
| 66-1415 | 88957150 | 5189279AA | 66-3419 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Nissan, Toyota, Europe Japan Korea |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
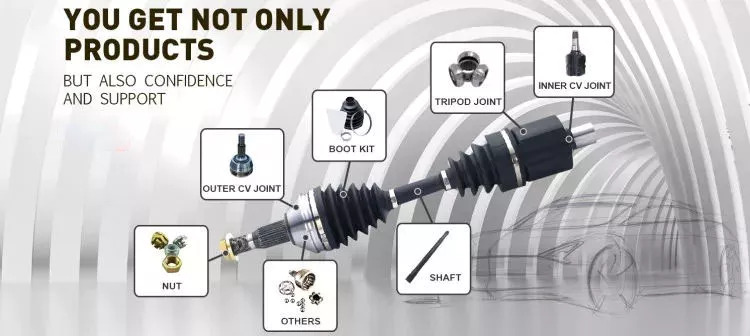
How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

Can drive shafts be customized for specific vehicle or equipment requirements?
Yes, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements. Customization allows manufacturers to tailor the design, dimensions, materials, and other parameters of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility and optimal performance within a particular vehicle or equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts can be customized:
1. Dimensional Customization:
Drive shafts can be customized to match the dimensional requirements of the vehicle or equipment. This includes adjusting the overall length, diameter, and spline configuration to ensure proper fitment and clearances within the specific application. By customizing the dimensions, the drive shaft can be seamlessly integrated into the driveline system without any interference or limitations.
2. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for drive shafts can be customized based on the specific requirements of the vehicle or equipment. Different materials, such as steel alloys, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, can be selected to optimize strength, weight, and durability. The material selection can be tailored to meet the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the application, ensuring the drive shaft’s reliability and longevity.
3. Joint Configuration:
Drive shafts can be customized with different joint configurations to accommodate specific vehicle or equipment requirements. For example, universal joints (U-joints) may be suitable for applications with lower operating angles and moderate torque demands, while constant velocity (CV) joints are often used in applications requiring higher operating angles and smoother power transmission. The choice of joint configuration depends on factors such as operating angle, torque capacity, and desired performance characteristics.
4. Torque and Power Capacity:
Customization allows drive shafts to be designed with the appropriate torque and power capacity for the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers can analyze the torque requirements, operating conditions, and safety margins of the application to determine the optimal torque rating and power capacity of the drive shaft. This ensures that the drive shaft can handle the required loads without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
5. Balancing and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can be customized with precision balancing and vibration control measures. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, increased wear, and potential driveline issues. By employing dynamic balancing techniques during the manufacturing process, manufacturers can minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation. Additionally, vibration dampers or isolation systems can be integrated into the drive shaft design to further mitigate vibrations and enhance overall system performance.
6. Integration and Mounting Considerations:
Customization of drive shafts takes into account the integration and mounting requirements of the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers work closely with the vehicle or equipment designers to ensure that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the driveline system. This includes adapting the mounting points, interfaces, and clearances to ensure proper alignment and installation of the drive shaft within the vehicle or equipment.
7. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate with vehicle manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft customization process. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can address specific needs, optimize performance, and ensure compatibility with the vehicle or equipment. This collaborative approach enhances the customization process and results in drive shafts that meet the exact requirements of the application.
8. Compliance with Standards:
Customized drive shafts can be designed to comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, ensures that the customized drive shafts meet quality, safety, and performance requirements. Adhering to these standards provides assurance that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into the specific vehicle or equipment.
In summary, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements through dimensional customization, material selection, joint configuration, torque and power capacity optimization, balancing and vibration control, integration and mounting considerations, collaboration with stakeholders, and compliance with industry standards. Customization allows drive shafts to be precisely tailored to the needs of the application, ensuring compatibility, reliability, and optimal performance.

How do drive shafts contribute to transferring rotational power in various applications?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in transferring rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in various applications. Whether it’s in vehicles or machinery, drive shafts enable efficient power transmission and facilitate the functioning of different systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to transferring rotational power:
1. Vehicle Applications:
In vehicles, drive shafts are responsible for transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move. The drive shaft connects the gearbox or transmission output shaft to the differential, which further distributes the power to the wheels. As the engine generates torque, it is transferred through the drive shaft to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward. This power transfer allows the vehicle to accelerate, maintain speed, and overcome resistance, such as friction and inclines.
2. Machinery Applications:
In machinery, drive shafts are utilized to transfer rotational power from the engine or motor to various driven components. For example, in industrial machinery, drive shafts may be used to transmit power to pumps, generators, conveyors, or other mechanical systems. In agricultural machinery, drive shafts are commonly employed to connect the power source to equipment such as harvesters, balers, or irrigation systems. Drive shafts enable these machines to perform their intended functions by delivering rotational power to the necessary components.
3. Power Transmission:
Drive shafts are designed to transmit rotational power efficiently and reliably. They are capable of transferring substantial amounts of torque from the engine to the wheels or driven components. The torque generated by the engine is transmitted through the drive shaft without significant power losses. By maintaining a rigid connection between the engine and the driven components, drive shafts ensure that the power produced by the engine is effectively utilized in performing useful work.
4. Flexible Coupling:
One of the key functions of drive shafts is to provide a flexible coupling between the engine/transmission and the wheels or driven components. This flexibility allows the drive shaft to accommodate angular movement and compensate for misalignment between the engine and the driven system. In vehicles, as the suspension system moves or the wheels encounter uneven terrain, the drive shaft adjusts its length and angle to maintain a constant power transfer. This flexibility helps prevent excessive stress on the drivetrain components and ensures smooth power transmission.
5. Torque and Speed Transmission:
Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). Drive shafts must be capable of handling the torque requirements of the application without excessive twisting or bending. Additionally, they need to maintain the desired rotational speed to ensure the proper functioning of the driven components. Proper design, material selection, and balancing of the drive shafts contribute to efficient torque and speed transmission.
6. Length and Balance:
The length and balance of drive shafts are critical factors in their performance. The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven components. It should be appropriately sized to avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Drive shafts are carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can affect the overall performance, comfort, and longevity of the drivetrain system.
7. Safety and Maintenance:
Drive shafts require proper safety measures and regular maintenance. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts, reducing the risk of injury. Safety shields or guards may also be installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards. Regular maintenance includes inspecting the drive shaft for wear, damage, or misalignment, and ensuring proper lubrication of the U-joints. These measures help prevent failures, ensure optimal performance, and extend the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, drive shafts play a vital role in transferring rotational power in various applications. Whether in vehicles or machinery, drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. They provide a flexible coupling, handle torque and speed transmission, accommodate angular movement, and contribute to the safety and maintenance of the system. By effectively transferring rotational power, drive shafts facilitate the functioning and performance of vehicles and machinery in numerous industries.


editor by CX 2024-03-15
China Custom Professional Drive Shaft Cardan Shaft with High Performance for Rolling Mill Drive Line
Product Description
Rolling Mill of Professional Cardan Shaft with ISO Certificate
Brief Introduction
Processing flow
Applications
Quality Control
Product Description
| structure | universal | Flexible or Rigid | Rigid | Standard or Nonstandard | Nonstandard |
| Material | Alloy steel | Brand name | HangZhou XIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS. | Place of origin | ZheJiang ,China |
| Model | SWC Medium | Raw materials | heat treatment | Length | depend on specification |
| Flange DIA | 160mm~620mm | Nominal torque | depend on required specification(please confirm with us) | coating | heavy duty industrial paint |
| Paint clour | customization | Application | Rolling mill machinery | OEM/ODM | Available |
| Certification | ISO,TUV,SGS | Price | calculate according to required specification | Custom service | Available |
Packaging & Delivery
Packaging details:Standard plywood case
Delivery detail: 15 -20 working days,depend on the actual produce condition
FAQ
Q1: What is the location of your company?
A1: Our company is located in the HangZhou City ,ZheJiang ,China.Welcome to visit our factory at anytime!
Q2: How does your factory do regarding quality control?
A2: Our standard QC system to control quality.
Q3: What is your delivery time?
A3: Usually within 25 days after the receipt of payment.Delivery time must depend on the actual produce condition.
Q4: What are your strengths?
A4: 1.We are the manufacturer,having competitive advantage in price.
2.A large part of money is put into advancing CNC equipments and productR&D department annual,the performance of cardan shaft can be guaranteed.
3.About quality issues or follow-up after-sales service,we report directly to the boss.
4.We have the ambitions to exploring and developing the world’s cardan shaft market and we believe we can.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Hollow Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do manufacturers ensure the compatibility of driveline components with different vehicles?
Manufacturers employ various measures to ensure the compatibility of driveline components with different vehicles. These measures involve careful design, engineering, testing, and standardization processes to meet the specific requirements of each vehicle type. Let’s explore how manufacturers ensure compatibility:
1. Vehicle-Specific Design:
Manufacturers design driveline components with specific vehicle types in mind. Each vehicle type, such as passenger cars, trucks, SUVs, or commercial vehicles, has unique requirements in terms of power output, torque capacity, weight distribution, space constraints, and intended usage. Manufacturers consider these factors during the component design phase to ensure that the driveline components are optimized for compatibility with the intended vehicle type.
2. Engineering and Simulation:
Manufacturers employ advanced engineering techniques and simulation tools to evaluate the performance and compatibility of driveline components. They use computer-aided design (CAD) software and finite element analysis (FEA) simulations to model and analyze the behavior of the components under various operating conditions. This allows them to identify any potential compatibility issues, such as excessive stress, misalignment, or interference, and make necessary design adjustments before moving to the production stage.
3. Prototyping and Testing:
Manufacturers create prototypes of driveline components and subject them to rigorous testing to ensure compatibility. These tests include bench testing, dynamometer testing, and vehicle-level testing. By simulating real-world operating conditions, manufacturers can evaluate the performance, durability, and compatibility of the components. They assess factors such as power transmission efficiency, torque capacity, heat dissipation, noise and vibration levels, and overall drivability to ensure that the components meet the requirements and are compatible with the intended vehicle.
4. Standardization:
Manufacturers adhere to industry standards and specifications to ensure compatibility and interchangeability of driveline components. These standards cover various aspects such as dimensions, material properties, spline profiles, shaft diameters, and mounting interfaces. By following established standards, manufacturers can ensure that their driveline components can be seamlessly integrated into different vehicles from various manufacturers, promoting compatibility and ease of replacement or upgrade.
5. Collaborative Development:
Manufacturers often collaborate closely with vehicle manufacturers during the development process to ensure compatibility. This collaboration involves sharing specifications, design requirements, and performance targets. By working together, driveline manufacturers can align their component designs with the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications, ensuring that the driveline components fit within the vehicle’s space constraints, mating interfaces, and intended usage. This collaborative approach helps optimize compatibility and integration between the driveline components and the vehicle’s overall system.
6. Continuous Improvement:
Manufacturers continuously improve their driveline components based on feedback, field data, and advancements in technology. They gather information from vehicle manufacturers, end-users, and warranty claims to identify any compatibility issues or performance shortcomings. This feedback loop helps drive refinements and enhancements in the design, manufacturing processes, and material selection of the driveline components, ensuring better compatibility and performance in future iterations.
Overall, manufacturers employ a combination of vehicle-specific design, engineering and simulation, prototyping and testing, standardization, collaborative development, and continuous improvement to ensure the compatibility of driveline components with different vehicles. These efforts help optimize power transmission, reliability, and performance, while ensuring a seamless integration of the driveline components into the diverse range of vehicles present in the market.
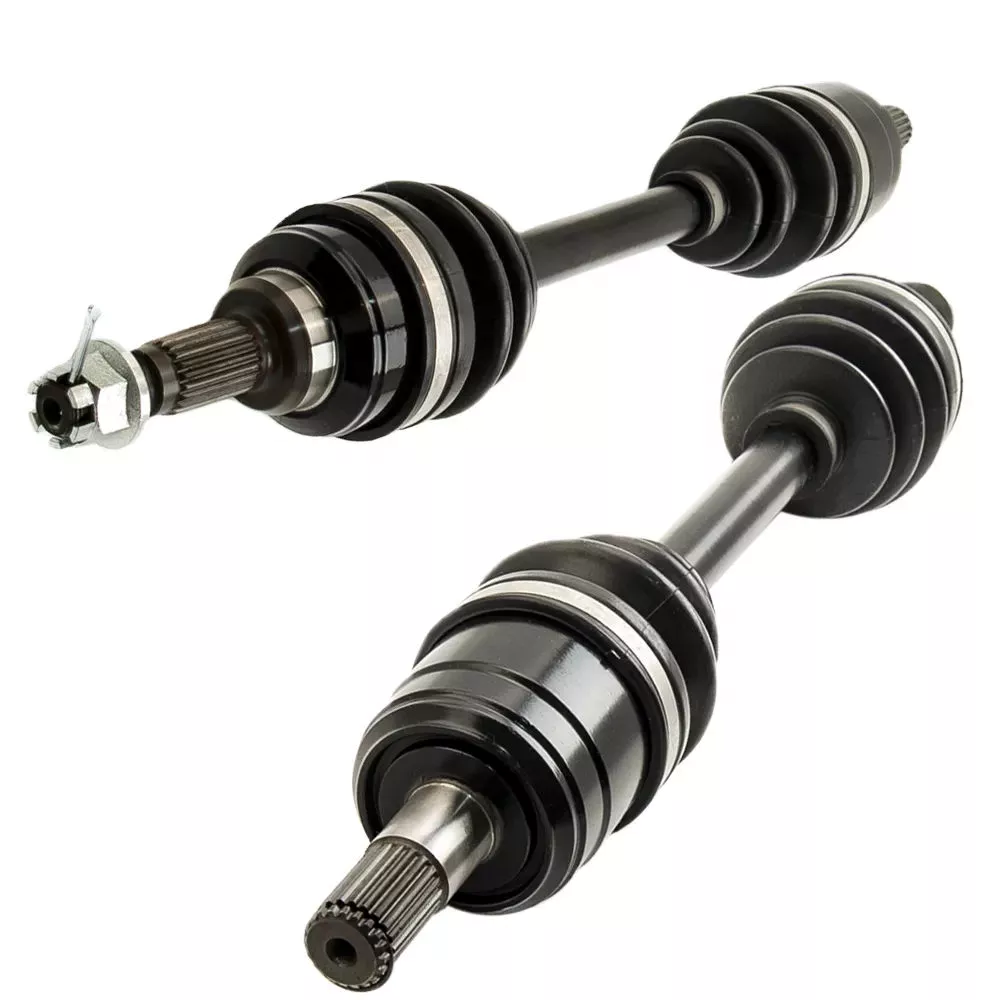

Can driveline components be customized for specific vehicle or equipment requirements?
Yes, driveline components can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements. Manufacturers and suppliers offer a range of options for customization to ensure optimal performance, compatibility, and integration with different vehicles or equipment. Customization allows for tailoring the driveline components to specific powertrain configurations, operating conditions, torque requirements, and space constraints. Let’s explore the details of customization for driveline components:
1. Powertrain Configuration:
Driveline components can be customized to accommodate different powertrain configurations. Whether it’s a front-wheel drive, rear-wheel drive, or all-wheel drive system, manufacturers can design and provide specific components such as differentials, gearboxes, and drive shafts that are compatible with the required power distribution and torque transfer characteristics of the particular configuration.
2. Torque Capacity:
Driveline components can be customized to handle specific torque requirements. Different vehicles or equipment may have varying torque outputs based on their intended applications. Manufacturers can engineer and produce driveline components with varying torque-handling capabilities to ensure reliable and efficient power transmission for a range of applications, from passenger vehicles to heavy-duty trucks or machinery.
3. Size and Configuration:
Driveline components can be customized in terms of size, shape, and configuration to fit within the space constraints of different vehicles or equipment. Manufacturers understand that each application may have unique packaging limitations, such as limited available space or specific mounting requirements. Through customization, driveline components can be designed and manufactured to align with these specific dimensional and packaging constraints.
4. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for driveline components can be customized based on the required strength, weight, and durability characteristics. Different vehicles or equipment may demand specific material properties to optimize performance, such as lightweight materials for improved fuel efficiency or high-strength alloys for heavy-duty applications. Manufacturers can provide customized driveline components with materials selected to meet the specific performance and operational requirements.
5. Performance Optimization:
Driveline components can be customized to optimize performance in specific applications. Manufacturers can modify aspects such as gear ratios, differential configurations, or clutch characteristics to enhance acceleration, traction, efficiency, or specific performance attributes based on the intended use of the vehicle or equipment. This customization ensures that the driveline components are tailored to deliver the desired performance characteristics for the specific application.
6. Specialized Applications:
For specialized applications, such as off-road vehicles, racing cars, or industrial machinery, driveline components can be further customized to meet the unique demands of those environments. Manufacturers can develop specialized driveline components with features like enhanced cooling, reinforced construction, or increased torque capacity to withstand extreme conditions or heavy workloads.
Overall, customization of driveline components allows manufacturers to meet the specific requirements of different vehicles or equipment. From powertrain configuration to torque capacity, size and configuration, material selection, performance optimization, and specialized applications, customization ensures that driveline components are precisely designed and engineered to achieve the desired performance, compatibility, and integration with specific vehicles or equipment.

How do drivelines contribute to power transmission and motion in various applications?
Drivelines play a crucial role in power transmission and motion in various applications, including automotive vehicles, agricultural machinery, construction equipment, and industrial systems. They are responsible for transmitting power from the engine or power source to the driven components, enabling motion and providing the necessary torque to perform specific tasks. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drivelines contribute to power transmission and motion in various applications:
1. Automotive Vehicles: In automotive vehicles, such as cars, trucks, and motorcycles, drivelines transmit power from the engine to the wheels, enabling motion and propulsion. The driveline consists of components such as the engine, transmission, drive shafts, differentials, and axles. The engine generates power by burning fuel, and this power is transferred to the transmission. The transmission selects the appropriate gear ratio and transfers power to the drive shafts. The drive shafts transmit the power to the differentials, which distribute it to the wheels. The wheels, in turn, convert the rotational power into linear motion, propelling the vehicle forward or backward.
2. Agricultural Machinery: Drivelines are extensively used in agricultural machinery, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters. These machines require power transmission to perform various tasks, including plowing, tilling, planting, and harvesting. The driveline in agricultural machinery typically consists of a power take-off (PTO) unit, drive shafts, gearboxes, and implement shafts. The PTO unit connects to the tractor’s engine and transfers power to the drive shafts. The drive shafts transmit power to the gearboxes, which further distribute it to the implement shafts. The implement shafts drive the specific agricultural implements, enabling them to perform their intended functions.
3. Construction Equipment: Drivelines are essential in construction equipment, such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes. These machines require power transmission to perform tasks such as digging, lifting, pushing, and hauling. The driveline in construction equipment typically consists of an engine, transmission, drive shafts, hydraulic systems, and various gear mechanisms. The engine generates power, which is transferred to the transmission. The transmission, along with the hydraulic systems and gear mechanisms, converts and controls the power to drive the different components of the equipment, allowing them to perform their specific functions.
4. Industrial Systems: Drivelines are widely used in industrial systems and machinery, including conveyor systems, manufacturing equipment, and heavy-duty machinery. These applications require power transmission for material handling, processing, and production. The driveline in industrial systems often involves electric motors, gearboxes, drive shafts, couplings, and driven components. The electric motor provides rotational power, which is transmitted through the driveline components to drive the machinery or conveyors, facilitating the desired motion and power transmission within the industrial system.
5. Power Generation: Drivelines are also employed in power generation applications, such as generators and turbines. These systems require power transmission to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The driveline in power generation often consists of a prime mover, such as an internal combustion engine or a steam turbine, connected to a generator. The driveline components, such as couplings, gearboxes, and drive shafts, transmit the rotational power from the prime mover to the generator, which converts it into electrical power.
6. Marine and Aerospace Applications: Drivelines are utilized in marine vessels and aerospace systems to facilitate propulsion and motion. In marine applications, drivelines transfer power from engines or turbines to propellers or water jets, enabling the vessel to move through the water. In aerospace applications, drivelines transmit power from engines to various components, such as rotors or propellers, providing the necessary thrust for flight.
In summary, drivelines are integral to power transmission and motion in a wide range of applications. They enable the transfer of power from the engine or power source to the driven components, allowing for the generation of torque and the performance of specific tasks. Drivelines play a vital role in automotive vehicles, agricultural machinery, construction equipment, industrial systems, power generation, and marine and aerospace applications, contributing to efficient power transmission, motion, and the overall functionality of these diverse systems.


editor by CX 2024-03-15