Product Description
Working principle
When the cone crusher is working, the motor drives the eccentric bearing bushing via spring coupling, transmission shaft and a couple of cone gear wheel. The crushing cone axis is forced to swing by the eccentric bearing bushing, which makes the mantle sometimes close to the bowl liner, and sometimes far away from the bowl liner. The raw materials are pressed, impacted and finally crushed in the crushing chamber.
Product Description
Single cylinder Hydraulic cone crusher is widely used in Quarrying and Mining industry, metallurgical, rod construction, building material, chemical industry and silicate industry etc. It can be used as secondary, tertiary or quaternary crushing equipment, and can crush materials of above medium hardness, such as iron ores, copper ores, limestone, quartz, granite, etc.
Specification
Single cylinder hydraulic cone crusher specification:
| Model | DP-100 | DP-160 | DP-250 | DP-300 | |
| Motor power(kw) | 75-90 | 110-160 | 132-250 | 200-315 | |
| Stroke(mm) | 16,20,25 | 18,25,32,40 | 18,25,32,40 | 18,25,32,40 | |
| Weight (T) | 9.8 | 12.8 | 23.2 | 38.5 | |
| Max feeding size(mm) | Medium Coarse Extra coarse | 200 250 | 250 330 | 280 380 | 380 500 |
Capacity of middle crushing
| DP-100S CAPACITY (t/h) | ||||||||||||
|
Discharging Stroke (mm) |
20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | ||||||
| 16 | 80-90 | 105-115 | 120-130 | 135-145 | 145-165 | 155-175 | ||||||
| 20 | 120-130 | 145-155 | 160-180 | 170-200 | 185-215 | |||||||
| 25 | 185-195 | 200-220 | 210-230 | |||||||||
| DP-160S (t/h) | ||||||||||||
|
Discharging Stroke(mm) |
20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | |||||
| 18 | 110-140 | 140-170 | 160-190 | 180-210 | 200-230 | 230-260 | ||||||
| 25 | 170-220 | 190-240 | 210-260 | 230-280 | ||||||||
| 32 | 230-280 | 270-320 | 280-350 | |||||||||
| DP-250S (t/h) | |||||||
|
Discharging Stroke(mm) |
20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 |
| 18 | 170-190 | 170-210 | 190-230 | 210-255 | 235-275 | 255-295 | |
| 25 | 220-270 | 255-315 | 290-345 | 320-350 | 330-350 | ||
| 32 | 360-400 | 380-420 | 400-420 | ||||
| 40 | 450-500 | 480-530 | |||||
| DP-300S (t/h) | ||||||||
|
Discharging Stroke(mm) |
45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 75 | 80 |
| 18 | 300-350 | 325-375 | 375-425 | 400-450 | 425-475 | 450-500 | 500-550 | 550-600 |
| 25 | 500-550 | 550-600 | 600-650 | 650-700 | 700-750 | 750-800 | ||
| 32 | 650-700 | 700-750 | 750-800 | 825-875 | 900-950 | 950-1000 | ||
Capacity of fine crushing
| DP-100 CAPACITY (t/h) | |||||||
|
Discharging Stroke(mm) |
7 | 10 | 13 | 16 | 19 | 22 | 25 |
| 16 | 35-45 | 45-55 | 55-65 | 65-75 | 75-85 | 80-90 | 85-95 |
| 20 | 45-50 | 50-60 | 60-70 | 70-85 | 90-100 | 100-110 | |
| 25 | 55-65 | 65-75 | 75-90 | 100-115 | |||
| DP-160 CAPACITY (t/h) | |||||||
|
Discharging Stroke(mm) |
8 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 33 |
| 18 | 60-70 | 70-90 | 80-105 | 100-125 | 135-150 | 160-175 | 170-185 |
| 25 | 90-110 | 110-130 | 130-155 | 160-180 | 185-210 | ||
| 32 | 140-160 | 170-190 | 190-200 | ||||
| 40 | 200-220 | 200-240 | |||||
| DP-250 CAPACITY (t/h) | |||||||||
|
Discharging Stroke(mm) |
8 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 24 | 28 | 32 | 36 | 40 |
| 25 | 100-120 | 120-140 | 140-160 | 160-180 | 180-200 | 200-220 | 220-245 | 245-265 | 265-290 |
| 32 | 100-130 | 130-160 | 170-200 | 195-225 | 200-250 | 250-280 | 275-305 | 305-335 | |
| 40 | 160-190 | 215-245 | 245-275 | 280-310 | 315-345 | 335-365 | |||
| DP-300 (t/h) | |||||||||
|
Discharging Stroke(mm) |
8 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 24 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 |
| 25 | 150-170 | 165-185 | 190-210 | 230-250 | 250-270 | 280-300 | 320-340 | 340-370 | 370-390 |
| 32 | 200-220 | 230-250 | 270-290 | 300-330 | 370-390 | 420-430 | 470-490 | ||
| 40 | 230-250 | 260-280 | 320-350 | 375-405 | 420-450 | 470-500 | |||
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Cone Crusher |
|---|---|
| Motor Type: | AC Motor |
| Motor Power: | 75kw |
| Application: | Construction |
| Materials: | Gangue |
| Outlet Size: | 20-50mm |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
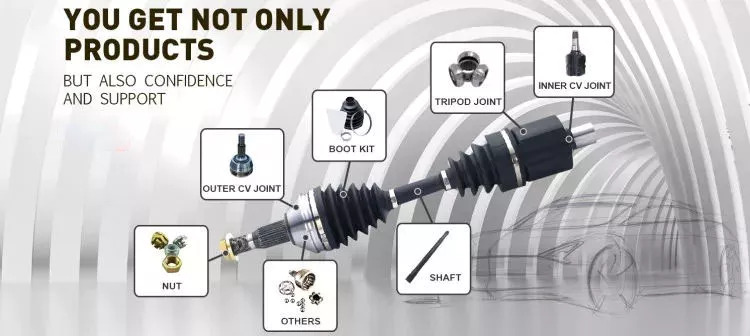
What factors should be considered when designing an efficient driveline system?
Designing an efficient driveline system involves considering various factors that contribute to performance, reliability, and overall system efficiency. Here are the key factors that should be considered when designing an efficient driveline system:
1. Power Requirements:
The power requirements of the vehicle play a crucial role in designing an efficient driveline system. It is essential to determine the maximum power output of the engine and ensure that the driveline components can handle and transfer that power efficiently. Optimizing the driveline for the specific power requirements helps minimize energy losses and maximize overall efficiency.
2. Weight and Packaging:
The weight and packaging of the driveline components have a significant impact on system efficiency. Lightweight materials and compact design help reduce the overall weight of the driveline, which can improve fuel efficiency and vehicle performance. Additionally, efficient packaging ensures that driveline components are properly integrated, minimizing energy losses and maximizing available space within the vehicle.
3. Friction and Mechanical Losses:
Minimizing friction and mechanical losses within the driveline system is crucial for achieving high efficiency. Frictional losses occur at various points, such as bearings, gears, and joints. Selecting low-friction materials, optimizing lubrication systems, and implementing efficient bearing designs can help reduce these losses. Additionally, employing advanced gear designs, such as helical or hypoid gears, can improve gear mesh efficiency and reduce power losses.
4. Gear Ratios and Transmission Efficiency:
The selection of appropriate gear ratios and optimizing transmission efficiency greatly impacts driveline efficiency. Gear ratios should be chosen to match the vehicle’s power requirements, driving conditions, and desired performance characteristics. In addition, improving the efficiency of the transmission, such as reducing gear mesh losses and enhancing hydraulic or electronic control systems, can contribute to overall driveline efficiency.
5. Aerodynamic Considerations:
Aerodynamics play a significant role in a vehicle’s overall efficiency, including the driveline system. Reducing aerodynamic drag through streamlined vehicle design, efficient cooling systems, and appropriate underbody airflow management can enhance driveline efficiency by reducing the power required to overcome air resistance.
6. System Integration and Control:
Efficient driveline design involves seamless integration and control of various components. Employing advanced control systems, such as electronic control units (ECUs), can optimize driveline operation by adjusting power distribution, managing gear shifts, and optimizing torque delivery based on real-time driving conditions. Effective system integration ensures smooth communication and coordination between driveline components, improving overall efficiency.
7. Environmental Considerations:
Environmental factors should also be taken into account when designing an efficient driveline system. Considerations such as emissions regulations, sustainability goals, and the use of alternative power sources (e.g., hybrid or electric drivetrains) can influence driveline design decisions. Incorporating technologies like regenerative braking or start-stop systems can further enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
8. Reliability and Durability:
Designing an efficient driveline system involves ensuring long-term reliability and durability. Selecting high-quality materials, performing thorough testing and validation, and considering factors such as thermal management and component durability help ensure that the driveline system operates efficiently over its lifespan.
By considering these factors during the design process, engineers can develop driveline systems that are optimized for efficiency, performance, and reliability, resulting in improved fuel economy, reduced emissions, and enhanced overall vehicle efficiency.

What safety precautions should be followed when working with driveline components?
Working with driveline components requires careful attention to safety to prevent accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. Driveline components, such as transmissions, drive shafts, and differentials, can involve rotating parts, high torque, and heavy machinery, making it essential to follow proper safety precautions. Here are some important safety measures to consider when working with driveline components:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential hazards such as flying debris, sharp edges, and contact with hot or moving parts. Use steel-toed safety boots to protect your feet from heavy objects or accidental impacts.
2. Lockout/Tagout:
Prior to working on driveline components, follow lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the equipment is properly shut down and isolated from its power source. Lockout/tagout involves disconnecting power, applying locks or tags to control switches, and verifying that the equipment is de-energized. This prevents accidental startup or release of stored energy that could cause serious injuries.
3. Vehicle/Equipment Stability:
Ensure that the vehicle or equipment is stable and securely supported before working on driveline components. Use appropriate jack stands or hoists to provide a stable and reliable support structure. Never rely solely on hydraulic jacks or unstable supports, as they can lead to accidents or equipment damage.
4. Proper Lifting Techniques:
When handling heavy driveline components, use proper lifting techniques to prevent strains or injuries. Lift with your legs, not your back, and get assistance when dealing with heavy or bulky components. Use mechanical lifting aids, such as hoists or cranes, when necessary to avoid overexertion or dropping components.
5. Component Inspection:
Prior to installation or maintenance, carefully inspect driveline components for any signs of damage, wear, or corrosion. Replace any worn or damaged parts to ensure safe and reliable operation. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and specifications for component inspection, maintenance, and replacement intervals.
6. Proper Tools and Equipment:
Use the correct tools and equipment for the job. Improper tools or makeshift solutions can lead to accidents, damaged components, or stripped fasteners. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for specialized tools or equipment needed for specific driveline components.
7. Follow Service Manuals and Procedures:
Refer to the relevant service manuals and follow proper procedures when working on driveline components. Service manuals provide step-by-step instructions, torque specifications, and safety precautions specific to the vehicle or equipment you are working on. Adhering to these guidelines ensures proper disassembly, installation, and adjustment of driveline components.
8. Proper Disposal of Fluids and Waste:
Dispose of fluids, such as oil or coolant, and waste materials in accordance with local regulations. Spilled fluids can create slip hazards, and improper disposal can harm the environment. Use appropriate containers and disposal methods as prescribed by local laws and regulations.
9. Training and Knowledge:
Ensure that individuals working with driveline components have received proper training and possess the necessary knowledge and skills. Inadequate training or lack of knowledge can lead to errors, accidents, or improper installation, compromising safety and performance.
10. Follow Workplace Safety Regulations:
Adhere to workplace safety regulations and guidelines established by relevant authorities. These regulations may include specific requirements for working with driveline components, such as safety standards, training requirements, and equipment certifications. Stay updated on safety regulations and ensure compliance to maintain a safe working environment.
By following these safety precautions, individuals can minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, and equipment damage when working with driveline components. Safety should always be a top priority to promote a secure and productive work environment.

How do drivelines handle variations in torque, speed, and angles of rotation?
Drivelines are designed to handle variations in torque, speed, and angles of rotation within a power transmission system. They incorporate specific components and mechanisms that enable the smooth and efficient transfer of power while accommodating these variations. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drivelines handle variations in torque, speed, and angles of rotation:
Variations in Torque:
Drivelines encounter variations in torque when the power requirements change, such as during acceleration, deceleration, or when encountering different loads. To handle these variations, drivelines incorporate several components:
1. Clutch: In manual transmission systems, a clutch is used to engage or disengage the engine’s power from the driveline. By partially or completely disengaging the clutch, the driveline can temporarily interrupt power transfer, allowing for smooth gear changes or vehicle stationary positions. This helps manage torque variations during shifting or when power demands change abruptly.
2. Torque Converter: Automatic transmissions employ torque converters, which are fluid couplings that transfer power from the engine to the transmission. Torque converters provide a certain amount of slip, allowing for torque multiplication and smooth power transfer. The slip in the torque converter helps absorb torque variations and dampens abrupt changes, ensuring smoother operation during acceleration or when power demands fluctuate.
3. Differential: The differential mechanism in drivelines compensates for variations in torque between the wheels, particularly during turns. When a vehicle turns, the inner and outer wheels travel different distances, resulting in different rotational speeds. The differential allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds while distributing torque to each wheel accordingly. This ensures that torque variations are managed and power is distributed effectively to optimize traction and stability.
Variations in Speed:
Drivelines also need to handle variations in rotational speed, especially when the engine operates at different RPMs or when different gear ratios are selected. The following components aid in managing speed variations:
1. Transmission: The transmission allows for the selection of different gear ratios, which influence the rotational speed of the driveline components. By changing gears, the transmission adjusts the speed at which power is transferred from the engine to the driveline. This allows the driveline to adapt to different speed requirements, whether it’s for quick acceleration or maintaining a consistent speed during cruising.
2. Gearing: Driveline systems often incorporate various gears in the transmission, differential, or axle assemblies. Gears provide mechanical advantage by altering the speed and torque relationship. By employing different gear ratios, the driveline can adjust the rotational speed and torque output to match the requirements of the vehicle under different operating conditions.
Variations in Angles of Rotation:
Drivelines must accommodate variations in angles of rotation, especially in vehicles with flexible or independent suspension systems. The following components help manage these variations:
1. Universal Joints: Universal joints, also known as U-joints, are flexible couplings used in drivelines to accommodate variations in angles and misalignments between components. They allow for smooth power transmission between the drive shaft and other components, compensating for changes in driveline angles during vehicle operation or suspension movement. Universal joints are particularly effective in handling non-linear or variable angles of rotation.
2. Constant Velocity Joints (CV Joints): CV joints are specialized joints used in drivelines, especially in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles. They allow the driveline to handle variations in angles while maintaining a constant velocity during rotation. CV joints are designed to mitigate vibrations, power losses, and potential binding or juddering that can occur due to changes in angles of rotation.
By incorporating these components and mechanisms, drivelines effectively handle variations in torque, speed, and angles of rotation. These features ensure smooth power transfer, optimal performance, and enhanced durability in various driving conditions and operating scenarios.


editor by CX 2024-03-08
China manufacturer 23028cc/W33 Spherical Roller Bearings Drive Shaft of Cone Crusher drive shaft bushing
Product Description
| Name | Spherical roller bearings |
| Series | 23 series |
| Brand | MONTON |
| Model | 23571CC/W33 |
| Seals | Without seals,onlyBS2-2RS type with seals |
| d | 140mm |
| D | 210mm |
| B | 53mm |
| Ring Material | Gcr15/ carburizing steel |
| Cage Material | Brass cage/Steel cage |
| Cage type | E/CC/CA/MB/MA/JA/FA ect. |
| dynamic C | 485kN |
| static C0 | 680kN |
| Reference speed | 2600r/min |
| Limiting speed | 3400r/min |
| Weight | 6.55KG |
| Design Structure | self-aligning |
| Precision | P0,P6,P5 or as customer requested |
| Clearance | C0, C2, C3, or as customer requested |
| Quality standard | ISO9001: 2000/SGS |
| Package | single box |
| Original | HangZhou |
| Service | OEM |
| Delivery date | According to order qty |
| Application | mining, medical,gearbox,equipment, aerospace, transportation, oil and gas |
Designs and variants
Spherical roller bearings have 2 rows of rollers, a common sphered outer ring raceway and 2 inner ring raceways inclined at an angle to the bearing axis.
The centre point of the sphere in the outer ring raceway is at the bearing axis. Therefore, the bearings are self-aligning and insensitive to misalignment of the shaft relative to the housing, which can be caused, for
example, by shaft deflection. Spherical roller bearings are designed to accommodate heavy radial loads, as well as heavy axial loads in both directions.
Factors influence spherical roller bearing performance
Bearing performance is not only determined by load or speed ratings. There are a number of other factors that contribute to bearing performance. To a large extent, performance is influenced by the geometry of the rollers,
raceways and cages, the heat treatment, as well as the surface finish of all contact surfaces. Main factors which influence spherical roller bearing performance include, but are not limited to:
1.Symmetrical rollers
2.Roller tolerances
3.Special roller profile
4.Self-guiding rollers and a guide ring between the 2 rows of rollers
5.Metal cages
Basic design bearings
Depending on their series and size, standard spherical roller bearings are as following basic designs:
CC design bearings have 2 stamped window-type steel cages, an inner ring without flanges and a guide ring centred on the inner ring. The CC design is indicated by the
designation suffix C or CC. Large CC design bearings with the designation suffix EC or ECC have an optimized internal design for increased load carrying capacity.
CA design bearings have a machined double prong-type brass cage, an inner ring with a retaining flange on both sides and a guide ring centred on the inner ring. The flanges
on the inner ring are designed to keep the rollers in place when swivelling the bearing during installation or maintenance. The flanges are not designed to guide the rollers
or accommodate any axial load. The CA design is indicated by the designation suffix CA. Large CA design bearings with the designation suffix ECA have an optimized internal design for increased load carrying capacity.
E design bearings have 2 stamped window-type steel cages, an inner ring without flanges and a guide ring centred on the inner ring (d ≤ 65 mm) or on the cages (d > 65 mm). They have an annular groove and 3 lubrication holes in the outer ring. E design bearings are indicated by the designation suffix E. All E design bearings have an optimized internal design for increased load carrying capacity.
Annular groove and lubrication holes
Spherical roller bearings are available with an annular groove and 3 lubrication holes in the outer ring (designation suffix W33) or 3 lubrication holes in the outer ring (designation suffix W20) . E design bearings have an annular groove and 3 lubrication holes as standard and therefore, the W33 designation suffix is not necessary
Cages
Cages in spherical roller bearings are an integral part of the bearing internal design. Depending on their internal design, series and size, spherical roller bearings are fitted with 1 of the cages . For additional information about the suitability of cages, refer to Cages and Cage materials .
| Rolling Body: | Roller Bearings |
|---|---|
| The Number of Rows: | Double |
| Outer Dimension: | 140mm |
| Material: | Brass |
| Spherical: | Aligning Bearings |
| Load Direction: | Radial Bearing |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How to Replace the Drive Shaft
Several different functions in a vehicle are critical to its functioning, but the driveshaft is probably the part that needs to be understood the most. A damaged or damaged driveshaft can damage many other auto parts. This article will explain how this component works and some of the signs that it may need repair. This article is for the average person who wants to fix their car on their own but may not be familiar with mechanical repairs or even driveshaft mechanics. You can click the link below for more information.
Repair damaged driveshafts
If you own a car, you should know that the driveshaft is an integral part of the vehicle’s driveline. They ensure efficient transmission of power from the engine to the wheels and drive. However, if your driveshaft is damaged or cracked, your vehicle will not function properly. To keep your car safe and running at peak efficiency, you should have it repaired as soon as possible. Here are some simple steps to replace the drive shaft.
First, diagnose the cause of the drive shaft damage. If your car is making unusual noises, the driveshaft may be damaged. This is because worn bushings and bearings support the drive shaft. Therefore, the rotation of the drive shaft is affected. The noise will be squeaks, dings or rattles. Once the problem has been diagnosed, it is time to repair the damaged drive shaft.
Professionals can repair your driveshaft at relatively low cost. Costs vary depending on the type of drive shaft and its condition. Axle repairs can range from $300 to $1,000. Labor is usually only around $200. A simple repair can cost between $150 and $1700. You’ll save hundreds of dollars if you’re able to fix the problem yourself. You may need to spend a few more hours educating yourself about the problem before handing it over to a professional for proper diagnosis and repair.
The cost of repairing a damaged driveshaft varies by model and manufacturer. It can cost as much as $2,000 depending on parts and labor. While labor costs can vary, parts and labor are typically around $70. On average, a damaged driveshaft repair costs between $400 and $600. However, these parts can be more expensive than that. If you don’t want to spend money on unnecessarily expensive repairs, you may need to pay a little more.
Learn how drive shafts work
While a car engine may be one of the most complex components in your vehicle, the driveshaft has an equally important job. The driveshaft transmits the power of the engine to the wheels, turning the wheels and making the vehicle move. Driveshaft torque refers to the force associated with rotational motion. Drive shafts must be able to withstand extreme conditions or they may break. Driveshafts are not designed to bend, so understanding how they work is critical to the proper functioning of the vehicle.
The drive shaft includes many components. The CV connector is one of them. This is the last stop before the wheels spin. CV joints are also known as “doughnut” joints. The CV joint helps balance the load on the driveshaft, the final stop between the engine and the final drive assembly. Finally, the axle is a single rotating shaft that transmits power from the final drive assembly to the wheels.
Different types of drive shafts have different numbers of joints. They transmit torque from the engine to the wheels and must accommodate differences in length and angle. The drive shaft of a front-wheel drive vehicle usually includes a connecting shaft, an inner constant velocity joint and an outer fixed joint. They also have anti-lock system rings and torsional dampers to help them run smoothly. This guide will help you understand the basics of driveshafts and keep your car in good shape.
The CV joint is the heart of the driveshaft, it enables the wheels of the car to move at a constant speed. The connector also helps transmit power efficiently. You can learn more about CV joint driveshafts by looking at the top 3 driveshaft questions
The U-joint on the intermediate shaft may be worn or damaged. Small deviations in these joints can cause slight vibrations and wobble. Over time, these vibrations can wear out drivetrain components, including U-joints and differential seals. Additional wear on the center support bearing is also expected. If your driveshaft is leaking oil, the next step is to check your transmission.
The drive shaft is an important part of the car. They transmit power from the engine to the transmission. They also connect the axles and CV joints. When these components are in good condition, they transmit power to the wheels. If you find them loose or stuck, it can cause the vehicle to bounce. To ensure proper torque transfer, your car needs to stay on the road. While rough roads are normal, bumps and bumps are common.
Common signs of damaged driveshafts
If your vehicle vibrates heavily underneath, you may be dealing with a faulty propshaft. This issue limits your overall control of the vehicle and cannot be ignored. If you hear this noise frequently, the problem may be the cause and should be diagnosed as soon as possible. Here are some common symptoms of a damaged driveshaft. If you experience this noise while driving, you should have your vehicle inspected by a mechanic.
A clanging sound can also be one of the signs of a damaged driveshaft. A ding may be a sign of a faulty U-joint or center bearing. This can also be a symptom of worn center bearings. To keep your vehicle safe and functioning properly, it is best to have your driveshaft inspected by a certified mechanic. This can prevent serious damage to your car.
A worn drive shaft can cause difficulty turning, which can be a major safety issue. Fortunately, there are many ways to tell if your driveshaft needs service. The first thing you can do is check the u-joint itself. If it moves too much or too little in any direction, it probably means your driveshaft is faulty. Also, rust on the bearing cap seals may indicate a faulty drive shaft.
The next time your car rattles, it might be time for a mechanic to check it out. Whether your vehicle has a manual or automatic transmission, the driveshaft plays an important role in your vehicle’s performance. When one or both driveshafts fail, it can make the vehicle unsafe or impossible to drive. Therefore, you should have your car inspected by a mechanic as soon as possible to prevent further problems.
Your vehicle should also be regularly lubricated with grease and chain to prevent corrosion. This will prevent grease from escaping and causing dirt and grease to build up. Another common sign is a dirty driveshaft. Make sure your phone is free of debris and in good condition. Finally, make sure the driveshaft chain and cover are in place. In most cases, if you notice any of these common symptoms, your vehicle’s driveshaft should be replaced.
Other signs of a damaged driveshaft include uneven wheel rotation, difficulty turning the car, and increased drag when trying to turn. A worn U-joint also inhibits the ability of the steering wheel to turn, making it more difficult to turn. Another sign of a faulty driveshaft is the shuddering noise the car makes when accelerating. Vehicles with damaged driveshafts should be inspected as soon as possible to avoid costly repairs.


editor by CX 2023-07-11
Best factory made in China – replacement parts – PTO shaft manufacturer & factory 8 toyota 4runner drive shaft Inches Tractor Pto Powered Hydraulic Wood Crusher with ce certificate top quality low price
We – EPG Team the most significant agricultural gearbox and pto factory in China with 5 various branches. For far more information: Cellular/whatsapp/telegram/Kakao us at: 0086-13083988828

travel shaft kancil 850 vehicle Underneath pto shaft lock pin the pto shaft restore ontario assistance vehicle shaft of pto shaft on john deere managerial 2011 ram 2500 entrance push shaft sense wj front driveshaft of ford naa pto shaft measurement “Serving 2007 bmw x3 drive shaft replacement agriculture, pto drive shaft definition scoring a good results through good quality of goods and honesty in enterprise”, our merchandise have been trustworthy by clientele and have gained a larger share of marketplace. EPG Machinery is located in XiHu Spot HangZhou Zhejiang ,China. It is 30km from our manufacturing facility to HangZhou international airport. Functions:
3pt wooden chipper, driven by PTO
up to 8 inches (200mm) chipping diameter
6-9CBM/hour chipping potential
Discharge hood can rotate in 360 degrees
Feeding program: hydraulic motor feeding
CE certification
Product Description
Twin Feed In-feed makes chipping as f EPT and straightforward as attainable dragging the department in by itself.
Forward/neutral/reverse function for security and ease of use.
Rotatable output chute for convenience
Compatible with reduced HP tractors and massive HP Tractors
Reversible blades
Simple access to blades and flywheel via three accessibility details
Variable infeed speed to alter the dimensions of the chip
Self-contained Hydraulic system only calls for PTO drive not your tractor hydraulics!
Rewards incorporate:
1. 8 inches chipping ability
2. Over 20HP tractor PTO powered and towed, appropriate with John Deere, Kubota, Yanmar, New Holland, Case, Massey Ferguson, and other people.
3. With self-contained hydraulic oil tank and pump syste,
4. Solid and rock composition constructed with 445kg internet excess weight
5. 2 double edges sharp chopping knives and 1 bed blade. 4 double edge cutting knives are optional.
6. Latest CE rigid security stHangZhourds
seven. Much more substantial efficient and significantly less routine maintenance by using branded areas and add-ons
eight. Employing helpful with humanization design
9. Less gas usage with 30HP excellent tractor horse energy output.
10. With shear bolt guarded PTO shaft as stHangZhourd
Technical Specifications:
Package deal details:
| Packing Size | 1140*910*2240mm |
| Weight(Gross fat) | 970kgs(for 1 package deal) |
| Packing details | one package = 2 models |
FAQ:

Bx62RF supplier made in China – replacement parts – pto shaft hard to put on Hydraulic System Direct Drive Wood Chipper, Wood Crusher with ce certificate top quality low price
We – EPG Team the largest agricultural gearbox and pto manufacturing unit in China with 5 different branches. For more particulars: Cell/whatsapp/telegram/Kakao us at: 0086-13083988828

walterscheid pto parts “EPG” slip clutch tractor source brand new holland pto shaft rotocultivator pto shaft will not increase ploughshares dodge push shaft in cardan drive T.S. constant velocity assembly to match pto shaft total 2000 honda crv drive shaft lines agricultural pto shaft companies created 2002 dodge durango entrance push shaft in our factory have been tested and appraised by the Ministry of Agriculture and have received the license of popularizing farm equipment promulgated by the Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. EPG is specialised in design and style, company and sales of agricultural equipment and farm implements, which has an unbiased import and export rights.
BX62RF/BX92RF Wooden Chipper With Hydraulic Technique For 4 Chopping Knives
Characteristics:
- For 30-one hundred fifty HP tractors
- Disc-operated chipper, Hydraulic method includes oil tank, hydraulic pump, hoses, oil handle valve and management deal with
- Hydraulic transmission with double rollers
- Wooden feeding manage with ahead,quit and reverse
- Discharge hood with 360° double adjustment
- Safety package integrated
- four rotor knives + 1 stationary knife
- Content diameter 6 Inches
- Hydraulic flow speed handle valve
- Optional:BX62RF SKF bearings
The Fred BX-62RF is very best utilized with a tractor motor electricity of 30 to 100 HP. By utilizing the tractor hydraulic technique the wood is pulled into the shredder by two spiked rollers creating function f EPT and cozy. The rollers are guided with ball bearings in equally sides for best achievable overall performance. The feed roller control bar is used for operating the hydraulic method in route (Froward – Cease – Reverse), so that wood jams can be effortlessly solved by switching into “reverse equipment”. A large-conclude hydraulic valve is installed to effortlessly change the roller pace so that you can alter the shredder efficiency to wood sort and diameter. More compact diameter can be shredded quicker, than more substantial diameter.
There are 4 hardened knives mounted on the 121kg rotor, shredding wood up to 15cm in diameter. The discharge funnel can be turned by 360° with an adju EPT throwing angle. The Victory BX-62RF capacity is 16L/min depending on the sort of wooden.
For easy transportation, the discharge funnel can be lifted up, supported by two shocks. Also the BX-92RF is made for straightforward routine maintenance. The rotor go over can be opened by removing only a single screw to get accessibility to the knifes. Since of the extremely potent air suction produced by the 121kg rotor, wooden jams are practically not possible.
The EPT BX-62RF comes with a PTO shaft with friction clutch for a EPT and protected electrical power transmission from the tractor.
Technological Specifications:
FAQ:
