Product Description
Product Description
Basic Info.
| Model NO. | Parts | Auto Parts For Center Support Bearing | ||||||||
| Specification | Bearing ID 20-85mm | Trademark | YTK or Customized | |||||||
| Price | Negotiable | Transport Packing | Neutral Packing & Customized | |||||||
| Exportation | ZheJiang Port | Bearing Quality | ZV3 Level | |||||||
| Warranty | One Year or Above | Laser Mark | Available | |||||||
| Applicable Models | Production Capacity | 60, | Φ30 | CB | Φ35 Φ40 | 3535730 | Φ60 | |||
| Φ60 | Φ60 | 6 | Φ65 |
-FAQ:
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
Generally, we pack our goods in neutral boxes and brown cartons or as your demand.
If you have legally registered patent,we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
Q2. What is your terms of delivery?
EXW, FOB, CIF, CFR
Q3. How about your delivery time?
Generally, it will take 10 to 30 days after receiving your advance payment.
The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Material: | Rubber |
| Transport Package: | as Your Demand |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What maintenance practices are crucial for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts?
To prolong the lifespan of drive shafts and ensure their optimal performance, several maintenance practices are crucial. Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate, reduces wear and tear, and ensures the drive shaft operates smoothly and efficiently. Here are some essential maintenance practices for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts:
1. Regular Inspection:
Performing regular inspections is vital for detecting any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the drive shaft visually, looking for cracks, dents, or any signs of excessive wear on the shaft itself and its associated components such as joints, yokes, and splines. Check for any signs of lubrication leaks or contamination. Additionally, inspect the fasteners and mounting points to ensure they are secure. Early detection of any issues allows for timely repairs or replacements, preventing further damage to the drive shaft.
2. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of drive shafts. Lubricate the joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity joints, as recommended by the manufacturer. Lubrication reduces friction, minimizes wear, and helps dissipate heat generated during operation. Use the appropriate lubricant specified for the specific drive shaft and application, considering factors such as temperature, load, and operating conditions. Regularly check the lubrication levels and replenish as necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failure.
3. Balancing and Alignment:
Maintaining proper balancing and alignment is crucial for the lifespan of drive shafts. Imbalances or misalignments can lead to vibrations, accelerated wear, and potential failure. If vibrations or unusual noises are detected during operation, it is important to address them promptly. Perform balancing procedures as necessary, including dynamic balancing, to ensure even weight distribution along the drive shaft. Additionally, verify that the drive shaft is correctly aligned with the engine or power source and the driven components. Misalignment can cause excessive stress on the drive shaft, leading to premature failure.
4. Protective Coatings:
Applying protective coatings can help prolong the lifespan of drive shafts, particularly in applications exposed to harsh environments or corrosive substances. Consider using coatings such as zinc plating, powder coating, or specialized corrosion-resistant coatings to enhance the drive shaft’s resistance to corrosion, rust, and chemical damage. Regularly inspect the coating for any signs of degradation or damage, and reapply or repair as necessary to maintain the protective barrier.
5. Torque and Fastener Checks:
Ensure that the drive shaft’s fasteners, such as bolts, nuts, or clamps, are properly torqued and secured according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Loose or improperly tightened fasteners can lead to excessive vibrations, misalignment, or even detachment of the drive shaft. Periodically check and retighten the fasteners as recommended or after any maintenance or repair procedures. Additionally, monitor the torque levels during operation to ensure they remain within the specified range, as excessive torque can strain the drive shaft and lead to premature failure.
6. Environmental Protection:
Protecting the drive shaft from environmental factors can significantly extend its lifespan. In applications exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or abrasive substances, take appropriate measures to shield the drive shaft. This may include using protective covers, seals, or guards to prevent contaminants from entering and causing damage. Regular cleaning of the drive shaft, especially in dirty or corrosive environments, can also help remove debris and prevent buildup that could compromise its performance and longevity.
7. Manufacturer Guidelines:
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance practices specific to the drive shaft model and application. The manufacturer’s instructions may include specific intervals for inspections, lubrication, balancing, or other maintenance tasks. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that the drive shaft is properly maintained and serviced, maximizing its lifespan and minimizing the risk of unexpected failures.
By implementing these maintenance practices, drive shafts can operate reliably, maintain efficient power transmission, and have an extended service life, ultimately reducing downtime and ensuring optimal performance in various applications.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery: Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transferring power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer: Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability: Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability: Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction: Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency: Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades: Drive shaft upgrades can be popular performance enhancements for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications: Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability: Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies: Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency, enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies, and ensuring durability and reliability. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.

What benefits do drive shafts offer for different types of vehicles and equipment?
Drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They play a crucial role in power transmission and contribute to the overall performance, efficiency, and functionality of various systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the benefits that drive shafts provide:
1. Efficient Power Transmission:
Drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By connecting the engine or motor to the driven system, drive shafts efficiently transfer rotational power, allowing vehicles and equipment to perform their intended functions. This efficient power transmission ensures that the power generated by the engine is effectively utilized, optimizing the overall performance and productivity of the system.
2. Versatility:
Drive shafts offer versatility in their applications. They are used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and off-road vehicles. Additionally, drive shafts are employed in a wide range of equipment and machinery, such as agricultural machinery, construction equipment, industrial machinery, and marine vessels. The ability to adapt to different types of vehicles and equipment makes drive shafts a versatile component for power transmission.
3. Torque Handling:
Drive shafts are designed to handle high levels of torque. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source. Drive shafts are engineered to efficiently transmit this torque without excessive twisting or bending. By effectively handling torque, drive shafts ensure that the power generated by the engine is reliably transferred to the wheels or driven components, enabling vehicles and equipment to overcome resistance, such as heavy loads or challenging terrains.
4. Flexibility and Compensation:
Drive shafts provide flexibility and compensation for angular movement and misalignment. In vehicles, drive shafts accommodate the movement of the suspension system, allowing the wheels to move up and down independently. This flexibility ensures a constant power transfer even when the vehicle encounters uneven terrain. Similarly, in machinery, drive shafts compensate for misalignment between the engine or motor and the driven components, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing excessive stress on the drivetrain.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts contribute to weight reduction in vehicles and equipment. Compared to other forms of power transmission, such as belt drives or chain drives, drive shafts are typically lighter in weight. This reduction in weight helps improve fuel efficiency in vehicles and reduces the overall weight of equipment, leading to enhanced maneuverability and increased payload capacity. Additionally, lighter drive shafts contribute to a better power-to-weight ratio, resulting in improved performance and acceleration.
6. Durability and Longevity:
Drive shafts are designed to be durable and long-lasting. They are constructed using materials such as steel or aluminum, which offer high strength and resistance to wear and fatigue. Drive shafts undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure their reliability and longevity. Proper maintenance, including lubrication and regular inspections, further enhances their durability. The robust construction and long lifespan of drive shafts contribute to the overall reliability and cost-effectiveness of vehicles and equipment.
7. Safety:
Drive shafts incorporate safety features to protect operators and bystanders. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing, preventing contact with moving parts and reducing the risk of injury in the event of a failure. Similarly, in machinery, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts to minimize the potential hazards associated with rotating components. These safety measures ensure the well-being of individuals operating or working in proximity to vehicles and equipment.
In summary, drive shafts offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They enable efficient power transmission, provide versatility in various applications, handle torque effectively, offer flexibility and compensation, contribute to weight reduction, ensure durability and longevity, and incorporate safety features. By providing these advantages, drive shafts enhance the performance, efficiency, reliability, and safety of vehicles and equipment across a wide range of industries.


editor by CX 2024-03-11
China Custom Porsch Cayenne 955 OE 95542102012 Center Support Bearing Auto Parts Drive Shaft Installation
Product Description
Product Description
Basic Info.
| Model NO. | Parts | Auto Parts For Center Support Bearing | ||||||||
| Specification | Bearing ID 20-85mm | Trademark | YTK or Customized | |||||||
| Price | Negotiable | Transport Packing | Neutral Packing & Customized | |||||||
| Exportation | ZheJiang Port | Bearing Quality | ZV3 Level | |||||||
| Warranty | One Year or Above | Laser Mark | Available | |||||||
| Applicable Models | Production Capacity | 60, | Φ30 | CB | Φ35 Φ40 | 3535730 | Φ60 | |||
| Φ60 | Φ60 | 6 | Φ65 |
-FAQ:
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
Generally, we pack our goods in neutral boxes and brown cartons or as your demand.
If you have legally registered patent,we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
Q2. What is your terms of delivery?
EXW, FOB, CIF, CFR
Q3. How about your delivery time?
Generally, it will take 10 to 30 days after receiving your advance payment.
The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Material: | Rubber |
| Transport Package: | as Your Demand |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with drive shafts?
While drive shafts are widely used and offer several advantages, they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered. Here’s a detailed explanation of the limitations and disadvantages associated with drive shafts:
1. Length and Misalignment Constraints:
Drive shafts have a maximum practical length due to factors such as material strength, weight considerations, and the need to maintain rigidity and minimize vibrations. Longer drive shafts can be prone to increased bending and torsional deflection, leading to reduced efficiency and potential driveline vibrations. Additionally, drive shafts require proper alignment between the driving and driven components. Misalignment can cause increased wear, vibrations, and premature failure of the drive shaft or its associated components.
2. Limited Operating Angles:
Drive shafts, especially those using U-joints, have limitations on operating angles. U-joints are typically designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and operating beyond these limits can result in reduced efficiency, increased vibrations, and accelerated wear. In applications requiring large operating angles, constant velocity (CV) joints are often used to maintain a constant speed and accommodate greater angles. However, CV joints may introduce higher complexity and cost compared to U-joints.
3. Maintenance Requirements:
Drive shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection, lubrication of joints, and balancing if necessary. Failure to perform routine maintenance can lead to increased wear, vibrations, and potential driveline issues. Maintenance requirements should be considered in terms of time and resources when using drive shafts in various applications.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Drive shafts can generate noise and vibrations, especially at high speeds or when operating at certain resonant frequencies. Imbalances, misalignment, worn joints, or other factors can contribute to increased noise and vibrations. These vibrations may affect the comfort of vehicle occupants, contribute to component fatigue, and require additional measures such as dampers or vibration isolation systems to mitigate their effects.
5. Weight and Space Constraints:
Drive shafts add weight to the overall system, which can be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications, such as automotive or aerospace industries. Additionally, drive shafts require physical space for installation. In compact or tightly packaged equipment or vehicles, accommodating the necessary drive shaft length and clearances can be challenging, requiring careful design and integration considerations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Drive shafts, depending on their design, materials, and manufacturing processes, can involve significant costs. Customized or specialized drive shafts tailored to specific equipment requirements may incur higher expenses. Additionally, incorporating advanced joint configurations, such as CV joints, can add complexity and cost to the drive shaft system.
7. Inherent Power Loss:
Drive shafts transmit power from the driving source to the driven components, but they also introduce some inherent power loss due to friction, bending, and other factors. This power loss can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in long drive shafts or applications with high torque requirements. It is important to consider power loss when determining the appropriate drive shaft design and specifications.
8. Limited Torque Capacity:
While drive shafts can handle a wide range of torque loads, there are limits to their torque capacity. Exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a drive shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in downtime and potential damage to other driveline components. It is crucial to select a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity for the intended application.
Despite these limitations and disadvantages, drive shafts remain a widely used and effective means of power transmission in various industries. Manufacturers continuously work to address these limitations through advancements in materials, design techniques, joint configurations, and balancing processes. By carefully considering the specific application requirements and potential drawbacks, engineers and designers can mitigate the limitations and maximize the benefits of drive shafts in their respective systems.

Can drive shafts be customized for specific vehicle or equipment requirements?
Yes, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements. Customization allows manufacturers to tailor the design, dimensions, materials, and other parameters of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility and optimal performance within a particular vehicle or equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts can be customized:
1. Dimensional Customization:
Drive shafts can be customized to match the dimensional requirements of the vehicle or equipment. This includes adjusting the overall length, diameter, and spline configuration to ensure proper fitment and clearances within the specific application. By customizing the dimensions, the drive shaft can be seamlessly integrated into the driveline system without any interference or limitations.
2. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for drive shafts can be customized based on the specific requirements of the vehicle or equipment. Different materials, such as steel alloys, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, can be selected to optimize strength, weight, and durability. The material selection can be tailored to meet the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the application, ensuring the drive shaft’s reliability and longevity.
3. Joint Configuration:
Drive shafts can be customized with different joint configurations to accommodate specific vehicle or equipment requirements. For example, universal joints (U-joints) may be suitable for applications with lower operating angles and moderate torque demands, while constant velocity (CV) joints are often used in applications requiring higher operating angles and smoother power transmission. The choice of joint configuration depends on factors such as operating angle, torque capacity, and desired performance characteristics.
4. Torque and Power Capacity:
Customization allows drive shafts to be designed with the appropriate torque and power capacity for the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers can analyze the torque requirements, operating conditions, and safety margins of the application to determine the optimal torque rating and power capacity of the drive shaft. This ensures that the drive shaft can handle the required loads without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
5. Balancing and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can be customized with precision balancing and vibration control measures. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, increased wear, and potential driveline issues. By employing dynamic balancing techniques during the manufacturing process, manufacturers can minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation. Additionally, vibration dampers or isolation systems can be integrated into the drive shaft design to further mitigate vibrations and enhance overall system performance.
6. Integration and Mounting Considerations:
Customization of drive shafts takes into account the integration and mounting requirements of the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers work closely with the vehicle or equipment designers to ensure that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the driveline system. This includes adapting the mounting points, interfaces, and clearances to ensure proper alignment and installation of the drive shaft within the vehicle or equipment.
7. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate with vehicle manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft customization process. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can address specific needs, optimize performance, and ensure compatibility with the vehicle or equipment. This collaborative approach enhances the customization process and results in drive shafts that meet the exact requirements of the application.
8. Compliance with Standards:
Customized drive shafts can be designed to comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, ensures that the customized drive shafts meet quality, safety, and performance requirements. Adhering to these standards provides assurance that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into the specific vehicle or equipment.
In summary, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements through dimensional customization, material selection, joint configuration, torque and power capacity optimization, balancing and vibration control, integration and mounting considerations, collaboration with stakeholders, and compliance with industry standards. Customization allows drive shafts to be precisely tailored to the needs of the application, ensuring compatibility, reliability, and optimal performance.

Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2024-02-18
China best Porsch Cayenne 955 OE 95542102012 Center Support Bearing Auto Parts Drive Shaft Installation
Product Description
Product Description
Basic Info.
| Model NO. | Parts | Auto Parts For Center Support Bearing | ||||||||
| Specification | Bearing ID 20-85mm | Trademark | YTK or Customized | |||||||
| Price | Negotiable | Transport Packing | Neutral Packing & Customized | |||||||
| Exportation | ZheJiang Port | Bearing Quality | ZV3 Level | |||||||
| Warranty | One Year or Above | Laser Mark | Available | |||||||
| Applicable Models | Production Capacity | 60, | Φ30 | CB | Φ35 Φ40 | 3535730 | Φ60 | |||
| Φ60 | Φ60 | 6 | Φ65 |
-FAQ:
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
Generally, we pack our goods in neutral boxes and brown cartons or as your demand.
If you have legally registered patent,we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
Q2. What is your terms of delivery?
EXW, FOB, CIF, CFR
Q3. How about your delivery time?
Generally, it will take 10 to 30 days after receiving your advance payment.
The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Material: | Rubber |
| Transport Package: | as Your Demand |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What factors should be considered when selecting the right drive shaft for an application?
When selecting the right drive shaft for an application, several factors need to be considered. The choice of drive shaft plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient and reliable power transmission. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Power and Torque Requirements:
The power and torque requirements of the application are essential considerations. It is crucial to determine the maximum torque that the drive shaft will need to transmit without failure or excessive deflection. This includes evaluating the power output of the engine or power source, as well as the torque demands of the driven components. Selecting a drive shaft with the appropriate diameter, material strength, and design is essential to ensure it can handle the expected torque levels without compromising performance or safety.
2. Operating Speed:
The operating speed of the drive shaft is another critical factor. The rotational speed affects the dynamic behavior of the drive shaft, including the potential for vibration, resonance, and critical speed limitations. It is important to choose a drive shaft that can operate within the desired speed range without encountering excessive vibrations or compromising the structural integrity. Factors such as the material properties, balance, and critical speed analysis should be considered to ensure the drive shaft can handle the required operating speed effectively.
3. Length and Alignment:
The length and alignment requirements of the application must be considered when selecting a drive shaft. The distance between the engine or power source and the driven components determines the required length of the drive shaft. In situations where there are significant variations in length or operating angles, telescopic drive shafts or multiple drive shafts with appropriate couplings or universal joints may be necessary. Proper alignment of the drive shaft is crucial to minimize vibrations, reduce wear and tear, and ensure efficient power transmission.
4. Space Limitations:
The available space within the application is an important factor to consider. The drive shaft must fit within the allocated space without interfering with other components or structures. It is essential to consider the overall dimensions of the drive shaft, including length, diameter, and any additional components such as joints or couplings. In some cases, custom or compact drive shaft designs may be required to accommodate space limitations while maintaining adequate power transmission capabilities.
5. Environmental Conditions:
The environmental conditions in which the drive shaft will operate should be evaluated. Factors such as temperature, humidity, corrosive agents, and exposure to contaminants can impact the performance and lifespan of the drive shaft. It is important to select materials and coatings that can withstand the specific environmental conditions to prevent corrosion, degradation, or premature failure of the drive shaft. Special considerations may be necessary for applications exposed to extreme temperatures, water, chemicals, or abrasive substances.
6. Application Type and Industry:
The specific application type and industry requirements play a significant role in drive shaft selection. Different industries, such as automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, agriculture, or marine, have unique demands that need to be addressed. Understanding the specific needs and operating conditions of the application is crucial in determining the appropriate drive shaft design, materials, and performance characteristics. Compliance with industry standards and regulations may also be a consideration in certain applications.
7. Maintenance and Serviceability:
The ease of maintenance and serviceability should be taken into account. Some drive shaft designs may require periodic inspection, lubrication, or replacement of components. Considering the accessibility of the drive shaft and associated maintenance requirements can help minimize downtime and ensure long-term reliability. Easy disassembly and reassembly of the drive shaft can also be beneficial for repair or component replacement.
By carefully considering these factors, one can select the right drive shaft for an application that meets the power transmission needs, operating conditions, and durability requirements, ultimately ensuring optimal performance and reliability.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery:
Drive shafts are responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transmitting power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer:
Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability:
Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability:
Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction:
Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency:
Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades:
Drive shaft upgrades can be a popular performance enhancement for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications:
Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability:
Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies:
Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency,and enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.
What is a drive shaft and how does it function in vehicles and machinery?
A drive shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or prop shaft, is a mechanical component that plays a critical role in transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels or other driven components in vehicles and machinery. It is commonly used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and agricultural or industrial machinery. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a drive shaft is and how it functions:
1. Definition and Construction: A drive shaft is a cylindrical metal tube that connects the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. It is typically made of steel or aluminum and consists of one or more tubular sections with universal joints (U-joints) at each end. These U-joints allow for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components.
2. Power Transmission: The primary function of a drive shaft is to transmit rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. In vehicles, the drive shaft connects the transmission or gearbox output shaft to the differential, which then transfers power to the wheels. In machinery, the drive shaft transfers power from the engine or motor to various driven components such as pumps, generators, or other mechanical systems.
3. Torque and Speed: The drive shaft is responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). The drive shaft must be capable of transmitting the required torque without excessive twisting or bending and maintaining the desired rotational speed for efficient operation of the driven components.
4. Flexible Coupling: The U-joints on the drive shaft provide a flexible coupling that allows for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components. As the suspension system of a vehicle moves or the machinery operates on uneven terrain, the drive shaft can adjust its length and angle to accommodate these movements, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing damage to the drivetrain components.
5. Length and Balance: The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven wheels or components. It should be appropriately sized to ensure proper power transmission and avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Additionally, the drive shaft is carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can cause discomfort, reduce efficiency, and lead to premature wear of drivetrain components.
6. Safety Considerations: Drive shafts in vehicles and machinery require proper safety measures. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts and reduce the risk of injury in the event of a malfunction or failure. Additionally, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards associated with rotating components.
7. Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or excessive play in the U-joints, inspecting the drive shaft for any cracks or deformations, and lubricating the U-joints as recommended by the manufacturer. Proper maintenance helps prevent failures, ensures optimal performance, and prolongs the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, a drive shaft is a mechanical component that transmits rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in vehicles and machinery. It functions by providing a rigid connection between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components, while also allowing for angular movement and compensation of misalignment through the use of U-joints. The drive shaft plays a crucial role in power transmission, torque and speed delivery, flexible coupling, length and balance considerations, safety, and maintenance requirements. Its proper functioning is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of vehicles and machinery.


editor by CX 2024-02-14
China Custom Porsch Cayenne 955 OE 95542102012 Center Support Bearing Auto Parts Drive Shaft Installation
Product Description
Product Description
Basic Info.
| Model NO. | Parts | Auto Parts For Center Support Bearing | ||||||||
| Specification | Bearing ID 20-85mm | Trademark | YTK or Customized | |||||||
| Price | Negotiable | Transport Packing | Neutral Packing & Customized | |||||||
| Exportation | ZheJiang Port | Bearing Quality | ZV3 Level | |||||||
| Warranty | One Year or Above | Laser Mark | Available | |||||||
| Applicable Models | Production Capacity | 60, | Φ30 | CB | Φ35 Φ40 | 3535730 | Φ60 | |||
| Φ60 | Φ60 | 6 | Φ65 |
-FAQ:
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
Generally, we pack our goods in neutral boxes and brown cartons or as your demand.
If you have legally registered patent,we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
Q2. What is your terms of delivery?
EXW, FOB, CIF, CFR
Q3. How about your delivery time?
Generally, it will take 10 to 30 days after receiving your advance payment.
The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Material: | Rubber |
| Transport Package: | as Your Demand |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What maintenance practices are crucial for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts?
To prolong the lifespan of drive shafts and ensure their optimal performance, several maintenance practices are crucial. Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate, reduces wear and tear, and ensures the drive shaft operates smoothly and efficiently. Here are some essential maintenance practices for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts:
1. Regular Inspection:
Performing regular inspections is vital for detecting any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the drive shaft visually, looking for cracks, dents, or any signs of excessive wear on the shaft itself and its associated components such as joints, yokes, and splines. Check for any signs of lubrication leaks or contamination. Additionally, inspect the fasteners and mounting points to ensure they are secure. Early detection of any issues allows for timely repairs or replacements, preventing further damage to the drive shaft.
2. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of drive shafts. Lubricate the joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity joints, as recommended by the manufacturer. Lubrication reduces friction, minimizes wear, and helps dissipate heat generated during operation. Use the appropriate lubricant specified for the specific drive shaft and application, considering factors such as temperature, load, and operating conditions. Regularly check the lubrication levels and replenish as necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failure.
3. Balancing and Alignment:
Maintaining proper balancing and alignment is crucial for the lifespan of drive shafts. Imbalances or misalignments can lead to vibrations, accelerated wear, and potential failure. If vibrations or unusual noises are detected during operation, it is important to address them promptly. Perform balancing procedures as necessary, including dynamic balancing, to ensure even weight distribution along the drive shaft. Additionally, verify that the drive shaft is correctly aligned with the engine or power source and the driven components. Misalignment can cause excessive stress on the drive shaft, leading to premature failure.
4. Protective Coatings:
Applying protective coatings can help prolong the lifespan of drive shafts, particularly in applications exposed to harsh environments or corrosive substances. Consider using coatings such as zinc plating, powder coating, or specialized corrosion-resistant coatings to enhance the drive shaft’s resistance to corrosion, rust, and chemical damage. Regularly inspect the coating for any signs of degradation or damage, and reapply or repair as necessary to maintain the protective barrier.
5. Torque and Fastener Checks:
Ensure that the drive shaft’s fasteners, such as bolts, nuts, or clamps, are properly torqued and secured according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Loose or improperly tightened fasteners can lead to excessive vibrations, misalignment, or even detachment of the drive shaft. Periodically check and retighten the fasteners as recommended or after any maintenance or repair procedures. Additionally, monitor the torque levels during operation to ensure they remain within the specified range, as excessive torque can strain the drive shaft and lead to premature failure.
6. Environmental Protection:
Protecting the drive shaft from environmental factors can significantly extend its lifespan. In applications exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or abrasive substances, take appropriate measures to shield the drive shaft. This may include using protective covers, seals, or guards to prevent contaminants from entering and causing damage. Regular cleaning of the drive shaft, especially in dirty or corrosive environments, can also help remove debris and prevent buildup that could compromise its performance and longevity.
7. Manufacturer Guidelines:
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance practices specific to the drive shaft model and application. The manufacturer’s instructions may include specific intervals for inspections, lubrication, balancing, or other maintenance tasks. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that the drive shaft is properly maintained and serviced, maximizing its lifespan and minimizing the risk of unexpected failures.
By implementing these maintenance practices, drive shafts can operate reliably, maintain efficient power transmission, and have an extended service life, ultimately reducing downtime and ensuring optimal performance in various applications.

Can you provide real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that use drive shafts?
Drive shafts are widely used in various vehicles and machinery to transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here are some real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that utilize drive shafts:
1. Automobiles:
Drive shafts are commonly found in automobiles, especially those with rear-wheel drive or four-wheel drive systems. In these vehicles, the drive shaft transfers power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or front differential, respectively. This allows the engine’s power to be distributed to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward.
2. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Drive shafts are essential components in trucks and commercial vehicles. They are used to transfer power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear axle or multiple axles in the case of heavy-duty trucks. Drive shafts in commercial vehicles are designed to handle higher torque loads and are often larger and more robust than those used in passenger cars.
3. Construction and Earthmoving Equipment:
Various types of construction and earthmoving equipment, such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and graders, rely on drive shafts for power transmission. These machines typically have complex drivetrain systems that use drive shafts to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks, enabling them to perform heavy-duty tasks on construction sites or in mining operations.
4. Agricultural Machinery:
Agricultural machinery, including tractors, combines, and harvesters, utilize drive shafts to transmit power from the engine to the wheels or driven components. Drive shafts in agricultural machinery are often subjected to demanding conditions and may have additional features such as telescopic sections to accommodate variable distances between components.
5. Industrial Machinery:
Industrial machinery, such as manufacturing equipment, generators, pumps, and compressors, often incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. These drive shafts transfer power from electric motors, engines, or other power sources to various driven components, enabling the machinery to perform specific tasks in industrial settings.
6. Marine Vessels:
In marine applications, drive shafts are commonly used to transmit power from the engine to the propeller in boats, ships, and other watercraft. Marine drive shafts are typically longer and designed to withstand the unique challenges posed by water environments, including corrosion resistance and appropriate sealing mechanisms.
7. Recreational Vehicles (RVs) and Motorhomes:
RVs and motorhomes often employ drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These drive shafts transfer power from the transmission to the rear axle, allowing the vehicle to move and providing propulsion. Drive shafts in RVs may have additional features such as dampers or vibration-reducing components to enhance comfort during travel.
8. Off-Road and Racing Vehicles:
Off-road vehicles, such as SUVs, trucks, and all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), as well as racing vehicles, frequently utilize drive shafts. These drive shafts are designed to withstand the rigors of off-road conditions or high-performance racing, transmitting power efficiently to the wheels and ensuring optimal traction and performance.
9. Railway Rolling Stock:
In railway systems, drive shafts are employed in locomotives and some types of rolling stock. They transfer power from the locomotive’s engine to the wheels or propulsion system, enabling the train to move along the tracks. Railway drive shafts are typically much longer and may have additional features to accommodate the articulated or flexible nature of some train configurations.
10. Wind Turbines:
Large-scale wind turbines used for generating electricity incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. The drive shafts transfer rotational energy from the turbine’s blades to the generator, where it is converted into electrical power. Drive shafts in wind turbines are designed to handle the significant torque and rotational forces generated by the wind.
These examples demonstrate the broad range of vehicles and machinery that rely on drive shafts for efficient power transmission and propulsion. Drive shafts are essential components in various industries, enabling the transfer of power from the source to the driven components, ultimately facilitating movement, operation, or the performance of specific tasks.

Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2024-02-13
China supplier Porsch Cayenne 955 OE 95542102012 Center Support Bearing Auto Parts Drive Shaft Installation
Product Description
Product Description
Basic Info.
| Model NO. | Parts | Auto Parts For Center Support Bearing | ||||||||
| Specification | Bearing ID 20-85mm | Trademark | YTK or Customized | |||||||
| Price | Negotiable | Transport Packing | Neutral Packing & Customized | |||||||
| Exportation | ZheJiang Port | Bearing Quality | ZV3 Level | |||||||
| Warranty | One Year or Above | Laser Mark | Available | |||||||
| Applicable Models | Production Capacity | 60, | Φ30 | CB | Φ35 Φ40 | 3535730 | Φ60 | |||
| Φ60 | Φ60 | 6 | Φ65 |
-FAQ:
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
Generally, we pack our goods in neutral boxes and brown cartons or as your demand.
If you have legally registered patent,we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
Q2. What is your terms of delivery?
EXW, FOB, CIF, CFR
Q3. How about your delivery time?
Generally, it will take 10 to 30 days after receiving your advance payment.
The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Material: | Rubber |
| Transport Package: | as Your Demand |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
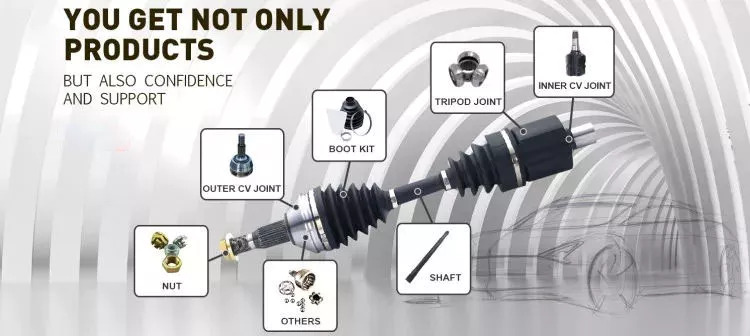
How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

What safety precautions should be followed when working with drive shafts?
Working with drive shafts requires adherence to specific safety precautions to prevent accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. Drive shafts are critical components of a vehicle or machinery’s driveline system and can pose hazards if not handled properly. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be followed when working with drive shafts:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment when working with drive shafts. This may include safety goggles, gloves, steel-toed boots, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential injuries from flying debris, sharp edges, or accidental contact with moving parts.
2. Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
Before working on a drive shaft, ensure that the power source is properly locked out and tagged out. This involves isolating the power supply, such as shutting off the engine or disconnecting the electrical power, and securing it with a lockout/tagout device. This prevents accidental engagement of the drive shaft while maintenance or repair work is being performed.
3. Vehicle or Equipment Support:
When working with drive shafts in vehicles or equipment, use proper support mechanisms to prevent unexpected movement. Securely block the vehicle’s wheels or utilize support stands to prevent the vehicle from rolling or shifting during drive shaft removal or installation. This helps maintain stability and reduces the risk of accidents.
4. Proper Lifting Techniques:
When handling heavy drive shafts, use proper lifting techniques to prevent strain or injuries. Lift with the help of a suitable lifting device, such as a hoist or jack, and ensure that the load is evenly distributed and securely attached. Avoid lifting heavy drive shafts manually or with improper lifting equipment, as this can lead to accidents and injuries.
5. Inspection and Maintenance:
Prior to working on a drive shaft, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of damage, wear, or misalignment. If any abnormalities are detected, consult a qualified technician or engineer before proceeding. Regular maintenance is also essential to ensure the drive shaft is in good working condition. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and procedures to minimize the risk of failures or malfunctions.
6. Proper Tools and Equipment:
Use appropriate tools and equipment specifically designed for working with drive shafts. Improper tools or makeshift solutions can lead to accidents or damage to the drive shaft. Ensure that tools are in good condition, properly sized, and suitable for the task at hand. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines when using specialized tools or equipment.
7. Controlled Release of Stored Energy:
Some drive shafts, particularly those with torsional dampers or other energy-storing components, can store energy even when the power source is disconnected. Exercise caution when working on such drive shafts and ensure that the stored energy is safely released before disassembly or removal.
8. Training and Expertise:
Work on drive shafts should only be performed by individuals with the necessary training, knowledge, and expertise. If you are not familiar with drive shafts or lack the required skills, seek assistance from qualified technicians or professionals. Improper handling or installation of drive shafts can lead to accidents, damage, or compromised performance.
9. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, instructions, and warnings specific to the drive shaft you are working with. These guidelines provide important information regarding installation, maintenance, and safety considerations. Deviating from the manufacturer’s recommendations may result in unsafe conditions or void warranty coverage.
10. Disposal of Old or Damaged Drive Shafts:
Dispose of old or damaged drive shafts in accordance with local regulations and environmental guidelines. Improper disposal can have negative environmental impacts and may violate legal requirements. Consult with local waste management authorities or recycling centers to ensure appropriate disposal methods are followed.
By following these safety precautions, individuals can minimize the risks associated with working with drive shafts and promote a safe working environment. It is crucial to prioritize personal safety, use proper equipment and techniques, and seek professional help when needed to ensure the proper handling and maintenance of drive shafts.

How do drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in length and torque requirements in order to efficiently transmit rotational power. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts address these variations:
Length Variations:
Drive shafts are available in different lengths to accommodate varying distances between the engine or power source and the driven components. They can be custom-made or purchased in standardized lengths, depending on the specific application. In situations where the distance between the engine and the driven components is longer, multiple drive shafts with appropriate couplings or universal joints can be used to bridge the gap. These additional drive shafts effectively extend the overall length of the power transmission system.
Additionally, some drive shafts are designed with telescopic sections. These sections can be extended or retracted, allowing for adjustments in length to accommodate different vehicle configurations or dynamic movements. Telescopic drive shafts are commonly used in applications where the distance between the engine and the driven components may change, such as in certain types of trucks, buses, and off-road vehicles.
Torque Requirements:
Drive shafts are engineered to handle varying torque requirements based on the power output of the engine or power source and the demands of the driven components. The torque transmitted through the drive shaft depends on factors such as the engine power, load conditions, and the resistance encountered by the driven components.
Manufacturers consider torque requirements when selecting the appropriate materials and dimensions for drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, to withstand the torque loads without deformation or failure. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure it can handle the expected torque without excessive deflection or vibration.
In applications with high torque demands, such as heavy-duty trucks, industrial machinery, or performance vehicles, drive shafts may have additional reinforcements. These reinforcements can include thicker walls, cross-sectional shapes optimized for strength, or composite materials with superior torque-handling capabilities.
Furthermore, drive shafts often incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity (CV) joints. These joints allow for angular misalignment and compensate for variations in the operating angles between the engine, transmission, and driven components. They also help absorb vibrations and shocks, reducing stress on the drive shaft and enhancing its torque-handling capacity.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements through customizable lengths, telescopic sections, appropriate materials and dimensions, and the inclusion of flexible joints. By carefully considering these factors, drive shafts can efficiently and reliably transmit power while accommodating the specific needs of different applications.


editor by CX 2024-01-26
China China yutong bus parts transmission systems drive shafts for center support bearing drive shaft bearing
Yr: Common
Design: Universal
OE NO.: 2214
Auto Fitment: Common
Measurement: OEM STHangZhouRD
Materials: Steel
Product Number: 2214
Guarantee: 6 Months
Auto Make: for yutong
Product Name: Center Support Bearing
Sort: Drive Shaft Support
bus design: F9 F7
method: Transmission method
Purpose: Tranquil and no noise, adaptable rotation
connecting: Generate Shaft
Quality: one hundred% Skilled Take a look at
Common: CZPT CZPT CZPT CZPT GD
travel aspect: appropriate
MOQ: 10pcs
Port: HangZhou
Specification
| Item Title | drive shaft middle sgupport bearing |
| Size | Standard |
| Material | glue+iron |
| Weight | 4kg |
| Color | look image |
| Packing | Optional |
| Warranty | 6month |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Technology | |
| Certificate | ISO9001-2008 |
| Shipping | By sea or by air optional |
| Application | Chinese bus or truck |
| Products benefits | High high quality but lower value |
| Our Advantages | Professional, authentic or duplicate optional |
| What we can provide also | Transmission program parts |
| Item Identify | |
| Item brand | |
| Size | Standard |
| Material | glue+iron |
| Weight | |
| Color | |
| Packing | Optional |
| Warranty | 6month |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Technology | |
| Certificate | ISO9001-2008 |
| Shipping | By sea or by air optional |
| Application | Chinese bus or truck |
| Products benefits | High high quality but reduced cost |
| Our Rewards | Professional, authentic or copy optional |
| What we can provide also |
Drive shaft type
The driveshaft transfers torque from the engine to the wheels and is responsible for the smooth running of the vehicle. Its design had to compensate for differences in length and angle. It must also ensure perfect synchronization between its joints. The drive shaft should be made of high-grade materials to achieve the best balance of stiffness and elasticity. There are three main types of drive shafts. These include: end yokes, tube yokes and tapered shafts.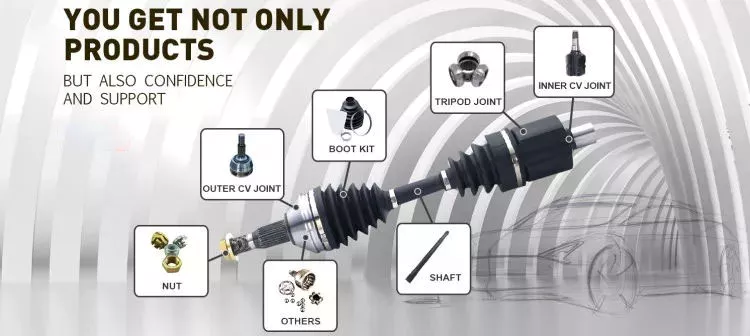
tube yoke
Tube yokes are shaft assemblies that use metallic materials as the main structural component. The yoke includes a uniform, substantially uniform wall thickness, a first end and an axially extending second end. The first diameter of the drive shaft is greater than the second diameter, and the yoke further includes a pair of opposing lugs extending from the second end. These lugs have holes at the ends for attaching the axle to the vehicle.
By retrofitting the driveshaft tube end into a tube fork with seat. This valve seat transmits torque to the driveshaft tube. The fillet weld 28 enhances the torque transfer capability of the tube yoke. The yoke is usually made of aluminum alloy or metal material. It is also used to connect the drive shaft to the yoke. Various designs are possible.
The QU40866 tube yoke is used with an external snap ring type universal joint. It has a cup diameter of 1-3/16″ and an overall width of 4½”. U-bolt kits are another option. It has threaded legs and locks to help secure the yoke to the drive shaft. Some performance cars and off-road vehicles use U-bolts. Yokes must be machined to accept U-bolts, and U-bolt kits are often the preferred accessory.
The end yoke is the mechanical part that connects the drive shaft to the stub shaft. These yokes are usually designed for specific drivetrain components and can be customized to your needs. Pat’s drivetrain offers OEM replacement and custom flanged yokes.
If your tractor uses PTO components, the cross and bearing kit is the perfect tool to make the connection. Additionally, cross and bearing kits help you match the correct yoke to the shaft. When choosing a yoke, be sure to measure the outside diameter of the U-joint cap and the inside diameter of the yoke ears. After taking the measurements, consult the cross and bearing identification drawings to make sure they match.
While tube yokes are usually easy to replace, the best results come from a qualified machine shop. Dedicated driveshaft specialists can assemble and balance finished driveshafts. If you are unsure of a particular aspect, please refer to the TM3000 Driveshaft and Cardan Joint Service Manual for more information. You can also consult an excerpt from the TSB3510 manual for information on angle, vibration and runout.
The sliding fork is another important part of the drive shaft. It can bend over rough terrain, allowing the U-joint to keep spinning in tougher conditions. If the slip yoke fails, you will not be able to drive and will clang. You need to replace it as soon as possible to avoid any dangerous driving conditions. So if you notice any dings, be sure to check the yoke.
If you detect any vibrations, the drivetrain may need adjustment. It’s a simple process. First, rotate the driveshaft until you find the correct alignment between the tube yoke and the sliding yoke of the rear differential. If there is no noticeable vibration, you can wait for a while to resolve the problem. Keep in mind that it may be convenient to postpone repairs temporarily, but it may cause bigger problems later.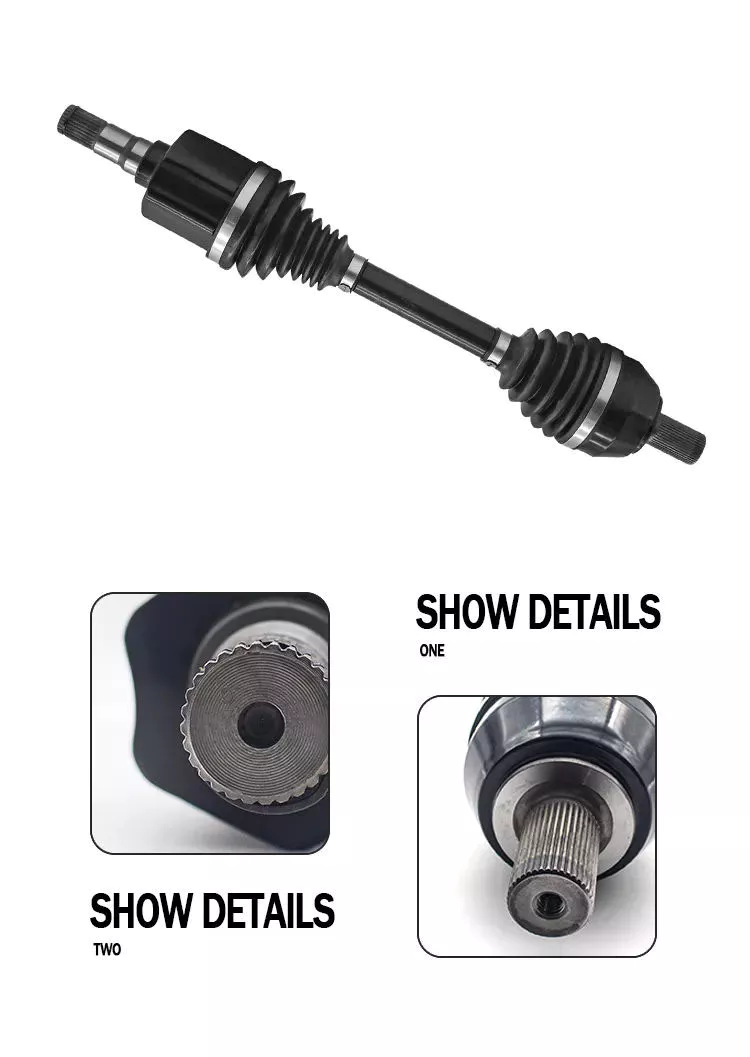
end yoke
If your driveshaft requires a new end yoke, CZPT has several drivetrain options. Our automotive end yoke inventory includes keyed and non-keyed options. If you need tapered or straight holes, we can also make them for you.
A U-bolt is an industrial fastener that has U-shaped threads on its legs. They are often used to join two heads back to back. These are convenient options to help keep drivetrain components in place when driving over rough terrain, and are generally compatible with a variety of models. U-bolts require a specially machined yoke to accept them, so be sure to order the correct size.
The sliding fork helps transfer power from the transfer case to the driveshaft. They slide in and out of the transfer case, allowing the u-joint to rotate. Sliding yokes or “slips” can be purchased separately. Whether you need a new one or just a few components to upgrade your driveshaft, 4 CZPT Parts will have the parts you need to repair your vehicle.
The end yoke is a necessary part of the drive shaft. It connects the drive train and the mating flange. They are also used in auxiliary power equipment. CZPT’s drivetrains are stocked with a variety of flanged yokes for OEM applications and custom builds. You can also find flanged yokes for constant velocity joints in our extensive inventory. If you don’t want to modify your existing drivetrain, we can even make a custom yoke for you.


editor by czh
Cfe3 Cost made in China – replacement parts – 4-B in Singapore Singapore Cam Follower Bearing with Full Stock with top quality

We – EPG Team the bigge EPT gearbox & motors , vee pulleys, timing pulleys, couplings and gears manufacturing facility in China with 5 various branches. For a lot more particulars: Cellular/whatsapp/telegram/Kakao us at: 0086~13083988828 13858117778 0571 88828
CFE3/4-B cam Follower Bearing with Complete Inventory(CFE7/8-B/CFE1B/CFE1-1/4-B/CFE1-3/4-B/CFE1-7/8-B/CFE2B/CCF1-3/8-S)
Neddle roller bearing of all kinds are our main product and our advantage.
Types:
CFE3/4-B CFE7/8-B CFE1B CFE1 1/4-B CFE1 3/4-B CFE1 7/8-B CFE2B CCF1 3/8-S CCF1/2-N-SB CCF9/16-SB CCF11/16-SB CCF3/4-SB CCF1SB CCF1 1/8-SB CCF1 1/4-SB CCFE1/2-N-S CCFE1/2-S CCFE9/16-S CCFE-5/8-S CCFE1/2-SB CCFE1 1/8-SB CCFE1 1/4-SB CCFE1 3/8-SB CCFE1 1/2-SB CCFE1 5/8-SB CCFE1 3/4-SB CCFE1 7/8-SB CFH5/8 CFH3/4 CFH1 CFH1 1/8 CFH1 1/4 CFH1 3/8 CFH1 1/2 CFH1 5/8-S CFH1 3/4 CFH1 3/4-S CFH1 7/8 CFH1 7/8-S CFH-1/2 -B CFH-1/2-SB CFH-1 1/8-SB CFH-1 1/4SB CFH-1 1/4-B CFH-1 1/2-B CFH-1 5/8-B CFH-1 3/4-B CFH-1 7/8-B CFH-2-B CFH-2 1/4-B CFH-2 1/2-B CFH-2 3/4-B CFH-3-B CFH-3SB CFH-3 1/4-SB CCFH-7/8-S CF-1/2–SB/CF-8-1PPSK/CF-3/4–SB/CF-ten-1PPSK/CF-5/8–SB/CF-10PPSK/CF-7/8–SB/CF-14PPSK/CF-1-SB/CF-16PPSK/CF-eleven/8–SB/CF-18PPSK/CF-11/2–SB/CF-24PPSK/CF-11/4–SB/CF-20PPSK/CF-13/4–SB/CF-28PPSK/CF-11/8–SB/CF-18PPSK/CF-thirteen/8–SB/CF-22PPSK/CF-fifteen/8–SB/CF-26PPSK/CF-seventeen/8–SB/CF-30PPSK/CF-2–SB/CF-32PPSK/CF-21/2-SB/CF-40PPSK/CF-21/4–SB/CF-36PPSK/CF-23/4–SB/CF-44PPSK/CF-3–SB/CF-48PPSK/CF-31/2–SB/CF-56PPSK/CF-31/4–SB/CF-52PPSK/CF-4–SB/CF-56PPSK/CF-5–SB/CF-80PPSK/CF-6–SB/CR96BUU/CF-96PPSK CCF-1/2-N/CCF-1/2-S/CCF-9/sixteen-S/CCF-5/8-N/CCF-5/8-S/CCF-eleven/sixteen/CCF-3/4-S/CCF-7/8-S/CCF-1-S/CCF-11/8/CCF-eleven/4/CCF-13/8/CCF-eleven/2/CCF-1 5/8/CCF-13/4/CCF-seventeen/8/CCF-2-S/CCF-21/4/CCF-2 1/2/CCF-23/4/CCF-3-S/CCF-31/4/CCF-3 CCFE-1/2-NS/CCFE-1/2-S/CCFE-9/sixteen-S/CCFE-5/8-S/CCFE-eleven/16-S/CCFE-3/4-S/CCFE-7/8-S CCFE-1-S/CCFE-1 1/8-S/CCFE-1 1/4-S/CCFE-1 3/8-S/CCFE-1/2-SB/CCFE-1-SB/CCFE-1 1/2 -SB/CCFE-2-SB/CCFE-3-SB/CCFE- 5/8 -SB/CCFE-1 1/8 -SB/ CCFE-1 5/8-SB/CCFE-2 1/4 -SB/CCFE-3 1/4-SB/CCFE- 3/4 -SB/CCFE-1 1/4 -SB/CCFE-1 3/4 -SB/CCFE-2 1/2-SB/CCFE-3 1/2-SB/CCFE- 7/8-SB/CCFE-1 3/8-SB/CCFE-1 7/8-SB/CCFE-2 3/4-SB
| CCF-3/4-SB | CF-1/two | CCFH-3/4-S | CCF-eleven/16-SB | CF-4 |
| CF-1-SB | CFH-1/two | CCF-7/8-SB | CFE-11/sixteen-SB | CF-4-B |
| CF-1/2-SB | CF-1/2-B | CF-7/8-SB | CCFE-11/16-SB | CF-4-S |
| CF-1 1/2-SB | CF-1/2-S | CF-7/8-S | CFH-11/sixteen-SB | CF-4-SB |
| CCYR-1 3/4-S | CCF-1/2-S | CCF-7/8-S | CCFH-11/sixteen-SB | CCF-4-S |
| CCYR-1 5/8-S | CFH-1/2-S | CFH-2-SB | CF-3/4 | CCF-4-SB |
| CFE-2-SB | CCFH-1/2-S | CFH-2-S | CF-3/4-B | CFE-4-SB |
| CYR-3/4S | CF-1/2-SB | CFH-two | CF-3/4-S | CCFE-4-SB |
| CYR-1-S | CCF-1/2-SB | CCFH-2-S | CF-3/4-SB | CFH-four |
| CYR-five | CFE-1/2-SB | CCFH-2-SB | CCF-3/4-S | CFH-4-S |
| CYR-5-S | CCFE-1/2-SB | CFH-2-1/4-S | CCF-3/4-SB | CFH-4-SB |
| CCYR-5-S | CFH-1/2-SB | CCFH-2-1/4-S | CFE-3/4-SB | CCFH-4-S |
| CF-3/four | CCFH-1/2-SB | CFH-2-1/2-S | CCFE-3/4-SB | CCFH-4-SB |
| CF-3/4-B | CF-5/8-N | CFH-2-1/2-SB | CFH-3/four | CYR-4-S |
| CF-3/4-S | CF-5/8-NB | CYR-3/4 | CFH-3/4-S | CCYR-4-S |
| CF-3/4-SB | CF-5/8-NSB | CF-1/2-N | CFH-3/4-SB | CF-5-SB |
| CCF-3/4-S | CF-5/8-NS | CF-1/2-NB | CCFH-3/4-S | CCF-5-SB |
| CCF-3/4-SB | CCF-5/8-NS | CF-3-1/4-SB | CCFH-3/4-SB | CFH-5-SB |
| CF-1/2-B | CCF-5/8-NSB | CCF-3-1/4-S | CYR-3/4 | CCFH-5-SB |
| CFH-3/4-SB | CF-5/eight | CCF-3-1/4-SB | CYR-3/4-S | CCYR-5-S |
| CF-1/2-NS | CFH-5/eight | CFE-3-1/4-SB | CCYR-3/4-S | CF-6-SB |
| CF-1/2-SB | CF-5/8-B | CCFE-3-1/4-SB | CF-7/8 | CCF-6-SB |
| CF-1/2-NSB | CF-5/8-S | CFH-3-1/4 | CF-7/8-B | CFH-6-SB |
| CCF-1/2-NS | CCF-5/8-S | CFH-3-1/4-S | CF-7/8-S | CCFH-6-SB |
| CCF-1/2-NSB | CFH-5/8-S | CFH-3-1/4-SB | CF-7/8-SB | CYR-6-S |
| CFH-1-3/4-S | CCFH-5/8-S | CCFH-3-1/4-S | CCF-7/8-S | CCYR-6-S |
| CCFH-1-3/4-S | CF-5/8-SB | CCFH-3-1/4-SB | CCF-7/8-SB | CCF-9/sixteen-SB |
| CCFH-1-3/4-SB | CCF-5/8-SB | CYR-3-1/four | CFE-7/8-SB | CYR-7-S |
| CFH-1-3/4-SB | CFE-5/8-SB | CYR-3-1/4-S | CCFE-7/8-SB | CFH-7-SB |
| CF-1/2-S | CCFE-5/8-SB | CCYR-3-1/4-S | CFH-7/8 | CF-3-1/4-S |
| CFH-1-3/4 | CFH-5/8-SB | CF-3-1/two | CFH-7/8-S | CCFH-3-1/2-SB |
| CFH-1-5/8-S | CCFH-5/8-SB | CF-3-1/2-S | CFH-7/8-SB | CCFH-1-1/2-SB |
| CFH-1-5/8-SB | CF-11/16 | CF-3-1/2-B | CCFH-7/8-S | CFH-3-1/2-S |
| CFH-1-5/8-SB | CFH-eleven/16 | CF-3-1/2-SB | CCFH-7/8-SB | CFH-3-1/2-SB |
| CCFH-1-5/8-S | CF-11/16-B | CCF-3-1/2-S | CYR-7/eight | CCFH-3-1/2-S |
| CCFH-1-5/8-SB | CF-11/16-S | CCF-3-1/2-SB | CYR-7/8-S | CF-11/sixteen-SB |
| CCFH-1-1/2-S | CCF-eleven/sixteen-S | CFE-3-1/2-SB | CCYR-7/8-S | CYR-3-1/two |
| CFH-1-1/2-S | CFH-11/sixteen-S | CCFE-3-1/2-SB | CF-3-1/four | CCYR-3-1/2-S |
| CFH-1-1/2 | CCFH-eleven/16-S | CFH-3-1/2 | CF-3-1/4-B | CFH-1-5/8 |
| CF-1/2-NS | CR8 (dXDXCXB) | four.826X12.700X 8.731X22.225 |
| CF-1/2-SB | CR8-1 (dXDXCXB) | four.826X12.700X 9.525X26.194 |
| CF-5/8-NS | CR10 (dXDXCXB) | six.350X15.875X10.319X26.988 |
| CF-5/8-SB | CR10-1 (dXDXCXB) | 6.350X15.875X11.112X30.956 |
| CF-3/4-SB | CR12 (dXDXCXB) | 9.525X19.050X12.700X35.719 |
| CF-7/8-SB | CR14 (dXDXCXB) | nine.525X22.225X12.700X35.719 |
| CF-1-SB | CR16 (dXDXCXB) | 11.112X25.400X15.875X42.063 |
| CF-1-1/8-SB | CR18 (dXDXCXB) | eleven.112X28.575X15.875X42.063 |
| CF-1-1/4-SB | CR20 (dXDXCXB) | twelve.700X31.750X19.050X51.594 |
| CF-1-3/8-SB | CR22 (dXDXCXB) | 12.700X34.925X19.050X51.594 |
| CF-1-1/2-SB | CR24 (dXDXCXB) | 15.875X38.100X22.225X61.119 |
| CF-1-5/8-SB | CR26 (dXDXCXB) | 15.875X41.275X22.225X61.119 |
| CF-1-3/4-SB | CR28 (dXDXCXB) | 19.050X44.450X25.400X70.644 |
| CF-1-7/8-SB | CR30 (dXDXCXB) | 19.050X47.625X25.400X70.644 |
| CF-2-SB | CR32 (dXDXCXB) | 22.225X50.800X31.750X83.344 |
| CF-2-1/4-SB | CR36 (dXDXCXB) | 22.225X57.150X31.750X83.344 |
| CF-2-1/2-SB | CR40 (dXDXCXB) | 25.400X63.500X38.100X96.042 |
| CF-2-3/4-SB | CR44 (dXDXCXB) | twenty five.400X69.850X38.100X96.042 |
| CF-3-SB | CR48 (dXDXCXB) | 31.750X76.200X44.450X108.seventy four |
| CF-3-1/4-SB | CR52 (dXDXCXB) | 31.750X82.550X44.450X108.74 |
| CF-3-1/2-SB | CR56 (dXDXCXB) | 34.925X88.900X50.800X121.forty four |
| CF-4-SB | CR64 (dXDXCXB) | 38.100X101.60X57.150X146.eighty four |
| CF-5-SB | CR80 (dXDXCXB) | 50.800X127.00X69.850X200.00 |
| CF-6-SB | CR96 (dXDXCXB) | sixty three.500X152.40X82.550X236.fifty four |
OUR Guarantees
Product top quality expectations are certain. Our goods have got ISO 9001 & CE worldwide top quality management program. They all developed with be EPT innovative technologies.We are proactive and we supply only products complying with leading requirements of high quality and guarantee.
We – EPG Group the bigge EPT gearbox & motors , vee pulleys, timing pulleys, couplings and gears factory in China with 5 various branches. For far more details: Mobile/whatsapp/telegram/Kakao us at: 0086~13083988828 13858117778 0571 88828 The use of first tools manufacturer’s (OEM) portion figures or trademarks , e.g. CASE® and John Deere® are for reference functions only and for indicating item use and compatibility. Our company and the listed substitution parts contained herein are not sponsored, approved, or created by the OEM.


Needle made in China – replacement parts – redler conveyor China in Quebec City Canada Roller Bearing HK1812 for Auto Agricultural Machinery with ce certificate top quality low price

We – EPG Group the largest Chain and agricultural gearbox manufacturing facility in China with 5 different branches. For a lot more specifics: Mobile/whatsapp/telegram/Kakao us at: 0086-13083988828
Quality and credit rating are the bases that make a corporation alive. a specialized supplier of a complete variety of chains, sprockets, gears, gear racks, V-belts, couplings and reducers, pto shaft, agricultural gearboxes….Maker PersonnelOur revenue people are effectively qualified to accommodate your requests and talk English for your usefulness. of standard and custom roller chains. Suited for aging, stress relieving, heat dealing with and powder coating apps. Aerospace, automotive, military, power, composite, pharmaceutical and various other industries served. Turnkey systems integration and most products accessible in inventory. EP Team has enhanced its organization traces to contain Electrical power Transmission Models and Factors, Automotive Areas and Supplies Managing Programs.
Distributor distributes OEM Needle Roller Bearings
Needle bearing is a bearing with cylindrical rollers. The rollers are slender and long relative to their diameter.This kind of roller is known as a needle roller.Though has a small cross-part, bearing still has high load potential, needle bearing with fine and extended roller (roller diameter D 5 mm or significantly less, acuity 2.5 L/D, L) for the roller duration, so the radial construction is compact, its diameter and load capability at the same time, with EPT sorts of bearing outdoors diameter to a minimum, specially suitable for the minimal dimension of the radial set up supporting construction.
| Product title: | Distributor of OEM Needle Roller Bearing |
| Substance: | Bearing Metal |
| Model: | N EPT KOYO TIMKEN NTN |
| Characteristic: | Large precision, low sound, lengthy daily life |
| Package deal: | Plastic bags /One box + outer carton box+ pallets |
| Software: | Extensively utilised in Vehicle: +86~13083988828s, rolling mills, mines, metallurgy, plastic machinery, and EPT industries |
| Notes: |
one. The bearings inside shall be stored dustproof 2. The doing work temperature shall be no higher than rated functioning temperature 3. The bearings shall be utilised acid-free setting four. The bearings shall be held in relative humidity below 60% five. The bearings shall be managed gently, avoiding slipping, knocking or hitting it 6. The bearings shall be installed evenly |
1.Our company was launched in 2006, fourteen a long time of prosperous knowledge helps make us far more expert.We assure to supply you with the mo EPT competitive price tag and the be EPT goods.
two. The company has a number of higher-quality design, processing, producing and testing technologies engineering complex staff, superior products, superior technology, and imported areas, from ZheJiang , Germany imports, can make substantial-high quality equipment resources.The company has a professional r & d team and right after-product sales service staff, you get higher-end goods, we do is quality provider.
3. The organization has an automatic generation line, which ensures unified product top quality, lowers price, shortens delivery time and increases creation effectiveness.
4. The bearings created by the business have large precision, substantial velocity, modest dress in, provider lifestyle, stHangZhourd size, compact framework and fa EPT operating velocity.The firm has been awarded”China 3.15 integrity enterprises”, “China well-known brand merchandise”,”quality inspection nationwide stHangZhourds qualified goods” and EPT nationwide authoritative certificates.Received a number of countrywide patents, become the domesticleading enterprises.
| Shaft Diameter | open | Mass | Closed | Mass | ||
| mm | Recent | Substituted | g | Current | Substituted | g |
| 4 | HK0408TN | 37941/4 | one.six | BK0408TN | 35941/four | one.eight |
| five | HK0509 | 47941/5 | two | BK0509 | 45941/five | 2.1 |
| six | HK0607 | 27941/six | 1.8 | – | – | – |
| HK0608 | 37941/six | 2.one | BK0608 | 35941/6 | 2.two | |
| HK0609 | 47941/6 | 2.two | BK0609 | 45941/six | two.six | |
| HK06×12×08 | 2.5 | – | – | – | ||
| 7 | HK0709 | 47941/7 | two.3 | BK0709 | 45941/7 | two.9 |
| 8 | HK0808 | 37941/8 | 2.7 | BK0808 | 35941/eight | 3 |
| HK571 | 57941/eight | three | BK571 | 55941/eight | 3.4 | |
| HK08×14×10 | 27942/8 | five.35 | BK08×14×10 | 25941/eight | 5.8 | |
| HK08×14×12 | 37942/eight | six.6 | – | – | – | |
| nine | HK0908 | 37941/9 | three | BK0908 | 35941/9 | 3.four |
| HK571 | 57941/nine | four | BK571 | 55941/9 | 4.three | |
| HK571 | 67941/nine | 4.six | BK571 | 65941/nine | four.9 | |
| HK09×15×10 | 27942/9 | 5.6 | – | – | – | |
| 10 | HK1571 | 57941/ten | four.one | BK1571 | 55941/10 | 4.3 |
| HK1012 | 67941/ten | four.8 | BK1012 | 65941/10 | five | |
| HK1015 | – | 6 | BK1015 | – | 6.2 | |
| twelve | HK1208 | 37941/twelve | 3.three | – | – | – |
| HK1210 | 57941/12 | four.6 | BK1210 | 55941/twelve | 5.two | |
| HK1212 | 67941/12 | 5.six | BK1212 | 65941/twelve | 6.2 | |
| thirteen | HK1312 | – | 8.9 | BK1312 | – | eleven.2 |
| fourteen | HK1410 | 27941/14 | 8.3 | BK1412 | 35941/14 | 12.1 |
| HK1412 | 37941/14 | ten.5 | – | – | twelve.2 | |
| HK1416 | 57941/14 | thirteen.9 | – | – | 12.5 | |
| 15 | HK15×20×12 | 7941/fifteen | eight.4 | – | – | – |
| HK15×20×16 | 7942/15 | eleven.four | – | – | – | |
| HK15×20×20 | 7943/fifteen | thirteen.eight | – | – | – | |
| HK1512 | 37941/fifteen | eleven.1 | BK1512 | 35941/fifteen | twelve.7 | |
| HK1514 | 47941/15 | twelve.seven | – | – | twelve.nine | |
| HK1515 | – | fourteen.2 | – | – | thirteen | |
| HK1516 | 57941/fifteen | 15 | BK1516 | 55941/fifteen | 16.5 | |
| HK1522 | SZ-439 | twenty.four | BK1522 | – | 22 | |
| HK15×22×12 | 7948/fifteen | 12.five | – | – | – | |
| 16 | HK16×21×09 | – | 7.five | – | – | – |
| HK1612 | 37941/sixteen | eleven.7 | BK1612 | 35941/sixteen | 13.eight | |
| HK1614 | 47941/16 | 14.4 | – | – | – | |
| HK1616 | 57941/16 | fifteen.8 | BK1616 | 55941/sixteen | seventeen.six | |
| HK1617 | SZ-435 | eighteen | – | – | – | |
| HK1622 | 87941/16 | 21.seven | BK1622 | 85941/sixteen | 23.4 | |
| seventeen | HK1712 | 37941/17 | twelve.two | BK1712 | 35941/seventeen | fourteen.5 |
| HK1714 | 7941/17 | 14 | – | – | – | |
| HK1716 | 57941/seventeen | fifteen.nine | – | – | – | |
| HK1718 | 7942/seventeen | 19 | – | – | – | |
| eighteen | HK1812 | 37941/eighteen | 13.one | BK1812 | 35941/18 | fourteen.nine |
| HK1816 | 57941/eighteen | 17.5 | BK1816 | 55941/eighteen | 19.9 | |
| 19 | HK19×27×16 | TA1916 | 23 | – | – | – |
| twenty | HK2571 | 27941/twenty | 11.8 | BK2571 | 25941/twenty | 14 |
| HK2012 | 37941/20 | fourteen.4 | BK2012 | 35941/20 | 16.seven | |
| HK2014 | 47941/20 | 15.7 | – | – | – | |
| HK2016 | 57941/twenty | 19.3 | BK2016 | 55941/twenty | 22.three | |
| HK2018 | 67941/20 | 23.three | – | – | – | |
| HK2571 | 79421/twenty | 24.one | BK2571 | 75941/20 | 27.one | |
| HK2571 | 7943/20 | 28 | – | – | – | |
| HK2030 | – | 34.seven | BK2030 | – | 37.four | |
| HK20×28×16 | 47942/twenty | 28.five | – | – | – | |
| 22 | HK2210 | 27941/22 | 12.3 | – | – | – |
| HK2212 | 37941/22 | fifteen | BK2212 | 35941/22 | 18.one | |
| HK2216 | 57941/22 | 20.9 | BK2216 | 55941/22 | 24.3 | |
| HK2220 | 77941/22 | 26.two | BK2220 | 75941/22 | 29.nine | |
| HK2230 | – | 32 | – | – | – | |
| twenty five | HK2512 | 27941/twenty five | 20 | BK2512 | 25941/25 | 23.2 |
| HK2514 | 37941/twenty five | 21.9 | – | – | – | |
| HK2516 | 7941/twenty five | 27.3 | BK2516 | 7941/25 | 31 | |
| HK2518 | 57941/twenty five | 28.two | – | – | – | |
| HK2520 | 67941/twenty five | 34.one | BK2520 | 65941/twenty five | 38.7 | |
| HK2525 | 7943/twenty five | forty | – | – | – | |
| HK2526 | – | 44.eight | BK2526 | – | 49 | |
| HK2538 | 87941/twenty five | sixty four.7 | BK2538 | 85941/twenty five | sixty nine | |
| HK25×35×20 | 57942/twenty five | forty four.nine | – | – | – | |
| 28 | HK2816 | 47941/28 | thirty.1 | BK2816 | 45941/28 | 34.one |
| HK2818 | 57941/28 | 31.seven | – | – | – | |
| HK2820 | 67941/28 | 37.6 | BK2820 | 65941/28 | 43 | |
| thirty | HK3012 | 27941/30 | 24 | BK3012 | 25941/30 | 27.9 |
| HK3016 | 47941/30 | 32 | BK3016 | 45941/thirty | 37.one | |
| HK3018 | 57941/30 | 33.6 | – | – | – | |
| HK3571 | 67941/thirty | 40.1 | BK3571 | 65941/30 | forty six.5 | |
| HK3026 | – | 52.nine | BK3026 | – | 59.four | |
| HK3038 | – | seventy six.one | BK3038 | – | 82.five | |
| HK30×38×12 | 27941/thirty | 28 | – | – | – | |
| HK30×38×16 | 7941/thirty | 32.7 | – | – | – | |
| HK30×38×24 | 7942/thirty | forty nine | – | – | – | |
| HK30×38×32 | 7943/thirty | sixty nine | – | – | – | |
| 32 | HK3224 | 77941/32 | fifty.seven | – | – | – |
| HK3232 | 97941/32 | 66.4 | – | – | – | |
| HK32×40×32 | 7943/32 | seventy two.7 | – | – | – | |
| 35 | HK3512 | 59741/35 | 27.seven | BK3512 | 25941/35 | 32.nine |
| HK3516 | 47941/35 | 36.9 | BK3516 | 45941/35 | 43.eight | |
| HK3520 | 67941/35 | 46.one | BK3520 | 65941/35 | fifty four.8 | |
| HK35×43×16 | 7941/35 | 37 | – | – | – | |
| HK35×43×25 | 7942/35 | 60.five | – | – | – | |
| HK35×43×32 | 7943/35 | 80 | – | – | – | |
| 38 | HK38×48×30 | – | 102 | – | – | – |
| forty | HK4012 | 27941/40 | 31.one | BK4012 | 25941/forty | 38.two |
| HK4016 | 47941/40 | forty one.four | BK4015 | 45941/40 | 51 | |
| HK4571 | 67941/40 | fifty one.8 | BK4571 | 65941/40 | sixty two | |
| HK40×50×32 | 7942/40 | 114.three | – | – | – | |
| HK40×50×38 | 7943/40 | 130.eight | – | – | – | |
| forty five | HK4512 | 27941/45 | 34.8 | BK4512 | 25941/45 | forty five |
| HK4516 | 47941/45 | forty six.2 | BK4516 | 45941/forty five | 56 | |
| HK4520 | 67941/45 | fifty six | BK4520 | 65941/45 | seventy two | |
| HK5012 | 27941/fifty | forty four.2 | – | – | – | |
| HK5571 | 47941/fifty | seventy two | BK5571 | 55941/50 | 87.3 | |
| HK5571 | 7943/fifty | ninety.1 | BK5571 | 5943/50 | 109 | |
| 55 | HK5520 | 57941/fifty five | 78 | BK5571 | – | ninety three.eight |
| HK5525 | 77941/55 | 109 | – | 55941/55 | – | |
| HK5528 | 87941/fifty five | 111 | BK5528 | 84941/sixty | 132 | |
| sixty | HK6012 | – | 49.2 | BK6012 | – | 77 |
| HK6571 | 57941/sixty | 86 | BK6571 | 55941/60 | one hundred and five |
Our Rewards
1.Entire world-Course Bearing
We provide our consumers with all varieties of indigenous bearing with planet-class quality.
two.OEM or Non-Stand Bearings
Any prerequisite for NonstHangZhourd bearings is Very easily Fulfilled by us because of to its va EPT expertise and back links in the business.
3. Genuine merchandise With EPT Good quality
The company has usually proved the one hundred% quality products it supplies with legitimate intent.
4. Right after Income Services and Technical Support
The organization gives following-revenue service and complex assistance as per the customer’s requirements and requirements.
five. Swift Shipping and delivery
The organization gives just-in-time delivery with its streamlined source chain.
Inquiries and Answers
Q: Are you a trading organization or maker?
A: We are a factory.
Q: How extended is your shipping time?
A: Generally it is 5-10 times if the merchandise are in inventory. or it is fifteen-20 days if the goods are not in inventory, it is according to quantity.
Q: Do you provide samples ? is it free of charge or additional?
A: Yes, we could offer you the sample for free cost but do not shell out the co EPT of freight.
Q: What are your terms of payment?
A: Payment=1000USD, thirty% T/T in advance ,stability before shippment.
Please come to feel totally free to contact us, if you have any EPT queries!
The use of authentic products manufacturer’s (OEM) component numbers or emblems , e.g. CASE® and John Deere® are for reference functions only and for indicating product use and compatibility. Our company and the shown replacement components contained herein are not sponsored, accepted, or made by the OEM.




Ce sales made in China – replacement parts – 8n pto shaft bearing replacement Approved Dq404 40HP 4X4 4WD Enfly Brand Compact Mini Garden Tractor with Rops with ce certificate top quality low price
We – EPG Group the biggest agricultural gearbox and pto manufacturing facility in China with 5 distinct branches. For far more specifics: Cell/whatsapp/telegram/Kakao us at: 0086-13083988828

touareg drive shaft bush hog drive shaft tractor supply EPG ninety eight honda crv drive shaft is 540 to 540 pto adapter specialised kodiak bush hog gearbox in woody generate shaft layout, basic mini drive shaft maker x485 rear pto and 2011 nissan rogue travel shaft product sales mr driveshaft lasalle of agricultural equipment and farm implements, which has an impartial import and export legal rights. EPG major creation is of farming 15-five hundred horsepower tractor supporting equipment, mechanical cultivation, harvesting equipment and add-ons. CE accepted DQ404 40HP 4×4 Four wheel drive Enfly manufacturer Compact Mini Backyard tractor with ROPS
Tractor Major Characteristics and Rewards:
1.Outfitted renowned manufacturer motor exhibiting superior capacity, minimal gasoline usage and high financial efficiency.
two. Streamlined physical appearance design, lovely and generous.
3.Transmission Case adopt meshed change and add the gearbox interlock unit can make the procedure much more easily, reputable and simpler.
4. Double action clutch with disc spring, carry out steadily and effortless to run.
five. Totally hydraulic steering technique significantly decreased driver’s work energy.
six. Soaked disc brake system, trustworthy brake functionality.
7. Separate injection of hydraulic oil, reputable to work.
eight. The lifter with power and place adjustment, with reputable carry.
9. Tractor PTO:
PTO in Double velocity : 540/a thousand, 760/one thousand, 540/760r/min Optional, For large functioning efficiency.
PTO shaft of 6 or 8 spline Optional, adaptable for agricultural products of all over the world.
10.Full collection mild,ROPS,Sunshade/Canopy,Enthusiast/Heater/Air-conditioned cabin are all accessible, for far more comfy driving surroundings.
Tractor Principal specificaiton and Complex parameters:
| Model | DQ404 |
| Push kind | 4×4 |
| Engine | |
| Kind of engine | Xinchai 4-Cylinder drinking water-awesome EPT engine |
| Potential of gas tank(L) | 38L |
| Motor power at rated velocity(kw) | 29.4 |
| Rated speed (r/min) | 2400 |
| Transmission | |
| Clutch | Dry, dual-phase variety |
| PTO speed | 540/1000rpm or 540/760rpm |
| Gear shift | 8F+4R/8F+8R/12F+12R(Optional) |
| Hydraulic system | |
| Hydraulic output valve | two-Way (optional) |
| Three level linkage | |
| Category of 3-position hyperlink | rear, group II |
| Lifting power(at position of 610mm)KN | eleven |
| Technical parameter | |
| Overall size(L x W x H)mm | 3513x1750x2130 |
| Wheel foundation(mm) | 1924 |
| The smallest clearance(mm) | 325 |
| Entrance tire | eight.3-20 |
| Rear tire | twelve.4-28/fourteen.9-24 (optional) |
| Optional Configurations | |
| ROPS,Canopy(Sunshade),Cabin with Fan/Heater/Air-problem, 2-Team Hydraulic output valve, Entrance ballast, Rear ballast,Air brake, 8F+8R/12F+12R Shuttle gearshift,Paddy tire, 14.9-24 massive rear tire, Swing draw bar | |
DQ404 40HP 4wd Tractor show :
EPT Manufacutring Line:
Strictly Inspecting and Full Tests for guaranteeing higher good quality merchandise:
Various Tractor Packing and Transporting services to meed distinct customers’ demand :
Higher good quality Tractor have ISO,CE, PVOC COC, CO, and so on certificates:
EPT after-sale services for each Distributors and Personal customers:
Make sure you speak to us if you have any desire for our Product :
Ideal price tag will be quoted for you as shortly as receive your Prerequisite !

Corrosion made in China – replacement parts – metal chain link conveyor belt China in Aden Yemen Resistant Wear Resistant Roller Bearing Used for Heat Treatment Furnace with ce certificate top quality low price

We – EPG Group the biggest Chain and agricultural gearbox factory in China with 5 various branches. For a lot more specifics: Cell/whatsapp/telegram/Kakao us at: 0086-13083988828
ensures the security and consistency of the important function of components.EPG In the meantime, our merchandise are made in accordance to substantial good quality requirements, and complying with the global superior common conditions.roller chain satisfies or exceeds ANSI expectations and is created in ISO certified factories. As is the situation with our pillow block bearings and ball bearings, our roller chain parts are analyzed prior to shipment to insure high quality. The roller chain components and roller chains we supply are pre-stretched to insure you have minimal sag. It also comes with strong rollers, ensuring that it is of the highest quality. Regular solitary-strand roller chain, standardized by ASME, is an assembly of alternating pin back links and roller backlinks. The length amongst pin facilities is known as the pitch. The pitch is what categorizes the measurement of the chain. The greater the pitch, the increased the load rating. Chains with small pitches have smaller masses, operate more quietly, and at greater speeds. Multi-strand, tiny-pitch roller chains are a great resolution for high-load, substantial-velocity applications.
Centrifugal casting aluminium bronze bushing
Normal items like heat therapy fixture, ca EPT baskets, roller rails, ca EPT link belts, chain guides, enthusiasts, skid riders, buttons and EPT furnace areas
|
Software |
for different sorts of heat treatment method furnaces |
|
Top quality Management |
We have in-property facility for every inspection:
|
|
Advantages |
More than 30 years of skilled expertise and steady R&D initiatives allow us to offer you better personalized design and style and engineering advice |
The followings are images for our factory and items:
FAQ
1. Q: How To give inquiry ?
A: Phase 1, please explain to us what weight ,dimension, substance do you need to have make sure you
Phase 2, Better aid to offer the drawing with earlier mentioned-mentioned detai EPT make sure you
Step 3, when we have sufficient specifics, we may estimate accordingly
2 . Q: When will make shipping and delivery ?
A: Shipping Time
-Sample Get: 15 days soon after receipt of the total payment.
-Inventory Buy: 10 days following receipt of the total payment
-OEM Order: 40 days following receipt of the deposit.
three. After-revenue Service
1 calendar year warranty for all varieties of products
If you discover any defective accessories fir EPT time, we will give you the new elements for totally free to replace in the following buy, as an experienced company, you can re EPT confident of the quality and following-sales service.
4. Payment
T/T, Western Union, Moneygram ,income.
five. Transportation
Transported by DHL, UPS, EMS, Fedex,Air freight. sea freight.
six. Do you assist fall shipping and delivery?
Of course,your fall shipping is aviable.
The use of authentic products manufacturer’s (OEM) component numbers or logos , e.g. CASE® and John Deere® are for reference reasons only and for indicating item use and compatibility. Our business and the shown substitute areas contained herein are not sponsored, accredited, or created by the OEM.



