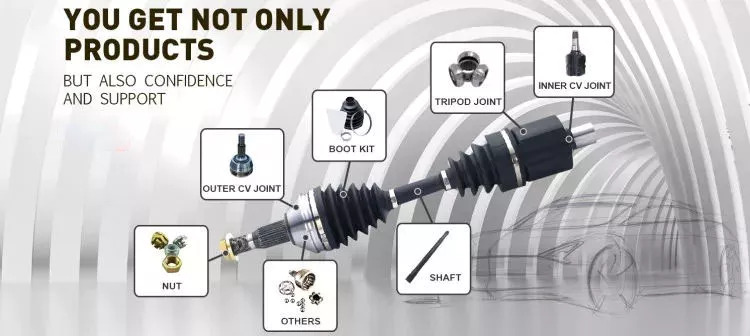
Product Description
Product Parameters
| Product Name | PERFECTRAIL Car Auto Parts Drive Cardan Propshaft Prop Propeller Shaft for CZPT Hilux CZPT Honda Civic Mazda CZPT Suzuki |
| Car Model | For American cars, For European cars, For Japanese cars, For Korean cars |
| OEM NO. | According to Clients’ Needs |
| Color | Same as pictrue |
| Material | OEM Standard |
| Warranty | 1 Year |
| MOQ | 1PC if we have stock, 50PCS for production. |
| Delivery Time | 7-45 days |
| Our Advantage | 1. Advanced design and skilled workmanship gurantee the standard of our products;
2. High-quality raw materials gurantee the good performance of our products; 3.Experienced teams and mangement gurantee the production efficiency and the delivery time; 4.Our good service bring you pleasant purchase. 5. The same length as original one. 6. Lower MOQ is acceptable with more models. 7.Laser Mark for free. 8.Pallet with Film for free. |
Detailed Photos
FAQ
/* May 10, 2571 16:49:51 */!function(){function d(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

Can drive shafts be customized for specific vehicle or equipment requirements?
Yes, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements. Customization allows manufacturers to tailor the design, dimensions, materials, and other parameters of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility and optimal performance within a particular vehicle or equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts can be customized:
1. Dimensional Customization:
Drive shafts can be customized to match the dimensional requirements of the vehicle or equipment. This includes adjusting the overall length, diameter, and spline configuration to ensure proper fitment and clearances within the specific application. By customizing the dimensions, the drive shaft can be seamlessly integrated into the driveline system without any interference or limitations.
2. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for drive shafts can be customized based on the specific requirements of the vehicle or equipment. Different materials, such as steel alloys, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, can be selected to optimize strength, weight, and durability. The material selection can be tailored to meet the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the application, ensuring the drive shaft’s reliability and longevity.
3. Joint Configuration:
Drive shafts can be customized with different joint configurations to accommodate specific vehicle or equipment requirements. For example, universal joints (U-joints) may be suitable for applications with lower operating angles and moderate torque demands, while constant velocity (CV) joints are often used in applications requiring higher operating angles and smoother power transmission. The choice of joint configuration depends on factors such as operating angle, torque capacity, and desired performance characteristics.
4. Torque and Power Capacity:
Customization allows drive shafts to be designed with the appropriate torque and power capacity for the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers can analyze the torque requirements, operating conditions, and safety margins of the application to determine the optimal torque rating and power capacity of the drive shaft. This ensures that the drive shaft can handle the required loads without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
5. Balancing and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can be customized with precision balancing and vibration control measures. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, increased wear, and potential driveline issues. By employing dynamic balancing techniques during the manufacturing process, manufacturers can minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation. Additionally, vibration dampers or isolation systems can be integrated into the drive shaft design to further mitigate vibrations and enhance overall system performance.
6. Integration and Mounting Considerations:
Customization of drive shafts takes into account the integration and mounting requirements of the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers work closely with the vehicle or equipment designers to ensure that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the driveline system. This includes adapting the mounting points, interfaces, and clearances to ensure proper alignment and installation of the drive shaft within the vehicle or equipment.
7. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate with vehicle manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft customization process. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can address specific needs, optimize performance, and ensure compatibility with the vehicle or equipment. This collaborative approach enhances the customization process and results in drive shafts that meet the exact requirements of the application.
8. Compliance with Standards:
Customized drive shafts can be designed to comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, ensures that the customized drive shafts meet quality, safety, and performance requirements. Adhering to these standards provides assurance that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into the specific vehicle or equipment.
In summary, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements through dimensional customization, material selection, joint configuration, torque and power capacity optimization, balancing and vibration control, integration and mounting considerations, collaboration with stakeholders, and compliance with industry standards. Customization allows drive shafts to be precisely tailored to the needs of the application, ensuring compatibility, reliability, and optimal performance.

Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.


editor by lmc 2024-11-08
China manufacturer Propeller Shaft / Drive Shaft for CHINAMFG 4runner / Hilux / Tundra / Tacoma / Land Cruiser Hot Sell America & Europe Market
Product Description
|
OEM No. |
936-739,37110-6A620,37140-60170 37110-6571,37110-60460 371/8822 0571 8 |
45710-S10-A01 |
12344543 |
27111-SC571 |
|
936-571 |
45710-S9A-E01 |
936-911 |
27111-AJ13D |
|
|
936-034 |
45710-S9A-J01 |
936-916 |
27101-84C00 |
|
|
for MITSUBISHI/NISSAN |
for TOYOTA |
|||
|
CARDONE |
OE |
CARDONE |
OE |
|
|
65-3009 |
MR580626 |
65-5007 |
37140-35180 |
|
|
65-6000 |
3401A571 |
65-9842 |
37140-35040 |
|
|
65-9480 |
37000-JM14A |
65-5571 |
37100-3D250 |
|
|
65-9478 |
37000-S3805 |
65-5030 |
37100-34120 |
|
|
65-6004 |
37000-S4203 |
65-9265 |
37110-3D070 |
|
|
65-6571 |
37041-90062 |
65-9376 |
37110-35880 |
|
|
936-262 |
37041-90014 |
65-5571 |
37110-3D220 |
|
|
938-030 |
37300-F3600 |
65-5571 |
37100-34111 |
|
|
936-363 |
37000-7C002 |
65-5018 |
37110-3D060 |
|
|
938-200 |
37000-7C001 |
65-5012 |
37100-5712 |
|
|
for KOREA CAR |
||||
|
for HYUNDAI/KIA |
||||
|
CARDONE |
OE |
CARDONE |
OE |
|
|
65-3502 |
49571-H1031 |
936-211 |
49100-3E450 |
|
|
65-3503 |
49300-2S000 |
936-210 |
49100-3E400 |
|
|
65-3500 |
49300-0L000 |
936-200 |
49300-2P500 |
|
KOWA is a special brand focus on Propeller shaft main for America and Europe market.
It is a brand created by NINGBNO CZPT AUTO PARTSCo.,ltd, who has been manufacturing
and trading all kinds of auto parts for more than 10 years.
KOWA brand with 1 year quality assurance at the factory price by MOQ 5pcs
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO, Ts16949 |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Toyota |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can drive shafts be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings?
Yes, drive shafts can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings. While there may be some differences in design and specifications based on the specific application requirements, the fundamental principles and functions of drive shafts remain applicable in both contexts. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Power Transmission:
Drive shafts serve the primary purpose of transmitting rotational power from a power source, such as an engine or motor, to driven components, which can be wheels, machinery, or other mechanical systems. This fundamental function applies to both automotive and industrial settings. Whether it’s delivering power to the wheels of a vehicle or transferring torque to industrial machinery, the basic principle of power transmission remains the same for drive shafts in both contexts.
2. Design Considerations:
While there may be variations in design based on specific applications, the core design considerations for drive shafts are similar in both automotive and industrial settings. Factors such as torque requirements, operating speeds, length, and material selection are taken into account in both cases. Automotive drive shafts are typically designed to accommodate the dynamic nature of vehicle operation, including variations in speed, angles, and suspension movement. Industrial drive shafts, on the other hand, may be designed for specific machinery and equipment, taking into consideration factors such as load capacity, operating conditions, and alignment requirements. However, the underlying principles of ensuring proper dimensions, strength, and balance are essential in both automotive and industrial drive shaft designs.
3. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is influenced by the specific requirements of the application, whether in automotive or industrial settings. In automotive applications, drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, durability, and ability to withstand varying operating conditions. In industrial settings, drive shafts may be made from a broader range of materials, including steel, stainless steel, or even specialized alloys, depending on factors such as load capacity, corrosion resistance, or temperature tolerance. The material selection is tailored to meet the specific needs of the application while ensuring efficient power transfer and durability.
4. Joint Configurations:
Both automotive and industrial drive shafts may incorporate various joint configurations to accommodate the specific requirements of the application. Universal joints (U-joints) are commonly used in both contexts to allow for angular movement and compensate for misalignment between the drive shaft and driven components. Constant velocity (CV) joints are also utilized, particularly in automotive drive shafts, to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and accommodate varying operating angles. These joint configurations are adapted and optimized based on the specific needs of automotive or industrial applications.
5. Maintenance and Service:
While maintenance practices may vary between automotive and industrial settings, the importance of regular inspection, lubrication, and balancing remains crucial in both cases. Both automotive and industrial drive shafts benefit from periodic maintenance to ensure optimal performance, identify potential issues, and prolong the lifespan of the drive shafts. Lubrication of joints, inspection for wear or damage, and balancing procedures are common maintenance tasks for drive shafts in both automotive and industrial applications.
6. Customization and Adaptation:
Drive shafts can be customized and adapted to meet the specific requirements of various automotive and industrial applications. Manufacturers often offer drive shafts with different lengths, diameters, and joint configurations to accommodate a wide range of vehicles or machinery. This flexibility allows for the adaptation of drive shafts to suit the specific torque, speed, and dimensional requirements of different applications, whether in automotive or industrial settings.
In summary, drive shafts can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings by considering the specific requirements of each application. While there may be variations in design, materials, joint configurations, and maintenance practices, the fundamental principles of power transmission, design considerations, and customization options remain applicable in both contexts. Drive shafts play a crucial role in both automotive and industrial applications, enabling efficient power transfer and reliable operation in a wide range of mechanical systems.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery: Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transferring power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer: Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability: Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability: Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction: Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency: Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades: Drive shaft upgrades can be popular performance enhancements for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications: Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability: Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies: Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency, enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies, and ensuring durability and reliability. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.

Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2024-02-26
China Hot selling Propeller Shaft / Drive Shaft for CHINAMFG 4runner / Hilux / Tundra / Tacoma / Land Cruiser Hot Sell America & Europe Market
Product Description
|
OEM No. |
936-739,37110-6A620,37140-60170 37110-6571,37110-60460 371/8822 0571 8 |
45710-S10-A01 |
12344543 |
27111-SC571 |
|
936-571 |
45710-S9A-E01 |
936-911 |
27111-AJ13D |
|
|
936-034 |
45710-S9A-J01 |
936-916 |
27101-84C00 |
|
|
for MITSUBISHI/NISSAN |
for TOYOTA |
|||
|
CARDONE |
OE |
CARDONE |
OE |
|
|
65-3009 |
MR580626 |
65-5007 |
37140-35180 |
|
|
65-6000 |
3401A571 |
65-9842 |
37140-35040 |
|
|
65-9480 |
37000-JM14A |
65-5571 |
37100-3D250 |
|
|
65-9478 |
37000-S3805 |
65-5030 |
37100-34120 |
|
|
65-6004 |
37000-S4203 |
65-9265 |
37110-3D070 |
|
|
65-6571 |
37041-90062 |
65-9376 |
37110-35880 |
|
|
936-262 |
37041-90014 |
65-5571 |
37110-3D220 |
|
|
938-030 |
37300-F3600 |
65-5571 |
37100-34111 |
|
|
936-363 |
37000-7C002 |
65-5018 |
37110-3D060 |
|
|
938-200 |
37000-7C001 |
65-5012 |
37100-5712 |
|
|
for KOREA CAR |
||||
|
for HYUNDAI/KIA |
||||
|
CARDONE |
OE |
CARDONE |
OE |
|
|
65-3502 |
49571-H1031 |
936-211 |
49100-3E450 |
|
|
65-3503 |
49300-2S000 |
936-210 |
49100-3E400 |
|
|
65-3500 |
49300-0L000 |
936-200 |
49300-2P500 |
|
KOWA is a special brand focus on Propeller shaft main for America and Europe market.
It is a brand created by NINGBNO CZPT AUTO PARTSCo.,ltd, who has been manufacturing
and trading all kinds of auto parts for more than 10 years.
KOWA brand with 1 year quality assurance at the factory price by MOQ 5pcs
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO, Ts16949 |
| Type: | Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Toyota |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
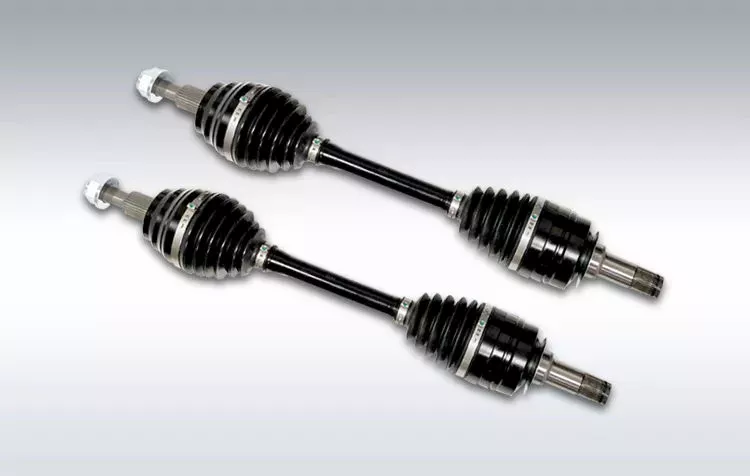

How do manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment?
Manufacturers employ various strategies and processes to ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. Compatibility refers to the ability of a drive shaft to effectively integrate and function within a specific piece of equipment or machinery. Manufacturers take into account several factors to ensure compatibility, including dimensional requirements, torque capacity, operating conditions, and specific application needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts:
1. Application Analysis:
Manufacturers begin by conducting a thorough analysis of the intended application and equipment requirements. This analysis involves understanding the specific torque and speed demands, operating conditions (such as temperature, vibration levels, and environmental factors), and any unique characteristics or constraints of the equipment. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the application, manufacturers can tailor the design and specifications of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility.
2. Customization and Design:
Manufacturers often offer customization options to adapt drive shafts to different equipment. This customization involves tailoring the dimensions, materials, joint configurations, and other parameters to match the specific requirements of the equipment. By working closely with the equipment manufacturer or end-user, manufacturers can design drive shafts that align with the equipment’s mechanical interfaces, mounting points, available space, and other constraints. Customization ensures that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the equipment, promoting compatibility and optimal performance.
3. Torque and Power Capacity:
Drive shaft manufacturers carefully determine the torque and power capacity of their products to ensure compatibility with different equipment. They consider factors such as the maximum torque requirements of the equipment, the expected operating conditions, and the safety margins necessary to withstand transient loads. By engineering drive shafts with appropriate torque ratings and power capacities, manufacturers ensure that the shaft can handle the demands of the equipment without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
4. Material Selection:
Manufacturers choose materials for drive shafts based on the specific needs of different equipment. Factors such as torque capacity, operating temperature, corrosion resistance, and weight requirements influence material selection. Drive shafts may be made from various materials, including steel, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, to provide the necessary strength, durability, and performance characteristics. The selected materials ensure compatibility with the equipment’s operating conditions, load requirements, and other environmental factors.
5. Joint Configurations:
Drive shafts incorporate joint configurations, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate different equipment needs. Manufacturers select and design the appropriate joint configuration based on factors such as operating angles, misalignment tolerances, and the desired level of smooth power transmission. The choice of joint configuration ensures that the drive shaft can effectively transmit power and accommodate the range of motion required by the equipment, promoting compatibility and reliable operation.
6. Quality Control and Testing:
Manufacturers implement stringent quality control processes and testing procedures to verify the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. These processes involve conducting dimensional inspections, material testing, torque and stress analysis, and performance testing under simulated operating conditions. By subjecting drive shafts to rigorous quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure that they meet the required specifications and performance criteria, guaranteeing compatibility with the intended equipment.
7. Compliance with Standards:
Manufacturers ensure that their drive shafts comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, provides assurance of quality, safety, and compatibility. Adhering to these standards helps manufacturers meet the expectations and requirements of equipment manufacturers and end-users, ensuring that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into different equipment.
8. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate closely with equipment manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft design and manufacturing processes. This collaborative approach ensures that the drive shafts are compatible with the intended equipment and meet the expectations of the end-users. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can continuously improve their products’ compatibility and performance.
In summary, manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment through a combination of application analysis, customization, torque and power capacity considerations, material selection, joint configurations, quality control and testing, compliance with standards, and collaboration with equipment manufacturers and end-users. These efforts enable manufacturers to design and produce drive shafts that seamlessly integrate with various equipment, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and compatibility in different applications.
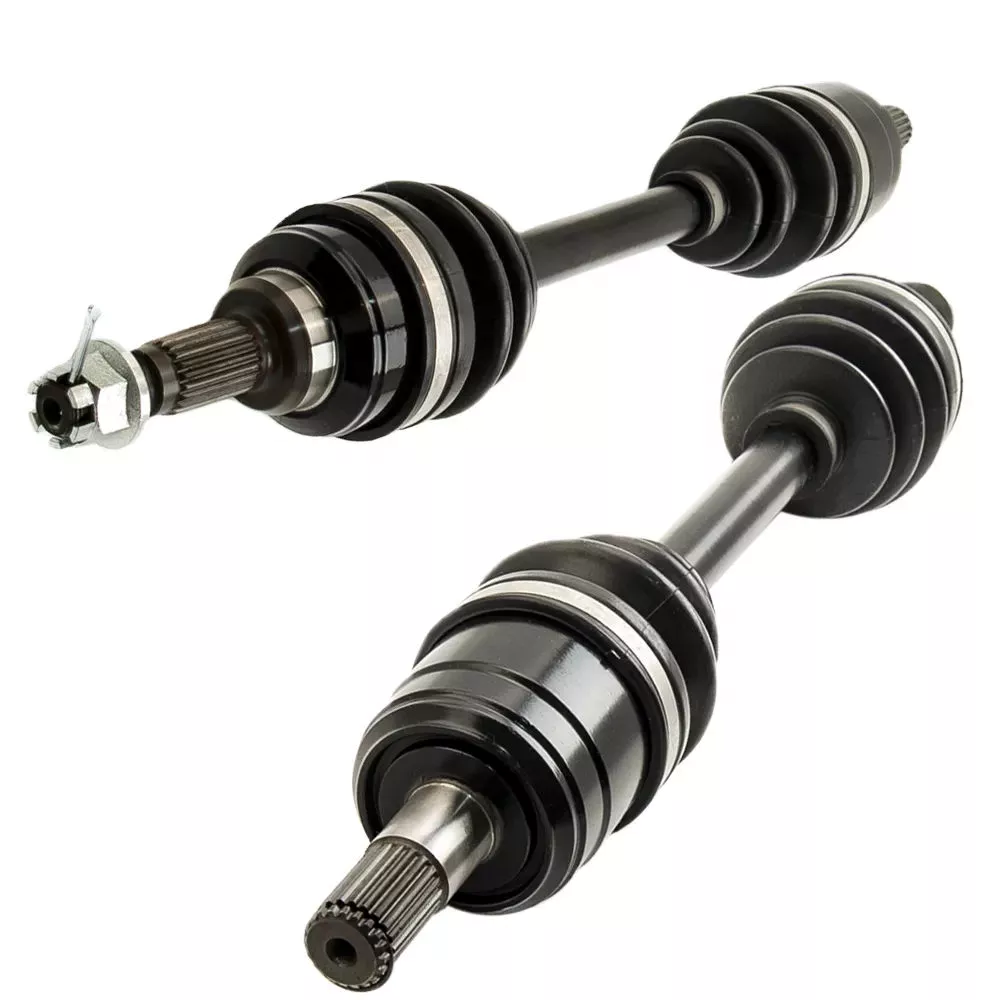

How do drive shafts handle variations in load and vibration during operation?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in load and vibration during operation by employing various mechanisms and features. These mechanisms help ensure smooth power transmission, minimize vibrations, and maintain the structural integrity of the drive shaft. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts handle load and vibration variations:
1. Material Selection and Design:
Drive shafts are typically made from materials with high strength and stiffness, such as steel alloys or composite materials. The material selection and design take into account the anticipated loads and operating conditions of the application. By using appropriate materials and optimizing the design, drive shafts can withstand the expected variations in load without experiencing excessive deflection or deformation.
2. Torque Capacity:
Drive shafts are designed with a specific torque capacity that corresponds to the expected loads. The torque capacity takes into account factors such as the power output of the driving source and the torque requirements of the driven components. By selecting a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity, variations in load can be accommodated without exceeding the drive shaft’s limits and risking failure or damage.
3. Dynamic Balancing:
During the manufacturing process, drive shafts can undergo dynamic balancing. Imbalances in the drive shaft can result in vibrations during operation. Through the balancing process, weights are strategically added or removed to ensure that the drive shaft spins evenly and minimizes vibrations. Dynamic balancing helps to mitigate the effects of load variations and reduces the potential for excessive vibrations in the drive shaft.
4. Dampers and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can incorporate dampers or vibration control mechanisms to further minimize vibrations. These devices are typically designed to absorb or dissipate vibrations that may arise from load variations or other factors. Dampers can be in the form of torsional dampers, rubber isolators, or other vibration-absorbing elements strategically placed along the drive shaft. By managing and attenuating vibrations, drive shafts ensure smooth operation and enhance overall system performance.
5. CV Joints:
Constant Velocity (CV) joints are often used in drive shafts to accommodate variations in operating angles and to maintain a constant speed. CV joints allow the drive shaft to transmit power even when the driving and driven components are at different angles. By accommodating variations in operating angles, CV joints help minimize the impact of load variations and reduce potential vibrations that may arise from changes in the driveline geometry.
6. Lubrication and Maintenance:
Proper lubrication and regular maintenance are essential for drive shafts to handle load and vibration variations effectively. Lubrication helps reduce friction between moving parts, minimizing wear and heat generation. Regular maintenance, including inspection and lubrication of joints, ensures that the drive shaft remains in optimal condition, reducing the risk of failure or performance degradation due to load variations.
7. Structural Rigidity:
Drive shafts are designed to have sufficient structural rigidity to resist bending and torsional forces. This rigidity helps maintain the integrity of the drive shaft when subjected to load variations. By minimizing deflection and maintaining structural integrity, the drive shaft can effectively transmit power and handle variations in load without compromising performance or introducing excessive vibrations.
8. Control Systems and Feedback:
In some applications, drive shafts may be equipped with control systems that actively monitor and adjust parameters such as torque, speed, and vibration. These control systems use sensors and feedback mechanisms to detect variations in load or vibrations and make real-time adjustments to optimize performance. By actively managing load variations and vibrations, drive shafts can adapt to changing operating conditions and maintain smooth operation.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in load and vibration during operation through careful material selection and design, torque capacity considerations, dynamic balancing, integration of dampers and vibration control mechanisms, utilization of CV joints, proper lubrication and maintenance, structural rigidity, and, in some cases, control systems and feedback mechanisms. By incorporating these features and mechanisms, drive shafts ensure reliable and efficient power transmission while minimizing the impact of load variations and vibrations on overall system performance.

How do drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in length and torque requirements in order to efficiently transmit rotational power. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts address these variations:
Length Variations:
Drive shafts are available in different lengths to accommodate varying distances between the engine or power source and the driven components. They can be custom-made or purchased in standardized lengths, depending on the specific application. In situations where the distance between the engine and the driven components is longer, multiple drive shafts with appropriate couplings or universal joints can be used to bridge the gap. These additional drive shafts effectively extend the overall length of the power transmission system.
Additionally, some drive shafts are designed with telescopic sections. These sections can be extended or retracted, allowing for adjustments in length to accommodate different vehicle configurations or dynamic movements. Telescopic drive shafts are commonly used in applications where the distance between the engine and the driven components may change, such as in certain types of trucks, buses, and off-road vehicles.
Torque Requirements:
Drive shafts are engineered to handle varying torque requirements based on the power output of the engine or power source and the demands of the driven components. The torque transmitted through the drive shaft depends on factors such as the engine power, load conditions, and the resistance encountered by the driven components.
Manufacturers consider torque requirements when selecting the appropriate materials and dimensions for drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, to withstand the torque loads without deformation or failure. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure it can handle the expected torque without excessive deflection or vibration.
In applications with high torque demands, such as heavy-duty trucks, industrial machinery, or performance vehicles, drive shafts may have additional reinforcements. These reinforcements can include thicker walls, cross-sectional shapes optimized for strength, or composite materials with superior torque-handling capabilities.
Furthermore, drive shafts often incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity (CV) joints. These joints allow for angular misalignment and compensate for variations in the operating angles between the engine, transmission, and driven components. They also help absorb vibrations and shocks, reducing stress on the drive shaft and enhancing its torque-handling capacity.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements through customizable lengths, telescopic sections, appropriate materials and dimensions, and the inclusion of flexible joints. By carefully considering these factors, drive shafts can efficiently and reliably transmit power while accommodating the specific needs of different applications.


editor by CX 2024-01-17
China wholesaler Factory Propeller Drive Shaft Front Rear Tail Shaft for CZPT 4runner Hilux Tundra Tacoma Land Cruiser Drive Line
Product Description
As a professional manufacturer for propeller shaft, we have +8/8822 0571 8
45710-S10-A01
12344543
27111-SC571
936-571
45710-S9A-E01
936-911
27111-AJ13D
936-034
45710-S9A-J01
936-916
27101-84C00
for MITSUBISHI/NISSAN
for TOYOTA
CARDONE
OE
CARDONE
OE
65-3009
MR580626
65-5007
37140-35180
65-6000
3401A571
65-9842
37140-35040
65-9480
37000-JM14A
65-5571
37100-3D250
65-9478
37000-S3805
65-5030
37100-34120
65-6004
37000-S4203
65-9265
37110-3D070
65-6571
37041-90062
65-9376
37110-35880
936-262
37041-90014
65-5571
37110-3D220
938-030
37300-F3600
65-5571
37100-34111
936-363
37000-7C002
65-5018
37110-3D060
938-200
37000-7C001
65-5012
37100-5712
for KOREA CAR
for HYUNDAI/KIA
CARDONE
OE
CARDONE
OE
65-3502
49571-H1031
936-211
49100-3E450
65-3503
49300-2S000
936-210
49100-3E400
65-3500
49300-0L000
936-200
49300-2P500
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO, IATF |
| Type: | Propeller Shaft/Drive Shaft |
| Application Brand: | Toyota |
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there different types of driveline configurations based on vehicle type?
Yes, there are different types of driveline configurations based on the type of vehicle. Driveline configurations vary depending on factors such as the vehicle’s propulsion system, drivetrain layout, and the number of driven wheels. Here’s a detailed explanation of the driveline configurations commonly found in different vehicle types:
1. Front-Wheel Drive (FWD):
In front-wheel drive vehicles, the driveline configuration involves the engine’s power being transmitted to the front wheels. The engine, transmission, and differential are typically integrated into a single unit called a transaxle, which is located at the front of the vehicle. This configuration simplifies the drivetrain layout, reduces weight, and improves fuel efficiency. Front-wheel drive is commonly found in passenger cars, compact cars, and some crossover SUVs.
2. Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD):
Rear-wheel drive vehicles have their driveline configuration where the engine’s power is transmitted to the rear wheels. In this setup, the engine is located at the front of the vehicle, and the drivetrain components, including the transmission and differential, are positioned at the rear. Rear-wheel drive provides better weight distribution, improved handling, and enhanced performance characteristics, making it popular in sports cars, luxury vehicles, and large trucks.
3. All-Wheel Drive (AWD) and Four-Wheel Drive (4WD):
All-wheel drive and four-wheel drive driveline configurations involve power being transmitted to all four wheels of the vehicle. These configurations provide better traction and handling in various driving conditions, particularly on slippery or off-road surfaces. AWD systems distribute power automatically between the front and rear wheels, while 4WD systems are often manually selectable and include a transfer case for shifting between 2WD and 4WD modes. AWD and 4WD configurations are commonly found in SUVs, crossovers, trucks, and off-road vehicles.
4. Front Engine, Rear-Wheel Drive (FR) and Rear Engine, Rear-Wheel Drive (RR):
In certain performance vehicles and sports cars, driveline configurations may involve a front engine with rear-wheel drive (FR) or a rear engine with rear-wheel drive (RR). FR configurations have the engine located at the front of the vehicle, transmitting power to the rear wheels. RR configurations have the engine located at the rear, driving the rear wheels. These configurations provide excellent balance, weight distribution, and handling characteristics, resulting in enhanced performance and driving dynamics.
5. Other Configurations:
There are also various specialized driveline configurations based on specific vehicle types and applications:
- Mid-Engine: Some high-performance sports cars and supercars feature a mid-engine configuration, where the engine is positioned between the front and rear axles. This configuration offers exceptional balance, handling, and weight distribution.
- Front-Engine, Front-Wheel Drive (FF): While less common, certain compact and economy cars employ a front-engine, front-wheel drive configuration. This layout simplifies packaging and interior space utilization.
- Part-Time 4WD: In certain off-road vehicles, there may be a part-time 4WD driveline configuration. These vehicles typically operate in 2WD mode but can engage 4WD when additional traction is needed.
These are some of the driveline configurations commonly found in different vehicle types. The choice of driveline configuration depends on factors such as the vehicle’s intended use, performance requirements, handling characteristics, and specific design considerations.

How do drivelines enhance the performance of different types of vehicles?
Drivelines significantly contribute to enhancing the performance of different types of vehicles by optimizing power delivery, improving traction, and tailoring the driving characteristics to suit specific needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drivelines enhance performance in various vehicle types:
1. Passenger Cars:
In passenger cars, driveline configurations, such as front-wheel drive (FWD), rear-wheel drive (RWD), and all-wheel drive (AWD), play a crucial role in performance. Here’s how drivelines enhance performance in passenger cars:
- FWD: Front-wheel drive systems provide better traction and stability, particularly in adverse weather conditions. FWD drivelines distribute weight more evenly over the front wheels, resulting in improved grip during acceleration and cornering.
- RWD: Rear-wheel drive drivelines offer better weight distribution, allowing for improved handling and balanced performance. RWD vehicles typically exhibit better acceleration and a more engaging driving experience, especially in performance-oriented cars.
- AWD: All-wheel drive drivelines deliver power to all four wheels, improving traction and stability in various driving conditions. AWD systems enhance performance by maximizing grip and providing optimal power distribution between the front and rear wheels.
2. Sports Cars and Performance Vehicles:
Driveline systems in sports cars and performance vehicles are designed to enhance acceleration, handling, and overall driving dynamics. Key features include:
- Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD): RWD drivelines are often favored in sports cars for their ability to deliver power to the rear wheels, resulting in better weight transfer during acceleration and improved handling characteristics.
- Performance-oriented AWD: Some high-performance vehicles employ advanced AWD systems that can variably distribute torque between the front and rear wheels. These systems enhance traction, stability, and cornering capabilities, allowing for superior performance on both dry and slippery surfaces.
- Torque Vectoring: Certain driveline systems incorporate torque vectoring technology, which actively varies the torque distribution between wheels. This enables precise control during cornering, reducing understeer and enhancing agility and stability.
3. Off-Road Vehicles:
Drivelines in off-road vehicles are designed to provide exceptional traction, durability, and maneuverability in challenging terrains. Key features include:
- Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) and All-Wheel Drive (AWD): 4WD and AWD drivelines are commonly used in off-road vehicles to improve traction on uneven surfaces. These drivelines distribute power to all wheels, allowing for better grip and enhanced off-road capability.
- Differential Locks: Off-road drivelines often incorporate differential locks that can be engaged to lock the wheels on an axle together. This feature ensures that power is evenly distributed to all wheels, maximizing traction and overcoming challenging obstacles.
- High Ground Clearance: Drivelines in off-road vehicles are designed to accommodate higher ground clearance, allowing for improved approach, departure, and breakover angles. This design feature enhances the vehicle’s ability to navigate over rough terrain without damaging the driveline components.
4. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Drivelines in trucks and commercial vehicles are engineered to provide high torque delivery, durability, and efficiency. Key features include:
- High Torque Handling: Drivelines in trucks and commercial vehicles are designed to handle high torque outputs from powerful engines, enabling efficient towing, hauling, and overall performance.
- Transmission Options: Drivelines in trucks often feature transmissions with multiple gear ratios, allowing drivers to select the appropriate gear for different load conditions. This enhances performance, fuel efficiency, and overall drivability.
- Efficient Power Transfer: Drivelines in commercial vehicles focus on maximizing power transfer efficiency, minimizing energy losses, and optimizing fuel economy. This is achieved through the use of efficient transmission designs, low-friction components, and advanced control systems.
5. Electric and Hybrid Vehicles:
Drivelines in electric and hybrid vehicles play a crucial role in delivering power from the electric motor(s) to the wheels. Key features include:
- Instant Torque: Electric drivelines offer instant torque delivery, providing quick acceleration andresponsive performance. This enhances the driving experience and allows for swift overtaking and merging.
- Regenerative Braking: Electric and hybrid drivelines can incorporate regenerative braking systems, which convert kinetic energy during braking into electrical energy. This improves overall efficiency and extends the vehicle’s range.
- Multi-Motor Systems: Some electric and hybrid drivelines utilize multiple motors to drive different axles or wheels independently. This enables advanced torque vectoring and enhances handling, stability, and traction control.
These are just a few examples of how drivelines enhance the performance of different types of vehicles. Driveline configurations, technologies, and engineering considerations are tailored to each vehicle type, optimizing power delivery, handling, traction, and other performance characteristics specific to their intended use and market segment.

How do drivelines handle variations in torque, speed, and angles of rotation?
Drivelines are designed to handle variations in torque, speed, and angles of rotation within a power transmission system. They incorporate specific components and mechanisms that enable the smooth and efficient transfer of power while accommodating these variations. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drivelines handle variations in torque, speed, and angles of rotation:
Variations in Torque:
Drivelines encounter variations in torque when the power requirements change, such as during acceleration, deceleration, or when encountering different loads. To handle these variations, drivelines incorporate several components:
1. Clutch: In manual transmission systems, a clutch is used to engage or disengage the engine’s power from the driveline. By partially or completely disengaging the clutch, the driveline can temporarily interrupt power transfer, allowing for smooth gear changes or vehicle stationary positions. This helps manage torque variations during shifting or when power demands change abruptly.
2. Torque Converter: Automatic transmissions employ torque converters, which are fluid couplings that transfer power from the engine to the transmission. Torque converters provide a certain amount of slip, allowing for torque multiplication and smooth power transfer. The slip in the torque converter helps absorb torque variations and dampens abrupt changes, ensuring smoother operation during acceleration or when power demands fluctuate.
3. Differential: The differential mechanism in drivelines compensates for variations in torque between the wheels, particularly during turns. When a vehicle turns, the inner and outer wheels travel different distances, resulting in different rotational speeds. The differential allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds while distributing torque to each wheel accordingly. This ensures that torque variations are managed and power is distributed effectively to optimize traction and stability.
Variations in Speed:
Drivelines also need to handle variations in rotational speed, especially when the engine operates at different RPMs or when different gear ratios are selected. The following components aid in managing speed variations:
1. Transmission: The transmission allows for the selection of different gear ratios, which influence the rotational speed of the driveline components. By changing gears, the transmission adjusts the speed at which power is transferred from the engine to the driveline. This allows the driveline to adapt to different speed requirements, whether it’s for quick acceleration or maintaining a consistent speed during cruising.
2. Gearing: Driveline systems often incorporate various gears in the transmission, differential, or axle assemblies. Gears provide mechanical advantage by altering the speed and torque relationship. By employing different gear ratios, the driveline can adjust the rotational speed and torque output to match the requirements of the vehicle under different operating conditions.
Variations in Angles of Rotation:
Drivelines must accommodate variations in angles of rotation, especially in vehicles with flexible or independent suspension systems. The following components help manage these variations:
1. Universal Joints: Universal joints, also known as U-joints, are flexible couplings used in drivelines to accommodate variations in angles and misalignments between components. They allow for smooth power transmission between the drive shaft and other components, compensating for changes in driveline angles during vehicle operation or suspension movement. Universal joints are particularly effective in handling non-linear or variable angles of rotation.
2. Constant Velocity Joints (CV Joints): CV joints are specialized joints used in drivelines, especially in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles. They allow the driveline to handle variations in angles while maintaining a constant velocity during rotation. CV joints are designed to mitigate vibrations, power losses, and potential binding or juddering that can occur due to changes in angles of rotation.
By incorporating these components and mechanisms, drivelines effectively handle variations in torque, speed, and angles of rotation. These features ensure smooth power transfer, optimal performance, and enhanced durability in various driving conditions and operating scenarios.


editor by CX 2023-10-26