Product Description
Spline Round Key Way Pin Threaded CZPT Hollow Through Hole Flat D Shape Knurling Spur Helical Worm Transmission Drive Auto Parts Gear Pinion Gearbox Axis Shaft
Features
1. High precision gear shaft for smooth, quiet operation.
2. Flexible for custom-made requests.
3. Stable transmission, low impact, vibration, and noise.
4. Heavy Load capability, more compact, but less complex.
Product Description
| Products | Spur Gear, Helical Gear, Herringbone Gear, Spiral Bevel Gear, Straight Bevel Gear, Worm Gear, Shaft, Pinion |
| Module | M0.3-M10 |
| Precision grade | DIN6, DIN7, DIN8, DIN10 |
| Pressure angle | 14.5 degree, 15 degree, 20 degree |
| Material | Medium Carbon Steel: 35#, 45# Carburizing Steel: 20CrMnTi, 20CrMnMo, 20CrMo Alloy Steel: 40Cr, 35CrMo, 42CrMo, 40CrNiMo Cast Iron: HT250, QT400 Copper, Stainless Steel, Brass, Nylon, POM, and so on |
| Heat treatment | Hardening & Tempering, Surface Quenching, Integral Quenching, Carburizing Quenching, Tempering, Normalizing, Nitriding |
| Surface treatment | Blacking, Polishing, Anodization, Chrome Plating, Zinc Plating, Nickel Plating |
| Application | Gearbox and reducer; Precision cutting machines, Lathes machines; Milling machines; Grinder machine; Automated mechanical systems; Automated warehousing systems. Gear hobbing machines, gear shapers, gear shaving machines, gear milling, gear grinding machines and many kinds of gear-related machines. |
| Machining process | Forging, Machining, Hobbing, Milling, Shaving, Grinding, Heat treatment… |
Detailed Photos
Our Advantages
Related Product
Company Profile
FAQ
Q: How to ship the worm gear to us?
A: It is available by air, sea, or train.
Q: How to pay the money?
A: T/T and L/C are preferred, with different currencies, including USD, EUR, RMB, etc.
Q: How can I know if the product is suitable for me?
A: >1ST confirm drawing and specification >2nd test sample >3rd start mass production.
Q: Can I come to your company to visit?
A: Yes, you are welcome to visit us at any time.
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Car, Gearbox |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample Worm gear with shaft
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Can drive shafts be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings?
Yes, drive shafts can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings. While there may be some differences in design and specifications based on the specific application requirements, the fundamental principles and functions of drive shafts remain applicable in both contexts. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Power Transmission:
Drive shafts serve the primary purpose of transmitting rotational power from a power source, such as an engine or motor, to driven components, which can be wheels, machinery, or other mechanical systems. This fundamental function applies to both automotive and industrial settings. Whether it’s delivering power to the wheels of a vehicle or transferring torque to industrial machinery, the basic principle of power transmission remains the same for drive shafts in both contexts.
2. Design Considerations:
While there may be variations in design based on specific applications, the core design considerations for drive shafts are similar in both automotive and industrial settings. Factors such as torque requirements, operating speeds, length, and material selection are taken into account in both cases. Automotive drive shafts are typically designed to accommodate the dynamic nature of vehicle operation, including variations in speed, angles, and suspension movement. Industrial drive shafts, on the other hand, may be designed for specific machinery and equipment, taking into consideration factors such as load capacity, operating conditions, and alignment requirements. However, the underlying principles of ensuring proper dimensions, strength, and balance are essential in both automotive and industrial drive shaft designs.
3. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is influenced by the specific requirements of the application, whether in automotive or industrial settings. In automotive applications, drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, durability, and ability to withstand varying operating conditions. In industrial settings, drive shafts may be made from a broader range of materials, including steel, stainless steel, or even specialized alloys, depending on factors such as load capacity, corrosion resistance, or temperature tolerance. The material selection is tailored to meet the specific needs of the application while ensuring efficient power transfer and durability.
4. Joint Configurations:
Both automotive and industrial drive shafts may incorporate various joint configurations to accommodate the specific requirements of the application. Universal joints (U-joints) are commonly used in both contexts to allow for angular movement and compensate for misalignment between the drive shaft and driven components. Constant velocity (CV) joints are also utilized, particularly in automotive drive shafts, to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and accommodate varying operating angles. These joint configurations are adapted and optimized based on the specific needs of automotive or industrial applications.
5. Maintenance and Service:
While maintenance practices may vary between automotive and industrial settings, the importance of regular inspection, lubrication, and balancing remains crucial in both cases. Both automotive and industrial drive shafts benefit from periodic maintenance to ensure optimal performance, identify potential issues, and prolong the lifespan of the drive shafts. Lubrication of joints, inspection for wear or damage, and balancing procedures are common maintenance tasks for drive shafts in both automotive and industrial applications.
6. Customization and Adaptation:
Drive shafts can be customized and adapted to meet the specific requirements of various automotive and industrial applications. Manufacturers often offer drive shafts with different lengths, diameters, and joint configurations to accommodate a wide range of vehicles or machinery. This flexibility allows for the adaptation of drive shafts to suit the specific torque, speed, and dimensional requirements of different applications, whether in automotive or industrial settings.
In summary, drive shafts can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings by considering the specific requirements of each application. While there may be variations in design, materials, joint configurations, and maintenance practices, the fundamental principles of power transmission, design considerations, and customization options remain applicable in both contexts. Drive shafts play a crucial role in both automotive and industrial applications, enabling efficient power transfer and reliable operation in a wide range of mechanical systems.
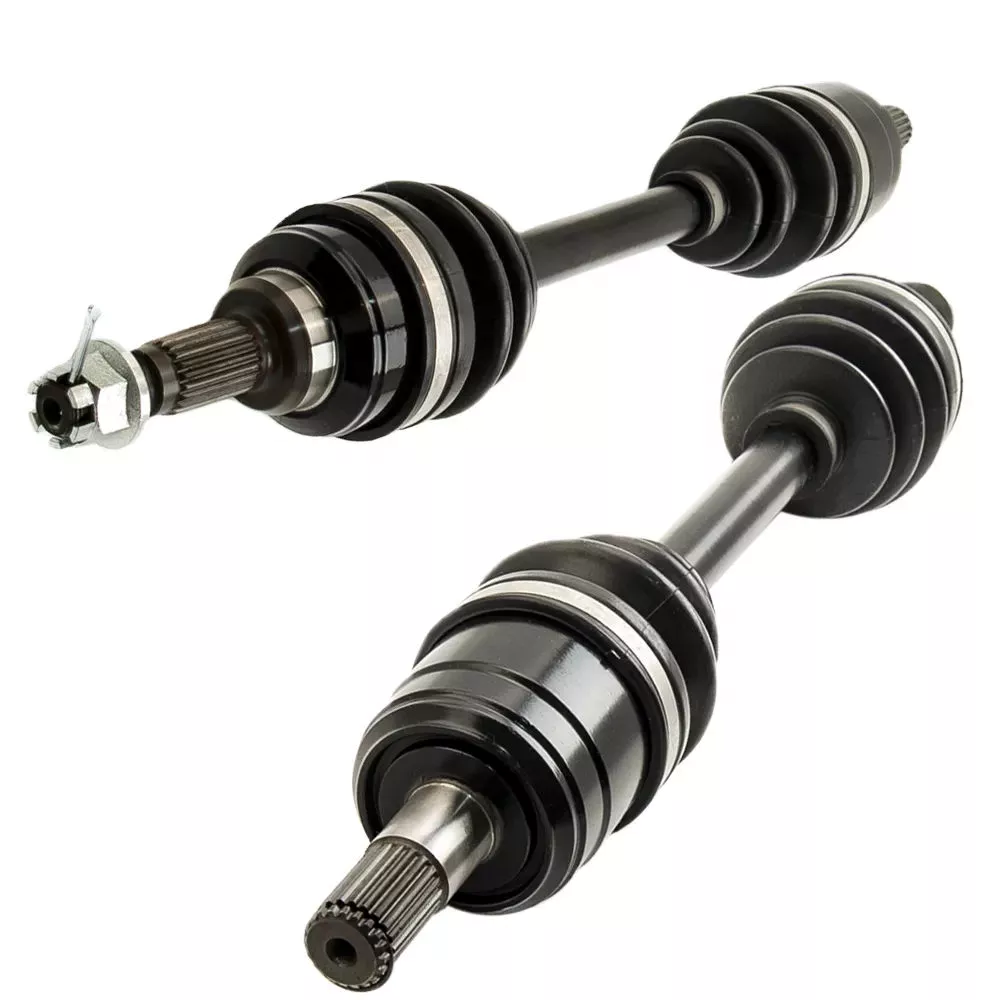

How do drive shafts handle variations in load and vibration during operation?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in load and vibration during operation by employing various mechanisms and features. These mechanisms help ensure smooth power transmission, minimize vibrations, and maintain the structural integrity of the drive shaft. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts handle load and vibration variations:
1. Material Selection and Design:
Drive shafts are typically made from materials with high strength and stiffness, such as steel alloys or composite materials. The material selection and design take into account the anticipated loads and operating conditions of the application. By using appropriate materials and optimizing the design, drive shafts can withstand the expected variations in load without experiencing excessive deflection or deformation.
2. Torque Capacity:
Drive shafts are designed with a specific torque capacity that corresponds to the expected loads. The torque capacity takes into account factors such as the power output of the driving source and the torque requirements of the driven components. By selecting a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity, variations in load can be accommodated without exceeding the drive shaft’s limits and risking failure or damage.
3. Dynamic Balancing:
During the manufacturing process, drive shafts can undergo dynamic balancing. Imbalances in the drive shaft can result in vibrations during operation. Through the balancing process, weights are strategically added or removed to ensure that the drive shaft spins evenly and minimizes vibrations. Dynamic balancing helps to mitigate the effects of load variations and reduces the potential for excessive vibrations in the drive shaft.
4. Dampers and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can incorporate dampers or vibration control mechanisms to further minimize vibrations. These devices are typically designed to absorb or dissipate vibrations that may arise from load variations or other factors. Dampers can be in the form of torsional dampers, rubber isolators, or other vibration-absorbing elements strategically placed along the drive shaft. By managing and attenuating vibrations, drive shafts ensure smooth operation and enhance overall system performance.
5. CV Joints:
Constant Velocity (CV) joints are often used in drive shafts to accommodate variations in operating angles and to maintain a constant speed. CV joints allow the drive shaft to transmit power even when the driving and driven components are at different angles. By accommodating variations in operating angles, CV joints help minimize the impact of load variations and reduce potential vibrations that may arise from changes in the driveline geometry.
6. Lubrication and Maintenance:
Proper lubrication and regular maintenance are essential for drive shafts to handle load and vibration variations effectively. Lubrication helps reduce friction between moving parts, minimizing wear and heat generation. Regular maintenance, including inspection and lubrication of joints, ensures that the drive shaft remains in optimal condition, reducing the risk of failure or performance degradation due to load variations.
7. Structural Rigidity:
Drive shafts are designed to have sufficient structural rigidity to resist bending and torsional forces. This rigidity helps maintain the integrity of the drive shaft when subjected to load variations. By minimizing deflection and maintaining structural integrity, the drive shaft can effectively transmit power and handle variations in load without compromising performance or introducing excessive vibrations.
8. Control Systems and Feedback:
In some applications, drive shafts may be equipped with control systems that actively monitor and adjust parameters such as torque, speed, and vibration. These control systems use sensors and feedback mechanisms to detect variations in load or vibrations and make real-time adjustments to optimize performance. By actively managing load variations and vibrations, drive shafts can adapt to changing operating conditions and maintain smooth operation.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in load and vibration during operation through careful material selection and design, torque capacity considerations, dynamic balancing, integration of dampers and vibration control mechanisms, utilization of CV joints, proper lubrication and maintenance, structural rigidity, and, in some cases, control systems and feedback mechanisms. By incorporating these features and mechanisms, drive shafts ensure reliable and efficient power transmission while minimizing the impact of load variations and vibrations on overall system performance.

How do drive shafts contribute to transferring rotational power in various applications?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in transferring rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in various applications. Whether it’s in vehicles or machinery, drive shafts enable efficient power transmission and facilitate the functioning of different systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to transferring rotational power:
1. Vehicle Applications:
In vehicles, drive shafts are responsible for transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move. The drive shaft connects the gearbox or transmission output shaft to the differential, which further distributes the power to the wheels. As the engine generates torque, it is transferred through the drive shaft to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward. This power transfer allows the vehicle to accelerate, maintain speed, and overcome resistance, such as friction and inclines.
2. Machinery Applications:
In machinery, drive shafts are utilized to transfer rotational power from the engine or motor to various driven components. For example, in industrial machinery, drive shafts may be used to transmit power to pumps, generators, conveyors, or other mechanical systems. In agricultural machinery, drive shafts are commonly employed to connect the power source to equipment such as harvesters, balers, or irrigation systems. Drive shafts enable these machines to perform their intended functions by delivering rotational power to the necessary components.
3. Power Transmission:
Drive shafts are designed to transmit rotational power efficiently and reliably. They are capable of transferring substantial amounts of torque from the engine to the wheels or driven components. The torque generated by the engine is transmitted through the drive shaft without significant power losses. By maintaining a rigid connection between the engine and the driven components, drive shafts ensure that the power produced by the engine is effectively utilized in performing useful work.
4. Flexible Coupling:
One of the key functions of drive shafts is to provide a flexible coupling between the engine/transmission and the wheels or driven components. This flexibility allows the drive shaft to accommodate angular movement and compensate for misalignment between the engine and the driven system. In vehicles, as the suspension system moves or the wheels encounter uneven terrain, the drive shaft adjusts its length and angle to maintain a constant power transfer. This flexibility helps prevent excessive stress on the drivetrain components and ensures smooth power transmission.
5. Torque and Speed Transmission:
Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). Drive shafts must be capable of handling the torque requirements of the application without excessive twisting or bending. Additionally, they need to maintain the desired rotational speed to ensure the proper functioning of the driven components. Proper design, material selection, and balancing of the drive shafts contribute to efficient torque and speed transmission.
6. Length and Balance:
The length and balance of drive shafts are critical factors in their performance. The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven components. It should be appropriately sized to avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Drive shafts are carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can affect the overall performance, comfort, and longevity of the drivetrain system.
7. Safety and Maintenance:
Drive shafts require proper safety measures and regular maintenance. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts, reducing the risk of injury. Safety shields or guards may also be installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards. Regular maintenance includes inspecting the drive shaft for wear, damage, or misalignment, and ensuring proper lubrication of the U-joints. These measures help prevent failures, ensure optimal performance, and extend the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, drive shafts play a vital role in transferring rotational power in various applications. Whether in vehicles or machinery, drive shafts enable efficient power transmission from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. They provide a flexible coupling, handle torque and speed transmission, accommodate angular movement, and contribute to the safety and maintenance of the system. By effectively transferring rotational power, drive shafts facilitate the functioning and performance of vehicles and machinery in numerous industries.


editor by CX 2023-12-13
China High efficiency hollow shaft worm speed gearbox reducer for servo drives electric drive shaft carrier bearing
Guarantee: 1year, One year,matter to proper procedure & set up
Applicable Industries: Production Plant, Machinery Fix Outlets, Home Use, Printing Retailers, Construction works , Energy & Mining, Marketing Business
Bodyweight (KG): 4 KG
Tailored support: OEM
Gearing Arrangement: Worm
Output Torque: 2.6—1195N.M
Input Velocity: 1400rpm
Output Speed: fourteen-280rpm
Coloration: Blue,Silver or Customised
Reduction Ratio: 5,7.5,ten,fifteen,20,twenty five,30,40,50,sixty,80,a hundred
Entire body material: Aluminium alloy & solid iron
Lubricant oil: Synthetic & Mineral
Oil seals: SKF,NAK & TTO
OEM & customised: Available
Packaging Information: 1 personal computer / carton,several cartons / wooden pallet
Port: ZheJiang ,HangZhou
Items Description SMRV Series WORMGear Models Highoutput torque Products Description Technical overall performance and assortment reference
| Motor electrical power | Design | speed ratio | output pace | output toruqe |
| .25kw 1400rpm | RV075 | 60 | 24rpm | 68.0N.M |
| RV075 | 80 | 18rpm | 80.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 100 | 14rpm | 94.0N.M | |
| .37kw 1400rpm | RV075 | 40 | 35rpm | 74.0N.M |
| RV075 | 50 | 28rpm | 88.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 60 | 24rpm | 97.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 80 | 18rpm | 119.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 100 | 14rpm | 139.0N.M | |
| .55kw 1400rpm | RV075 | 25 | 56rpm | 76.0N.M |
| RV075 | 30 | 47rpm | 87.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 40 | 35rpm | 108.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 50 | 28rpm | 128.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 60 | 24rpm | 144.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 80 | 18rpm | 177.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 100 | 14rpm | 206.0N.M | |
| .75kw 1400rpm | RV075 | 15 | 94rpm | 66.0N.M |
| RV075 | 20 | 70rpm | 85.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 25 | 56rpm | 101.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 30 | 47rpm | 117.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 40 | 35rpm | 147.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 50 | 28rpm | 174.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 60 | 24rpm | 196.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 80 | 18rpm | 250.0N.M | |
| 1.1kw 1400rpm | RV075 | 10 | 140rpm | 66.0N.M |
| RV075 | 15 | 94rpm | 95.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 20 | 70rpm | 122.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 25 | 56rpm | 148.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 30 | 47rpm | 171.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 40 | 35rpm | 216.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 50 | 28rpm | 263.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 60 | 24rpm | 297.0N.M | |
| one.5kw 1400rpm | RV075 | 7.5 | 186rpm | 68.0N.M |
| RV075 | 10 | 140rpm | 89.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 15 | 94rpm | 129.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 20 | 70rpm | 166.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 25 | 56rpm | 202.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 30 | 47rpm | 233.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 40 | 35rpm | 299.0N.M | |
| two.2kw 1400rpm | RV075 | 7.five | 186rpm | 99.0N.M |
| RV075 | 10 | 140rpm | 131.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 15 | 94rpm | 189.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 20 | 70rpm | 249.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 25 | 56rpm | 304.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 30 | 47rpm | 247.0N.M | |
| three.0kw 1400rpm | RV075 | 7.5 | 186rpm | 135.0N.M |
| RV075 | 10 | 140rpm | 178.0N.M | |
| RV075 | 15 | 94rpm | 258.0N.M | |
| 4.0kw 1400rpm | RV075 | 7.5 | 186rpm | 180.0N.M |
| RV075 | 10 | 140rpm | 237.0N.M |
| Merchandise identify | RV075 worm gear pace reducer/worm gearbox |
| Ratio | 7.5,ten,15,twenty,25,thirty,forty,50,60,80,100 |
| Electricity | 0.25~4. KW |
| Coloration | Blue/Silver/Black or on Ask for |
| Fat | 9 Kg |
| Material | Housing : Aluminum alloy |
| The equipment is produced of carburized 20CrMnTi with very good use resistance and no noise | |
| The wormwheel is Wheelhub forged iron QT500 and bronze ZQSn10-one | |
| The wormshaft:steel 20Cr with a carburized area and hardness of HRC60 | |
| One unit input variations | SMRV : fitted for motor flanged coupling |
| SMRV-E : motor flanged coupling with worm extension shaft | |
| SRV : with input shaft | |
| SRV-E : with double extension worm shaft | |
| Ideal motor pole | 2pole,4pole,6pole |
| Inch dimension | Available |
| Private customization | Available |
| Extra services | OEM |
| Top quality Assurance | 1 calendar year |
| Features | High precision, stable transmission and massive output torque.Also meens higher good quality, lengthy services lifestyle. |
| There are several cooling fins to comprehend quick warmth dissipation | |
| Suitable for omni-directional set up | |
| Can be effortlessly mounted with a variety of accessories like torque arms, distinct varieties of flanges, shafts and so on | |
| Good rust resistance |
How to Replace the Drive Shaft
Several different functions in a vehicle are critical to its functioning, but the driveshaft is probably the part that needs to be understood the most. A damaged or damaged driveshaft can damage many other auto parts. This article will explain how this component works and some of the signs that it may need repair. This article is for the average person who wants to fix their car on their own but may not be familiar with mechanical repairs or even driveshaft mechanics. You can click the link below for more information.
Repair damaged driveshafts
If you own a car, you should know that the driveshaft is an integral part of the vehicle’s driveline. They ensure efficient transmission of power from the engine to the wheels and drive. However, if your driveshaft is damaged or cracked, your vehicle will not function properly. To keep your car safe and running at peak efficiency, you should have it repaired as soon as possible. Here are some simple steps to replace the drive shaft.
First, diagnose the cause of the drive shaft damage. If your car is making unusual noises, the driveshaft may be damaged. This is because worn bushings and bearings support the drive shaft. Therefore, the rotation of the drive shaft is affected. The noise will be squeaks, dings or rattles. Once the problem has been diagnosed, it is time to repair the damaged drive shaft.
Professionals can repair your driveshaft at relatively low cost. Costs vary depending on the type of drive shaft and its condition. Axle repairs can range from $300 to $1,000. Labor is usually only around $200. A simple repair can cost between $150 and $1700. You’ll save hundreds of dollars if you’re able to fix the problem yourself. You may need to spend a few more hours educating yourself about the problem before handing it over to a professional for proper diagnosis and repair.
The cost of repairing a damaged driveshaft varies by model and manufacturer. It can cost as much as $2,000 depending on parts and labor. While labor costs can vary, parts and labor are typically around $70. On average, a damaged driveshaft repair costs between $400 and $600. However, these parts can be more expensive than that. If you don’t want to spend money on unnecessarily expensive repairs, you may need to pay a little more.
Learn how drive shafts work
While a car engine may be one of the most complex components in your vehicle, the driveshaft has an equally important job. The driveshaft transmits the power of the engine to the wheels, turning the wheels and making the vehicle move. Driveshaft torque refers to the force associated with rotational motion. Drive shafts must be able to withstand extreme conditions or they may break. Driveshafts are not designed to bend, so understanding how they work is critical to the proper functioning of the vehicle.
The drive shaft includes many components. The CV connector is one of them. This is the last stop before the wheels spin. CV joints are also known as “doughnut” joints. The CV joint helps balance the load on the driveshaft, the final stop between the engine and the final drive assembly. Finally, the axle is a single rotating shaft that transmits power from the final drive assembly to the wheels.
Different types of drive shafts have different numbers of joints. They transmit torque from the engine to the wheels and must accommodate differences in length and angle. The drive shaft of a front-wheel drive vehicle usually includes a connecting shaft, an inner constant velocity joint and an outer fixed joint. They also have anti-lock system rings and torsional dampers to help them run smoothly. This guide will help you understand the basics of driveshafts and keep your car in good shape.
The CV joint is the heart of the driveshaft, it enables the wheels of the car to move at a constant speed. The connector also helps transmit power efficiently. You can learn more about CV joint driveshafts by looking at the top 3 driveshaft questions
The U-joint on the intermediate shaft may be worn or damaged. Small deviations in these joints can cause slight vibrations and wobble. Over time, these vibrations can wear out drivetrain components, including U-joints and differential seals. Additional wear on the center support bearing is also expected. If your driveshaft is leaking oil, the next step is to check your transmission.
The drive shaft is an important part of the car. They transmit power from the engine to the transmission. They also connect the axles and CV joints. When these components are in good condition, they transmit power to the wheels. If you find them loose or stuck, it can cause the vehicle to bounce. To ensure proper torque transfer, your car needs to stay on the road. While rough roads are normal, bumps and bumps are common.
Common signs of damaged driveshafts
If your vehicle vibrates heavily underneath, you may be dealing with a faulty propshaft. This issue limits your overall control of the vehicle and cannot be ignored. If you hear this noise frequently, the problem may be the cause and should be diagnosed as soon as possible. Here are some common symptoms of a damaged driveshaft. If you experience this noise while driving, you should have your vehicle inspected by a mechanic.
A clanging sound can also be one of the signs of a damaged driveshaft. A ding may be a sign of a faulty U-joint or center bearing. This can also be a symptom of worn center bearings. To keep your vehicle safe and functioning properly, it is best to have your driveshaft inspected by a certified mechanic. This can prevent serious damage to your car.
A worn drive shaft can cause difficulty turning, which can be a major safety issue. Fortunately, there are many ways to tell if your driveshaft needs service. The first thing you can do is check the u-joint itself. If it moves too much or too little in any direction, it probably means your driveshaft is faulty. Also, rust on the bearing cap seals may indicate a faulty drive shaft.
The next time your car rattles, it might be time for a mechanic to check it out. Whether your vehicle has a manual or automatic transmission, the driveshaft plays an important role in your vehicle’s performance. When one or both driveshafts fail, it can make the vehicle unsafe or impossible to drive. Therefore, you should have your car inspected by a mechanic as soon as possible to prevent further problems.
Your vehicle should also be regularly lubricated with grease and chain to prevent corrosion. This will prevent grease from escaping and causing dirt and grease to build up. Another common sign is a dirty driveshaft. Make sure your phone is free of debris and in good condition. Finally, make sure the driveshaft chain and cover are in place. In most cases, if you notice any of these common symptoms, your vehicle’s driveshaft should be replaced.
Other signs of a damaged driveshaft include uneven wheel rotation, difficulty turning the car, and increased drag when trying to turn. A worn U-joint also inhibits the ability of the steering wheel to turn, making it more difficult to turn. Another sign of a faulty driveshaft is the shuddering noise the car makes when accelerating. Vehicles with damaged driveshafts should be inspected as soon as possible to avoid costly repairs.


editor by czh
High qualtiy best price SMR Shaft Mounted helical speed reducer worm gearbox 40 bevel gear box shaft drive unit txt shaft mounted gear speed reducer supplier factory manufacturer & exporter in China

EPG was awarded with “famous product of Zhejiang Province” and “famous brand of Zhejiang Province”.
Overview
Quick Details
Applicable Industries: :
Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Repair Shops, txt shaft mounted gear speed reducer
Gearing Arrangement: :
Helical
Output Torque: :
max 8000NM
Input Speed: :
1440
Output Speed: :
72, 110, 288
Place of Origin:Zhejiang, China Brand Name: :
OEM
Model Number: :
SMR
Rated Power: :
2.68~134.2
color of Shaft Mounted speed reducer: :
green blue gray
Supply Ability
Supply Ability: : 5000 Piece/Pieces per Month
Packaging & Delivery
Packaging Details: standard export packing and wood pallets packing Port: Shanghai or Ningbo Lead Time : :
| Quantity(Pieces) | 1 – 5000 | >5000 |
| Est. Time(days) | 30 | To be negotiated |
Online Customization

Product Description
Product Description
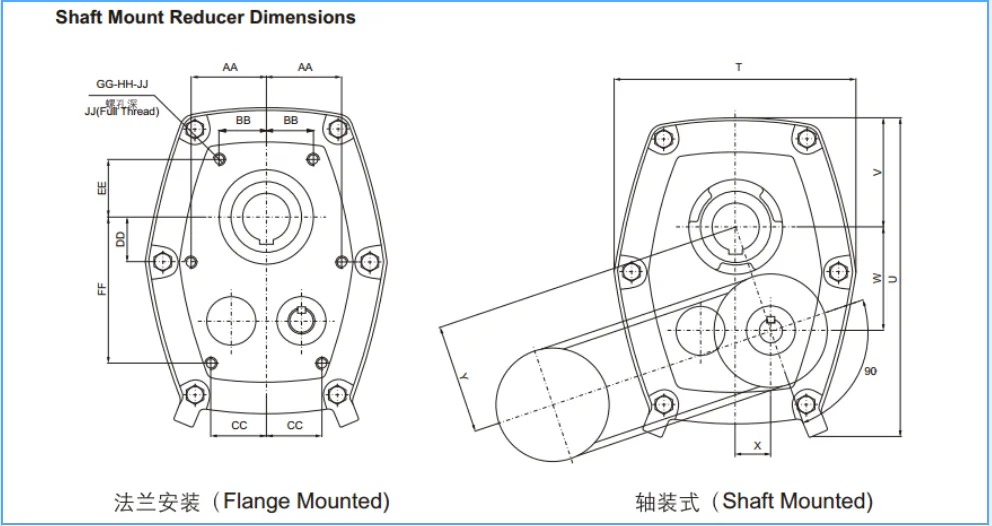
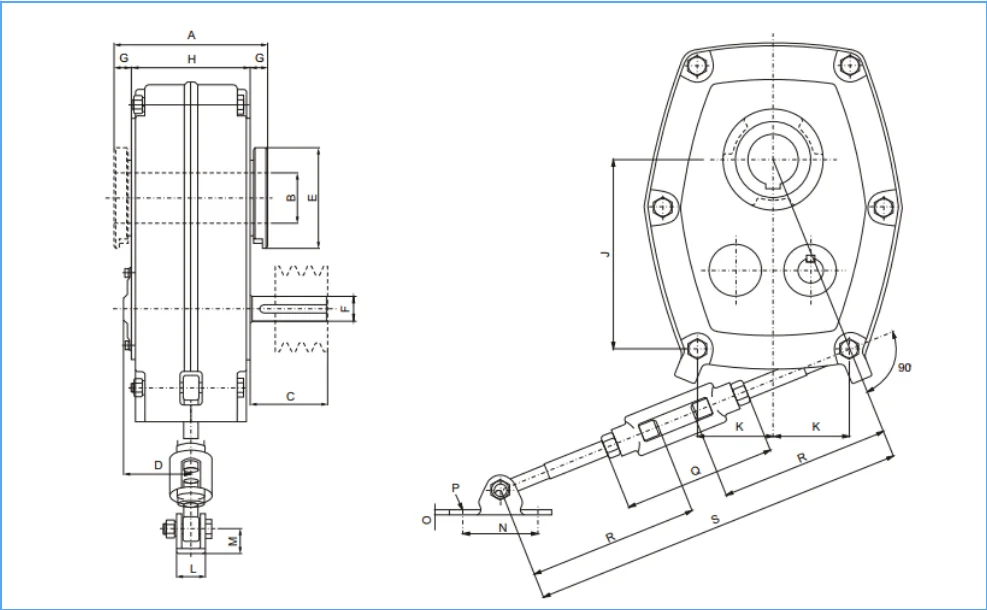
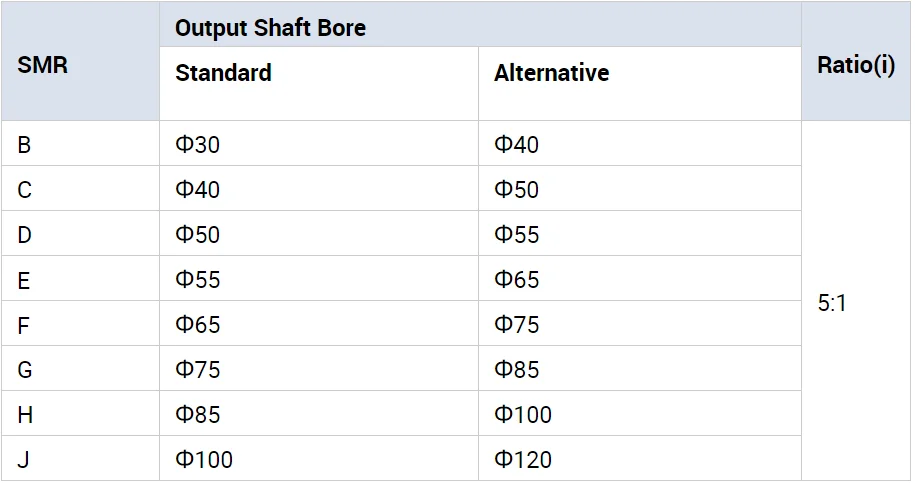
SMR Metric Series
Sizae: B-J
Ratio: 5:1, 13:1, 20:1
Maximum Output Torque: 8000 Nm
SMR Shafted mounted gear speed reducer:
1) Shafted mounted gear unit for conveyer systems
2) All gears are heat treated and fixed to achieve low noise and high output
3) Mounting dimensions are interchangeable with Fene
Product Paramenters
Product Paramenters
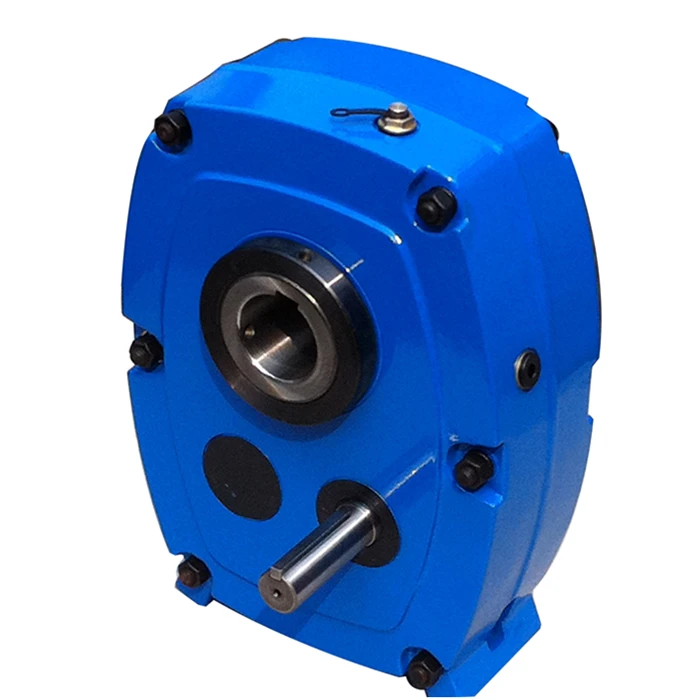
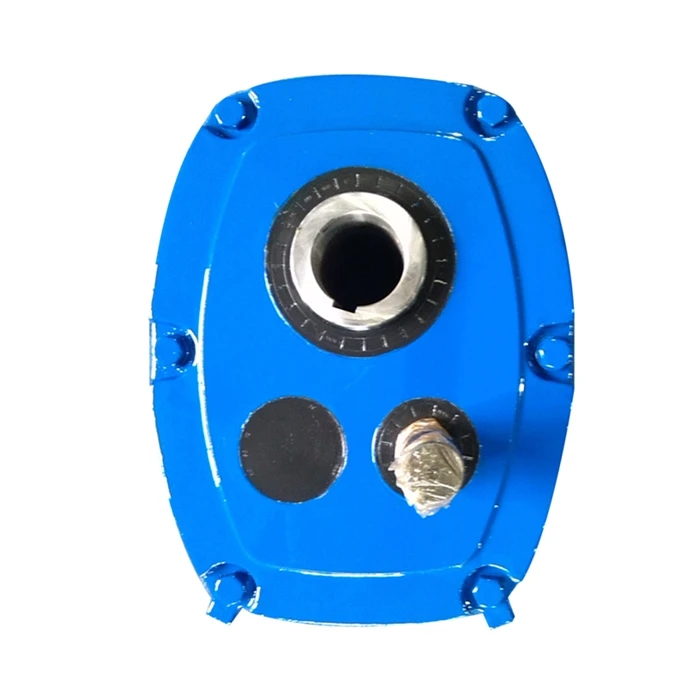









Related Products
RelaFURTHERMORE, WE CAN PRODUCE CUSTOMIZED VARIATORS, GEARED MOTORS, ELECTRIC MOTORS AND OTHER HYDRAULIC PRODUCTS ACCORDING TO CUSTOMERS’ DRAWINGS.ted Products
Product packaging
Product pacOne aspect of our application consulting is that we have been collecting and combining the experience in chain and sprocket applications in various areas for decades. This is particularly interesting for us whenever customers approach us with some exceeding and challenging requirements.kaging

FAQ
FAQ
Q: Are you trading company or manufacturer ?
A: HZPT group consists in 3 factories and 2 abroad sales cooperations.we are making vacuum pumps,air compressors and gearboxes.
Q: How long is your delivery time ? What is your terms of payment ?
A: Generally it is 30-45 days. The time may vary depending on the product and the level of customization. For standard products,
the payment is: 30% T/T in advance ,balance before shippment.,for customized products,50% downpayment is requested normally.
Q: What is the exact MOQ or price for your product ?
A: As an OEM company, we can provide and adapt our products to a wide range of needs.Thus, MOQ and price may greatly vary with detail size, material and further specifications;when you place orders,pleasure contact us in advance to communicate all details




Good worm drive gearbox with motor Cheap China in Johannesburg South Africa Quality 250W 350W 500W Ebike Rear DC Geared Motor for Electric Bike Conversion Kit with top quality

We – EPG Group the biggest gearbox & motors , couplings and gears factory in China with 5 different branches. For more details: Mobile/whatsapp/telegram/Kakao us at: 0086~13 571 88828 13858117778 571 88828
Good Quality 250W 350W 500W Ebike Rear DC Geared Motor for Electric Bike Conversion Kit
100G E-Bike Motor is simple, smart and high-torque. The key features different with others are as below:
1. Simple
Patented structure, integrated with PAS sensor
2. Smart Power
Providing smoothly launching and intelligent brake detection
3. High Torque
Providing uphill enhance and strong power
4. Wide Adaptability
Suitable for types of bikes (mountain bike, road bike & racing bike) and a variety of wheel sizes
SPECIFICATION
Application
PACKING AND DELIVERY
Packing material: Good carton box with foam
Packing size:
16”: 40*40*25cm
20″: 50*50*25cm
24″: 55*55*25cm
26″: 60*60*25cm
28″700c 29″: 65*65*25cm
Delivery:
We usually ship sample by express , bulk order by sea
The delivery time is 7 days for sample , and 15-30days for bulk
FAQ
1. Q:Can I place sample orders?
A: Yes, but an extra sample cost would be required depends on the product you choose.
2. Q: What’s your delivery time?
A: For sample we usually delivery in 7 days after receiving your deposit if there aren’t any special requests. And for quanitties the time would be longer.
3. Q: What’s your payment term?
A: T/T 30% deposit before production and 70% balance before shipping or getting the copy of B/L.
4. Q: What’s your warranty term?
A: We offer 1 year warranty for battery and 2 year warranty for other parts.
5. Q: Do you have products in stock?
A: Yes, we have some common parts in stock to ensure the delivery time.
6. Q: How do you control the quality?
A: We have QC people for items test at the end of production. Before the shipment, each part would be fully tested.
7. Q: OEM is possible or not?
A: Yes.
Any questions, please feel free to contact us.
The use of original equipment manufacturer’s (OEM) part numbers or trademarks , e.g. CASE® and John Deere® are for reference purposes only and for indicating product use and compatibility. Our company and the listed replacement parts contained herein are not sponsored, approved, or manufactured by the OEM.

