Product Description
You can kindly find the specification details below:
HangZhou Mastery Machinery Technology Co., LTD helps manufacturers and brands fulfill their machinery parts by precision manufacturing. High precision machinery products like the shaft, worm screw, bushing, couplings, joints……Our products are used widely in electronic motors, the main shaft of the engine, the transmission shaft in the gearbox, couplers, printers, pumps, drones, and so on. They cater to different industries, including automotive, industrial, power tools, garden tools, healthcare, smart home, etc.
Mastery caters to the industrial industry by offering high-level Cardan shafts, pump shafts, and a bushing that come in different sizes ranging from diameter 3mm-50mm. Our products are specifically formulated for transmissions, robots, gearboxes, industrial fans, and drones, etc.
Mastery factory currently has more than 100 main production equipment such as CNC lathe, CNC machining center, CAM Automatic Lathe, grinding machine, hobbing machine, etc. The production capacity can be up to 5-micron mechanical tolerance accuracy, automatic wiring machine processing range covering 3mm-50mm diameter bar.
Key Specifications:
| Name | Shaft/Motor Shaft/Drive Shaft/Gear Shaft/Pump Shaft/Worm Screw/Worm Gear/Bushing/Ring/Joint/Pin |
| Material | 40Cr/35C/GB45/70Cr/40CrMo |
| Process | Machining/Lathing/Milling/Drilling/Grinding/Polishing |
| Size | 2-400mm(Customized) |
| Diameter | φ12(Customized) |
| Diameter Tolerance | 0.008mm |
| Roundness | 0.01mm |
| Roughness | Ra0.4 |
| Straightness | 0.01mm |
| Hardness | Customized |
| Length | 32mm(Customized) |
| Heat Treatment | Customized |
| Surface treatment | Coating/Ni plating/Zn plating/QPQ/Carbonization/Quenching/Black Treatment/Steaming Treatment/Nitrocarburizing/Carbonitriding |
Quality Management:
- Raw Material Quality Control: Chemical Composition Analysis, Mechanical Performance Test, ROHS, and Mechanical Dimension Check
- Production Process Quality Control: Full-size inspection for the 1st part, Critical size process inspection, SPC process monitoring
- Lab ability: CMM, OGP, XRF, Roughness meter, Profiler, Automatic optical inspector
- Quality system: ISO9001, IATF 16949, ISO14001
- Eco-Friendly: ROHS, Reach.
Packaging and Shipping:
Throughout the entire process of our supply chain management, consistent on-time delivery is vital and very important for the success of our business.
Mastery utilizes several different shipping methods that are detailed below:
For Samples/Small Q’ty: By Express Services or Air Fright.
For Formal Order: By Sea or by air according to your requirement.
Mastery Services:
- One-Stop solution from idea to product/ODM&OEM acceptable
- Individual research and sourcing/purchasing tasks
- Individual supplier management/development, on-site quality check projects
- Muti-varieties/small batch/customization/trial orders are acceptable
- Flexibility on quantity/Quick samples
- Forecast and raw material preparation in advance are negotiable
- Quick quotes and quick responses
General Parameters:
If you are looking for a reliable machinery product partner, you can rely on Mastery. Work with us and let us help you grow your business using our customizable and affordable products. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with drive shafts?
While drive shafts are widely used and offer several advantages, they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered. Here’s a detailed explanation of the limitations and disadvantages associated with drive shafts:
1. Length and Misalignment Constraints:
Drive shafts have a maximum practical length due to factors such as material strength, weight considerations, and the need to maintain rigidity and minimize vibrations. Longer drive shafts can be prone to increased bending and torsional deflection, leading to reduced efficiency and potential driveline vibrations. Additionally, drive shafts require proper alignment between the driving and driven components. Misalignment can cause increased wear, vibrations, and premature failure of the drive shaft or its associated components.
2. Limited Operating Angles:
Drive shafts, especially those using U-joints, have limitations on operating angles. U-joints are typically designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and operating beyond these limits can result in reduced efficiency, increased vibrations, and accelerated wear. In applications requiring large operating angles, constant velocity (CV) joints are often used to maintain a constant speed and accommodate greater angles. However, CV joints may introduce higher complexity and cost compared to U-joints.
3. Maintenance Requirements:
Drive shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection, lubrication of joints, and balancing if necessary. Failure to perform routine maintenance can lead to increased wear, vibrations, and potential driveline issues. Maintenance requirements should be considered in terms of time and resources when using drive shafts in various applications.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Drive shafts can generate noise and vibrations, especially at high speeds or when operating at certain resonant frequencies. Imbalances, misalignment, worn joints, or other factors can contribute to increased noise and vibrations. These vibrations may affect the comfort of vehicle occupants, contribute to component fatigue, and require additional measures such as dampers or vibration isolation systems to mitigate their effects.
5. Weight and Space Constraints:
Drive shafts add weight to the overall system, which can be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications, such as automotive or aerospace industries. Additionally, drive shafts require physical space for installation. In compact or tightly packaged equipment or vehicles, accommodating the necessary drive shaft length and clearances can be challenging, requiring careful design and integration considerations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Drive shafts, depending on their design, materials, and manufacturing processes, can involve significant costs. Customized or specialized drive shafts tailored to specific equipment requirements may incur higher expenses. Additionally, incorporating advanced joint configurations, such as CV joints, can add complexity and cost to the drive shaft system.
7. Inherent Power Loss:
Drive shafts transmit power from the driving source to the driven components, but they also introduce some inherent power loss due to friction, bending, and other factors. This power loss can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in long drive shafts or applications with high torque requirements. It is important to consider power loss when determining the appropriate drive shaft design and specifications.
8. Limited Torque Capacity:
While drive shafts can handle a wide range of torque loads, there are limits to their torque capacity. Exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a drive shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in downtime and potential damage to other driveline components. It is crucial to select a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity for the intended application.
Despite these limitations and disadvantages, drive shafts remain a widely used and effective means of power transmission in various industries. Manufacturers continuously work to address these limitations through advancements in materials, design techniques, joint configurations, and balancing processes. By carefully considering the specific application requirements and potential drawbacks, engineers and designers can mitigate the limitations and maximize the benefits of drive shafts in their respective systems.

What safety precautions should be followed when working with drive shafts?
Working with drive shafts requires adherence to specific safety precautions to prevent accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. Drive shafts are critical components of a vehicle or machinery’s driveline system and can pose hazards if not handled properly. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be followed when working with drive shafts:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment when working with drive shafts. This may include safety goggles, gloves, steel-toed boots, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential injuries from flying debris, sharp edges, or accidental contact with moving parts.
2. Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
Before working on a drive shaft, ensure that the power source is properly locked out and tagged out. This involves isolating the power supply, such as shutting off the engine or disconnecting the electrical power, and securing it with a lockout/tagout device. This prevents accidental engagement of the drive shaft while maintenance or repair work is being performed.
3. Vehicle or Equipment Support:
When working with drive shafts in vehicles or equipment, use proper support mechanisms to prevent unexpected movement. Securely block the vehicle’s wheels or utilize support stands to prevent the vehicle from rolling or shifting during drive shaft removal or installation. This helps maintain stability and reduces the risk of accidents.
4. Proper Lifting Techniques:
When handling heavy drive shafts, use proper lifting techniques to prevent strain or injuries. Lift with the help of a suitable lifting device, such as a hoist or jack, and ensure that the load is evenly distributed and securely attached. Avoid lifting heavy drive shafts manually or with improper lifting equipment, as this can lead to accidents and injuries.
5. Inspection and Maintenance:
Prior to working on a drive shaft, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of damage, wear, or misalignment. If any abnormalities are detected, consult a qualified technician or engineer before proceeding. Regular maintenance is also essential to ensure the drive shaft is in good working condition. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and procedures to minimize the risk of failures or malfunctions.
6. Proper Tools and Equipment:
Use appropriate tools and equipment specifically designed for working with drive shafts. Improper tools or makeshift solutions can lead to accidents or damage to the drive shaft. Ensure that tools are in good condition, properly sized, and suitable for the task at hand. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines when using specialized tools or equipment.
7. Controlled Release of Stored Energy:
Some drive shafts, particularly those with torsional dampers or other energy-storing components, can store energy even when the power source is disconnected. Exercise caution when working on such drive shafts and ensure that the stored energy is safely released before disassembly or removal.
8. Training and Expertise:
Work on drive shafts should only be performed by individuals with the necessary training, knowledge, and expertise. If you are not familiar with drive shafts or lack the required skills, seek assistance from qualified technicians or professionals. Improper handling or installation of drive shafts can lead to accidents, damage, or compromised performance.
9. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, instructions, and warnings specific to the drive shaft you are working with. These guidelines provide important information regarding installation, maintenance, and safety considerations. Deviating from the manufacturer’s recommendations may result in unsafe conditions or void warranty coverage.
10. Disposal of Old or Damaged Drive Shafts:
Dispose of old or damaged drive shafts in accordance with local regulations and environmental guidelines. Improper disposal can have negative environmental impacts and may violate legal requirements. Consult with local waste management authorities or recycling centers to ensure appropriate disposal methods are followed.
By following these safety precautions, individuals can minimize the risks associated with working with drive shafts and promote a safe working environment. It is crucial to prioritize personal safety, use proper equipment and techniques, and seek professional help when needed to ensure the proper handling and maintenance of drive shafts.

What is a drive shaft and how does it function in vehicles and machinery?
A drive shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or prop shaft, is a mechanical component that plays a critical role in transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels or other driven components in vehicles and machinery. It is commonly used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and agricultural or industrial machinery. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a drive shaft is and how it functions:
1. Definition and Construction: A drive shaft is a cylindrical metal tube that connects the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. It is typically made of steel or aluminum and consists of one or more tubular sections with universal joints (U-joints) at each end. These U-joints allow for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components.
2. Power Transmission: The primary function of a drive shaft is to transmit rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. In vehicles, the drive shaft connects the transmission or gearbox output shaft to the differential, which then transfers power to the wheels. In machinery, the drive shaft transfers power from the engine or motor to various driven components such as pumps, generators, or other mechanical systems.
3. Torque and Speed: The drive shaft is responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). The drive shaft must be capable of transmitting the required torque without excessive twisting or bending and maintaining the desired rotational speed for efficient operation of the driven components.
4. Flexible Coupling: The U-joints on the drive shaft provide a flexible coupling that allows for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components. As the suspension system of a vehicle moves or the machinery operates on uneven terrain, the drive shaft can adjust its length and angle to accommodate these movements, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing damage to the drivetrain components.
5. Length and Balance: The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven wheels or components. It should be appropriately sized to ensure proper power transmission and avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Additionally, the drive shaft is carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can cause discomfort, reduce efficiency, and lead to premature wear of drivetrain components.
6. Safety Considerations: Drive shafts in vehicles and machinery require proper safety measures. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts and reduce the risk of injury in the event of a malfunction or failure. Additionally, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards associated with rotating components.
7. Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or excessive play in the U-joints, inspecting the drive shaft for any cracks or deformations, and lubricating the U-joints as recommended by the manufacturer. Proper maintenance helps prevent failures, ensures optimal performance, and prolongs the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, a drive shaft is a mechanical component that transmits rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in vehicles and machinery. It functions by providing a rigid connection between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components, while also allowing for angular movement and compensation of misalignment through the use of U-joints. The drive shaft plays a crucial role in power transmission, torque and speed delivery, flexible coupling, length and balance considerations, safety, and maintenance requirements. Its proper functioning is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of vehicles and machinery.


editor by CX 2024-05-17
China supplier Machinery Parts Rotor Gear Shaft Customized Machining Knurling High Precision with Factory Price for Auto Drive Factory Price Drive Line
Product Description
You can kindly find the specification details below:
HangZhou Mastery Machinery Technology Co., LTD helps manufacturers and brands fulfill their machinery parts by precision manufacturing. High precision machinery products like the shaft, worm screw, bushing, couplings, joints……Our products are used widely in electronic motors, the main shaft of the engine, the transmission shaft in the gearbox, couplers, printers, pumps, drones, and so on. They cater to different industries, including automotive, industrial, power tools, garden tools, healthcare, smart home, etc.
Mastery caters to the industrial industry by offering high-level Cardan shafts, pump shafts, and a bushing that come in different sizes ranging from diameter 3mm-50mm. Our products are specifically formulated for transmissions, robots, gearboxes, industrial fans, and drones, etc.
Mastery factory currently has more than 100 main production equipment such as CNC lathe, CNC machining center, CAM Automatic Lathe, grinding machine, hobbing machine, etc. The production capacity can be up to 5-micron mechanical tolerance accuracy, automatic wiring machine processing range covering 3mm-50mm diameter bar.
Key Specifications:
| Name | Shaft/Motor Shaft/Drive Shaft/Gear Shaft/Pump Shaft/Worm Screw/Worm Gear/Bushing/Ring/Joint/Pin |
| Material | 40Cr/35C/GB45/70Cr/40CrMo |
| Process | Machining/Lathing/Milling/Drilling/Grinding/Polishing |
| Size | 2-400mm(Customized) |
| Diameter | φ12(Customized) |
| Diameter Tolerance | 0.008mm |
| Roundness | 0.01mm |
| Roughness | Ra0.4 |
| Straightness | 0.01mm |
| Hardness | Customized |
| Length | 32mm(Customized) |
| Heat Treatment | Customized |
| Surface treatment | Coating/Ni plating/Zn plating/QPQ/Carbonization/Quenching/Black Treatment/Steaming Treatment/Nitrocarburizing/Carbonitriding |
Quality Management:
- Raw Material Quality Control: Chemical Composition Analysis, Mechanical Performance Test, ROHS, and Mechanical Dimension Check
- Production Process Quality Control: Full-size inspection for the 1st part, Critical size process inspection, SPC process monitoring
- Lab ability: CMM, OGP, XRF, Roughness meter, Profiler, Automatic optical inspector
- Quality system: ISO9001, IATF 16949, ISO14001
- Eco-Friendly: ROHS, Reach.
Packaging and Shipping:
Throughout the entire process of our supply chain management, consistent on-time delivery is vital and very important for the success of our business.
Mastery utilizes several different shipping methods that are detailed below:
For Samples/Small Q’ty: By Express Services or Air Fright.
For Formal Order: By Sea or by air according to your requirement.
Mastery Services:
- One-Stop solution from idea to product/ODM&OEM acceptable
- Individual research and sourcing/purchasing tasks
- Individual supplier management/development, on-site quality check projects
- Muti-varieties/small batch/customization/trial orders are acceptable
- Flexibility on quantity/Quick samples
- Forecast and raw material preparation in advance are negotiable
- Quick quotes and quick responses
General Parameters:
If you are looking for a reliable machinery product partner, you can rely on Mastery. Work with us and let us help you grow your business using our customizable and affordable products. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
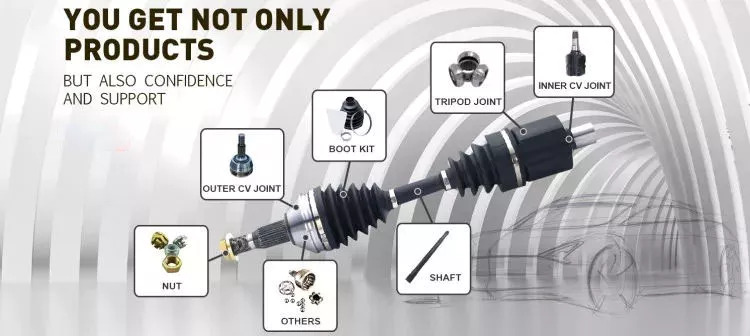
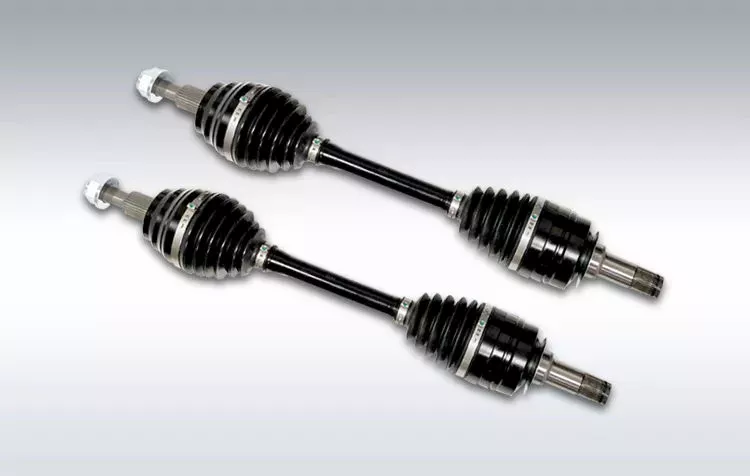
What factors should be considered when designing an efficient driveline system?
Designing an efficient driveline system involves considering various factors that contribute to performance, reliability, and overall system efficiency. Here are the key factors that should be considered when designing an efficient driveline system:
1. Power Requirements:
The power requirements of the vehicle play a crucial role in designing an efficient driveline system. It is essential to determine the maximum power output of the engine and ensure that the driveline components can handle and transfer that power efficiently. Optimizing the driveline for the specific power requirements helps minimize energy losses and maximize overall efficiency.
2. Weight and Packaging:
The weight and packaging of the driveline components have a significant impact on system efficiency. Lightweight materials and compact design help reduce the overall weight of the driveline, which can improve fuel efficiency and vehicle performance. Additionally, efficient packaging ensures that driveline components are properly integrated, minimizing energy losses and maximizing available space within the vehicle.
3. Friction and Mechanical Losses:
Minimizing friction and mechanical losses within the driveline system is crucial for achieving high efficiency. Frictional losses occur at various points, such as bearings, gears, and joints. Selecting low-friction materials, optimizing lubrication systems, and implementing efficient bearing designs can help reduce these losses. Additionally, employing advanced gear designs, such as helical or hypoid gears, can improve gear mesh efficiency and reduce power losses.
4. Gear Ratios and Transmission Efficiency:
The selection of appropriate gear ratios and optimizing transmission efficiency greatly impacts driveline efficiency. Gear ratios should be chosen to match the vehicle’s power requirements, driving conditions, and desired performance characteristics. In addition, improving the efficiency of the transmission, such as reducing gear mesh losses and enhancing hydraulic or electronic control systems, can contribute to overall driveline efficiency.
5. Aerodynamic Considerations:
Aerodynamics play a significant role in a vehicle’s overall efficiency, including the driveline system. Reducing aerodynamic drag through streamlined vehicle design, efficient cooling systems, and appropriate underbody airflow management can enhance driveline efficiency by reducing the power required to overcome air resistance.
6. System Integration and Control:
Efficient driveline design involves seamless integration and control of various components. Employing advanced control systems, such as electronic control units (ECUs), can optimize driveline operation by adjusting power distribution, managing gear shifts, and optimizing torque delivery based on real-time driving conditions. Effective system integration ensures smooth communication and coordination between driveline components, improving overall efficiency.
7. Environmental Considerations:
Environmental factors should also be taken into account when designing an efficient driveline system. Considerations such as emissions regulations, sustainability goals, and the use of alternative power sources (e.g., hybrid or electric drivetrains) can influence driveline design decisions. Incorporating technologies like regenerative braking or start-stop systems can further enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
8. Reliability and Durability:
Designing an efficient driveline system involves ensuring long-term reliability and durability. Selecting high-quality materials, performing thorough testing and validation, and considering factors such as thermal management and component durability help ensure that the driveline system operates efficiently over its lifespan.
By considering these factors during the design process, engineers can develop driveline systems that are optimized for efficiency, performance, and reliability, resulting in improved fuel economy, reduced emissions, and enhanced overall vehicle efficiency.

Can you provide real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that use drivelines?
Drivelines are used in a wide range of vehicles and machinery across various industries. These driveline systems are responsible for transmitting power from the engine or motor to the wheels or driven components. Here are some real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that utilize drivelines:
1. Automobiles:
Drivelines are integral to automobiles, providing power transmission from the engine to the wheels. Various driveline configurations are used, including:
- Front-Wheel Drive (FWD): Many compact cars and passenger vehicles employ front-wheel drive, where the driveline powers the front wheels.
- Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD): Rear-wheel drive is commonly found in sports cars, luxury vehicles, and trucks, with the driveline powering the rear wheels.
- All-Wheel Drive (AWD) and Four-Wheel Drive (4WD): AWD and 4WD drivelines distribute power to all four wheels, enhancing traction and stability. These systems are used in SUVs, off-road vehicles, and performance cars.
2. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Trucks, including pickup trucks, delivery trucks, and heavy-duty commercial vehicles, rely on drivelines to transmit power to the wheels. These drivelines are designed to handle higher torque and load capacities, enabling efficient operation in various work environments.
3. Agricultural Machinery:
Farm equipment, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters, utilize drivelines to transfer power from the engine to agricultural implements and wheels. Drivelines in agricultural machinery are engineered to withstand demanding conditions and provide optimal power delivery for field operations.
4. Construction and Earthmoving Equipment:
Construction machinery, including excavators, bulldozers, loaders, and graders, employ drivelines to power their movement and hydraulic systems. Drivelines in this sector are designed to deliver high torque and endurance for heavy-duty operations in challenging terrains.
5. Off-Road and Recreational Vehicles:
Off-road vehicles, such as ATVs (All-Terrain Vehicles), UTVs (Utility Task Vehicles), and recreational vehicles like dune buggies and sand rails, rely on drivelines to provide power to the wheels. These drivelines are engineered to handle extreme conditions and offer enhanced traction for off-road adventures.
6. Railway Locomotives and Rolling Stock:
Drivelines are utilized in railway locomotives and rolling stock to transmit power from the engines to the wheels. These driveline systems are designed to efficiently transfer high torque and provide reliable propulsion for trains and other rail vehicles.
7. Marine Vessels:
Drivelines are employed in various types of marine vessels, including boats, yachts, and ships. They transmit power from the engines to the propellers or water jets, enabling propulsion through water. Marine drivelines are designed to operate in wet environments and withstand the corrosive effects of saltwater.
8. Industrial Machinery:
Industrial machinery, such as manufacturing equipment, conveyor systems, and material handling machines, often utilize drivelines for power transmission. These drivelines enable the movement of components, products, and materials within industrial settings.
9. Electric and Hybrid Vehicles:
Drivelines are a crucial component in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles (HVs). In these vehicles, the drivelines transmit power from electric motors or a combination of engines and motors to the wheels. Electric drivelines play a significant role in the efficiency and performance of EVs and HVs.
These are just a few examples of vehicles and machinery that utilize drivelines. Driveline systems are essential in a wide range of applications, enabling efficient power transmission and propulsion across various industries.

How do drivelines handle variations in torque, speed, and angles of rotation?
Drivelines are designed to handle variations in torque, speed, and angles of rotation within a power transmission system. They incorporate specific components and mechanisms that enable the smooth and efficient transfer of power while accommodating these variations. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drivelines handle variations in torque, speed, and angles of rotation:
Variations in Torque:
Drivelines encounter variations in torque when the power requirements change, such as during acceleration, deceleration, or when encountering different loads. To handle these variations, drivelines incorporate several components:
1. Clutch: In manual transmission systems, a clutch is used to engage or disengage the engine’s power from the driveline. By partially or completely disengaging the clutch, the driveline can temporarily interrupt power transfer, allowing for smooth gear changes or vehicle stationary positions. This helps manage torque variations during shifting or when power demands change abruptly.
2. Torque Converter: Automatic transmissions employ torque converters, which are fluid couplings that transfer power from the engine to the transmission. Torque converters provide a certain amount of slip, allowing for torque multiplication and smooth power transfer. The slip in the torque converter helps absorb torque variations and dampens abrupt changes, ensuring smoother operation during acceleration or when power demands fluctuate.
3. Differential: The differential mechanism in drivelines compensates for variations in torque between the wheels, particularly during turns. When a vehicle turns, the inner and outer wheels travel different distances, resulting in different rotational speeds. The differential allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds while distributing torque to each wheel accordingly. This ensures that torque variations are managed and power is distributed effectively to optimize traction and stability.
Variations in Speed:
Drivelines also need to handle variations in rotational speed, especially when the engine operates at different RPMs or when different gear ratios are selected. The following components aid in managing speed variations:
1. Transmission: The transmission allows for the selection of different gear ratios, which influence the rotational speed of the driveline components. By changing gears, the transmission adjusts the speed at which power is transferred from the engine to the driveline. This allows the driveline to adapt to different speed requirements, whether it’s for quick acceleration or maintaining a consistent speed during cruising.
2. Gearing: Driveline systems often incorporate various gears in the transmission, differential, or axle assemblies. Gears provide mechanical advantage by altering the speed and torque relationship. By employing different gear ratios, the driveline can adjust the rotational speed and torque output to match the requirements of the vehicle under different operating conditions.
Variations in Angles of Rotation:
Drivelines must accommodate variations in angles of rotation, especially in vehicles with flexible or independent suspension systems. The following components help manage these variations:
1. Universal Joints: Universal joints, also known as U-joints, are flexible couplings used in drivelines to accommodate variations in angles and misalignments between components. They allow for smooth power transmission between the drive shaft and other components, compensating for changes in driveline angles during vehicle operation or suspension movement. Universal joints are particularly effective in handling non-linear or variable angles of rotation.
2. Constant Velocity Joints (CV Joints): CV joints are specialized joints used in drivelines, especially in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles. They allow the driveline to handle variations in angles while maintaining a constant velocity during rotation. CV joints are designed to mitigate vibrations, power losses, and potential binding or juddering that can occur due to changes in angles of rotation.
By incorporating these components and mechanisms, drivelines effectively handle variations in torque, speed, and angles of rotation. These features ensure smooth power transfer, optimal performance, and enhanced durability in various driving conditions and operating scenarios.


editor by CX 2024-04-22
China high quality Shaft CNC Machining Shaft Flange Shaft Roller Shaft Drive Shaft Gear Shaft Spline Shaft Logistics Equipment Shaft Conveyor Shaft Coater Shaft Drive Line
Product Description
Product Description
rotation axis of rotation is due to the fact that as an object rotates, its points move in circles, and the centers of these circles lie on the same line.
Rotation is a common type of motion. When an object rotates, its points move in circles. The centers of these circles lie on the same line. This line is called the axis of rotation. Doors, Windows, grinding wheels, motor rotors, etc., have fixed rotating shaft, can only be rotated, but not translational. Several forces act on a body, and their rotational action on the body depends on the algebraic sum of their torques. If the algebraic sum of moments is equal to zero, the object will rotate uniformly with the original angular velocity or stay at rest.
The drive shaft is a rotating body with high speed and little support, so its dynamic balance is very important. The general drive shaft before leaving the factory must enter the action balance test, and the balance machine has been adjusted. For front-engine rear-wheel drive cars is the shaft that transfers the rotation of the transmission to the main reducer, which can be several segments, and the segments can be connected by universal joints.
Hebe (ZheJiang ) Industrial Co., LTD was founded in 2018. The company covers an area of 1500 square meter and has 15 employees, including 1 designer and 2 CNC programmers. Heber Company specializes in providing all kinds of parts processing. The process includes CNC milling, CNC turning, CNC grinding, large CNC machining, Wire cutting, EDM machining. Our machining accuracy can reach 0.005mm. Surface grinding finish up to 0.8um.mirror polish is up to 0.4um.
company provides parts processing for various industries. For example, packaging machinery, slitter machine, aerospace, electronic machinery, cigarette machine, gear machinery, automatic assembly machine, power tools, semiconductor equipment, automobile production line, automobile, motorcycle, bicycle, 3D printer, plastic machinery, robot and so on. We can provide zinc plating, nickel plating, oxidation, heat treatment, chrome plating, PVD, spray, spray paint, black phosphating and other surface treatment processes.
Hebe can also provide mechanical assembly work for customers. We have skilled fitters and assembly workers. We can complete detailed work from CNC machining to assembly. PLC program, electronic parts procurement, automation components procurement, etc. We have assembled non – target automation equipment, slitting machines, packaging machines, etc.
| Equipment name | CNC lathe /CNC milling machine /CNC grinder /EDM/ vertical milling machine/linear cutting /4-5 axis CNC milling machine/large size CNC milling machine/Laser cutting/CNC Bending machine |
| Testing instrument | Inside diameter measurement/outside diameter measurement/caliper/height measurement/CMM measurement |
| Material | Steel/Aluminium alloy/ copper/ Alloy steel /Titanium alloy/ nylon /PTFE /Stainless steel /mold steel/ Brass/copper/tungsten steel/high strength stainless steel |
| Surface treatment | Polishing/electroplating/oxidation/spraying/nitriding/phosphating/heat treatment |
| Product packaging | 1200x800mm tray/500x500x500mm carton/Customizable wooden cases/Designable packaging scheme |
| Customer industry | Mechanical equipment/aerospace/automobile production line/automation equipment/bicycle/motorcycle/energy/chemical equipment/industrial electrical appliances |
| Software capability | CAD 2007/ UG 10.0/ Solidwork |
| Delivery time | Sample5-10 days/ Mass production 20-45days |
| Payment clause | 30% advance payment +70% delivery payment T/T |
| MOQ | 1PCS |
Packaging & Shipping
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Fastener, Auto and Motorcycle Accessory, Hardware Tool, Machinery Accessory |
|---|---|
| Standard: | GB, China GB Code |
| Surface Treatment: | Electroplating |
| Production Type: | Batch Production |
| Machining Method: | CNC Turning |
| Material: | Steel, Alloy, Aluminum |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What maintenance practices are essential for prolonging the lifespan of driveline components?
Implementing proper maintenance practices is crucial for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of driveline components. Regular maintenance helps identify potential issues, prevent major failures, and prolong the lifespan of driveline components. Here are some essential maintenance practices for prolonging the lifespan of driveline components:
1. Regular Inspections:
Performing regular visual inspections of driveline components is essential for detecting any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the driveline components, including driveshafts, universal joints, CV joints, differentials, and transmission components, for any cracks, leaks, excessive play, or unusual noise. Identifying and addressing issues early can prevent further damage and potential driveline failure.
2. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication of driveline components is crucial for minimizing friction, reducing wear, and ensuring smooth operation. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and use the appropriate type and grade of lubricant. Regularly check and maintain the lubrication levels in components such as bearings, gears, and joints to prevent excessive heat buildup and premature wear.
3. Fluid Changes:
Fluids play a vital role in driveline component performance and longevity. Regularly change fluids, such as transmission fluid, differential oil, and transfer case fluid, according to the manufacturer’s recommended intervals. Over time, these fluids can become contaminated or break down, leading to compromised performance and increased wear. Fresh fluids help maintain proper lubrication, cooling, and protection of driveline components.
4. Alignment and Balancing:
Proper alignment and balancing of driveline components are essential for minimizing vibration, reducing stress, and preventing premature wear. Periodically check and adjust the alignment of driveshafts, ensuring they are properly aligned with the transmission and differential. Additionally, balance rotating components, such as driveshafts or flywheels, to minimize vibrations and prevent excessive stress on driveline components.
5. Torque Check:
Regularly check and ensure that all driveline components are properly torqued according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Over time, fasteners can loosen due to vibrations or thermal expansion and contraction. Loose fasteners can lead to misalignment, excessive play, or even component failure. Regular torque checks help maintain the integrity and performance of the driveline system.
6. Maintenance of Supporting Systems:
Driveline components rely on the proper functioning of supporting systems, such as cooling systems and electrical systems. Ensure that cooling systems are functioning correctly, as overheating can cause driveline components to degrade or fail. Additionally, regularly inspect electrical connections, wiring harnesses, and sensors to ensure proper communication and operation of driveline components.
7. Proper Driving Techniques:
The way a vehicle is driven can significantly impact the lifespan of driveline components. Avoid aggressive driving, sudden acceleration, and excessive braking, as these actions can put undue stress on the driveline components. Smooth and gradual acceleration, proper shifting techniques, and avoiding excessive load or towing capacities help minimize wear and prolong component life.
8. Service and Maintenance Records:
Maintain comprehensive service and maintenance records for the driveline components. Keep track of all maintenance tasks, repairs, fluid changes, and inspections performed. These records help ensure that maintenance tasks are performed on time, provide a history of component performance, and assist in diagnosing any recurring issues or patterns.
By following these maintenance practices, vehicle owners can prolong the lifespan of driveline components, minimize the risk of failures, and ensure optimal performance and reliability of the driveline system.

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with driveline systems?
While driveline systems offer numerous advantages in terms of power transmission and vehicle performance, there are also some limitations and disadvantages associated with their use. It’s important to consider these factors when designing, operating, and maintaining driveline systems. Let’s explore some of the limitations and disadvantages:
1. Complex Design and Integration:
Driveline systems can be complex in design, especially in modern vehicles with advanced technologies. They often consist of multiple components, such as transmissions, differentials, transfer cases, and drive shafts, which need to be properly integrated and synchronized. The complexity of the driveline system can increase manufacturing and assembly challenges, as well as the potential for compatibility issues or failures if not designed and integrated correctly.
2. Energy Losses:
Driveline systems can experience energy losses during power transmission. These losses occur due to factors such as friction, heat generation, mechanical inefficiencies, and fluid drag in components like gearboxes, differentials, and torque converters. The energy losses can negatively impact overall efficiency and result in reduced fuel economy or power output, especially in systems with multiple driveline components.
3. Limited Service Life and Maintenance Requirements:
Driveline components, like any mechanical system, have a limited service life and require regular maintenance. Components such as clutches, bearings, gears, and drive shafts are subject to wear and tear, and may need to be replaced or repaired over time. Regular maintenance, including lubrication, adjustments, and inspections, is necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failures. Failure to perform proper maintenance can lead to driveline malfunctions, increased downtime, and costly repairs.
4. Weight and Space Constraints:
Driveline systems add weight and occupy space within a vehicle. The additional weight affects fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Moreover, the space occupied by driveline components can limit design flexibility, particularly in compact or electric vehicles where space optimization is crucial. Manufacturers must strike a balance between driveline performance, vehicle weight, and available space to meet the requirements of each specific vehicle type.
5. Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH):
Driveline systems can generate noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) during operation. Factors such as gear meshing, unbalanced rotating components, or improper driveline alignment can contribute to unwanted vibrations or noise. NVH issues can affect driving comfort, passenger experience, and vehicle refinement. Manufacturers employ various techniques, including vibration dampening materials, isolators, and precision engineering, to minimize NVH levels, but achieving complete elimination can be challenging.
6. Limited Torque Handling Capability:
Driveline systems have limitations in terms of torque handling capability. Excessive torque beyond the rated capacity of driveline components can lead to failures, such as shearing of gears, clutch slippage, or drive shaft breakage. High-performance vehicles or heavy-duty applications may require specialized driveline components capable of handling higher torque loads, which can increase costs and complexity.
7. Traction Limitations:
Driveline systems, particularly in vehicles with two-wheel drive configurations, may experience traction limitations, especially in slippery or off-road conditions. Power is typically transmitted to only one or two wheels, which can result in reduced traction and potential wheel slippage. This limitation can be mitigated by utilizing technologies such as limited-slip differentials, electronic traction control, or implementing all-wheel drive systems.
While driveline systems provide crucial power transmission and vehicle control, they do have limitations and disadvantages that need to be considered. Manufacturers, designers, and operators should carefully assess these factors and implement appropriate design, maintenance, and operational practices to optimize driveline performance, reliability, and overall vehicle functionality.

Can you explain the components of a typical driveline and their specific roles?
A typical driveline consists of several components that work together to transmit power from the engine or power source to the driven components, enabling motion and providing torque. Each component plays a specific role in the driveline system. Here’s an explanation of the key components of a typical driveline and their specific roles:
1. Engine: The engine is the power source of the driveline system. It converts fuel energy (such as gasoline or diesel) into mechanical power by the process of combustion. The engine generates rotational power, which is transferred to the driveline to initiate power transmission.
2. Transmission: The transmission is responsible for selecting the appropriate gear ratio and transmitting power from the engine to the driven components. It allows the driver or operator to control the speed and torque output of the driveline. In manual transmissions, the driver manually selects the gears, while in automatic transmissions, the gear shifts are controlled by the vehicle’s computer system.
3. Drive Shaft: The drive shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or prop shaft, is a tubular component that transmits rotational power from the transmission to the differential or the driven components. It typically consists of a hollow metal tube with universal joints at both ends to accommodate variations in driveline angles and allow for smooth power transfer.
4. Differential: The differential is a gearbox-like component that distributes power from the drive shaft to the wheels or driven axles while allowing them to rotate at different speeds, particularly during turns. It compensates for the difference in rotational speed between the inner and outer wheels in a turn, ensuring smooth and controlled operation of the driveline system.
5. Axles: Axles are shafts that connect the differential to the wheels. They transmit power from the differential to the wheels, allowing them to rotate and generate motion. In vehicles with independent suspension, each wheel typically has its own axle, while in solid axle configurations, a single axle connects both wheels on an axle assembly.
6. Clutch: In manual transmission systems, a clutch is employed to engage or disengage the engine’s power from the driveline. It allows the driver to smoothly engage the engine’s power to the transmission when shifting gears or coming to a stop. By disengaging the clutch, power transmission to the driveline is temporarily interrupted, enabling gear changes or vehicle stationary positions.
7. Torque Converter: Torque converters are used in automatic transmissions to transfer power from the engine to the transmission. They provide a fluid coupling between the engine and transmission, allowing for smooth power transmission and torque multiplication. The torque converter also provides a torque amplification effect, which helps in vehicle acceleration.
8. Universal Joints: Universal joints, also known as U-joints, are flexible couplings used in the driveline to accommodate variations in angles and misalignments between the components. They allow for the smooth transmission of power between the drive shaft and other components, compensating for changes in driveline angles during vehicle operation or suspension movement.
9. Constant Velocity Joints (CV Joints): CV joints are specialized joints used in some drivelines, particularly in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles. They enable smooth power transmission while accommodating variations in angles and allowing the wheels to turn at different speeds. CV joints maintain a constant velocity during rotation, minimizing vibrations and power losses.
10. Transfer Case: A transfer case is a component found in four-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive systems. It transfers power from the transmission to both the front and rear axles, allowing all wheels to receive power. The transfer case usually includes additional components such as a multi-speed gearbox and differential mechanisms to distribute power effectively to the axles.
These are the key components of a typical driveline and their specific roles. Each component is crucial in transferring power, enabling motion, and ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of vehicles and equipment.


editor by CX 2024-03-01
China supplier Gear Universal Joint Agricultural Machinery Transmission Shaft Baler Transmission Shaft High Horsepower Transmission Shaft Drive Shaft
Product Description
Gear universal joint agricultural machinery transmission shaft Baler transmission shaft High horsepower transmission shaft
Product Features: Electronic Processing Customization: Yes Brand: Electronic Processing
Model: Electric machine Applicable model: Agricultural machine Length: Electric machine mm
***Degree: diameter of electrode: electrode d Origin: electrode
Part number: Dianyi
| Type: | Transmission Shaft |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Agricultural Products Processing, Farmland Infrastructure, Tillage, Harvester, Planting and Fertilization, Grain Threshing, Cleaning and Drying |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Power Source: | Diesel |
| Weight: | Discuss Personally |
| After-sales Service: | One Year |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with drive shafts?
While drive shafts are widely used and offer several advantages, they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered. Here’s a detailed explanation of the limitations and disadvantages associated with drive shafts:
1. Length and Misalignment Constraints:
Drive shafts have a maximum practical length due to factors such as material strength, weight considerations, and the need to maintain rigidity and minimize vibrations. Longer drive shafts can be prone to increased bending and torsional deflection, leading to reduced efficiency and potential driveline vibrations. Additionally, drive shafts require proper alignment between the driving and driven components. Misalignment can cause increased wear, vibrations, and premature failure of the drive shaft or its associated components.
2. Limited Operating Angles:
Drive shafts, especially those using U-joints, have limitations on operating angles. U-joints are typically designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and operating beyond these limits can result in reduced efficiency, increased vibrations, and accelerated wear. In applications requiring large operating angles, constant velocity (CV) joints are often used to maintain a constant speed and accommodate greater angles. However, CV joints may introduce higher complexity and cost compared to U-joints.
3. Maintenance Requirements:
Drive shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection, lubrication of joints, and balancing if necessary. Failure to perform routine maintenance can lead to increased wear, vibrations, and potential driveline issues. Maintenance requirements should be considered in terms of time and resources when using drive shafts in various applications.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Drive shafts can generate noise and vibrations, especially at high speeds or when operating at certain resonant frequencies. Imbalances, misalignment, worn joints, or other factors can contribute to increased noise and vibrations. These vibrations may affect the comfort of vehicle occupants, contribute to component fatigue, and require additional measures such as dampers or vibration isolation systems to mitigate their effects.
5. Weight and Space Constraints:
Drive shafts add weight to the overall system, which can be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications, such as automotive or aerospace industries. Additionally, drive shafts require physical space for installation. In compact or tightly packaged equipment or vehicles, accommodating the necessary drive shaft length and clearances can be challenging, requiring careful design and integration considerations.
6. Cost Considerations:
Drive shafts, depending on their design, materials, and manufacturing processes, can involve significant costs. Customized or specialized drive shafts tailored to specific equipment requirements may incur higher expenses. Additionally, incorporating advanced joint configurations, such as CV joints, can add complexity and cost to the drive shaft system.
7. Inherent Power Loss:
Drive shafts transmit power from the driving source to the driven components, but they also introduce some inherent power loss due to friction, bending, and other factors. This power loss can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in long drive shafts or applications with high torque requirements. It is important to consider power loss when determining the appropriate drive shaft design and specifications.
8. Limited Torque Capacity:
While drive shafts can handle a wide range of torque loads, there are limits to their torque capacity. Exceeding the maximum torque capacity of a drive shaft can lead to premature failure, resulting in downtime and potential damage to other driveline components. It is crucial to select a drive shaft with sufficient torque capacity for the intended application.
Despite these limitations and disadvantages, drive shafts remain a widely used and effective means of power transmission in various industries. Manufacturers continuously work to address these limitations through advancements in materials, design techniques, joint configurations, and balancing processes. By carefully considering the specific application requirements and potential drawbacks, engineers and designers can mitigate the limitations and maximize the benefits of drive shafts in their respective systems.

Can you provide real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that use drive shafts?
Drive shafts are widely used in various vehicles and machinery to transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here are some real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that utilize drive shafts:
1. Automobiles:
Drive shafts are commonly found in automobiles, especially those with rear-wheel drive or four-wheel drive systems. In these vehicles, the drive shaft transfers power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or front differential, respectively. This allows the engine’s power to be distributed to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward.
2. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Drive shafts are essential components in trucks and commercial vehicles. They are used to transfer power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear axle or multiple axles in the case of heavy-duty trucks. Drive shafts in commercial vehicles are designed to handle higher torque loads and are often larger and more robust than those used in passenger cars.
3. Construction and Earthmoving Equipment:
Various types of construction and earthmoving equipment, such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and graders, rely on drive shafts for power transmission. These machines typically have complex drivetrain systems that use drive shafts to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks, enabling them to perform heavy-duty tasks on construction sites or in mining operations.
4. Agricultural Machinery:
Agricultural machinery, including tractors, combines, and harvesters, utilize drive shafts to transmit power from the engine to the wheels or driven components. Drive shafts in agricultural machinery are often subjected to demanding conditions and may have additional features such as telescopic sections to accommodate variable distances between components.
5. Industrial Machinery:
Industrial machinery, such as manufacturing equipment, generators, pumps, and compressors, often incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. These drive shafts transfer power from electric motors, engines, or other power sources to various driven components, enabling the machinery to perform specific tasks in industrial settings.
6. Marine Vessels:
In marine applications, drive shafts are commonly used to transmit power from the engine to the propeller in boats, ships, and other watercraft. Marine drive shafts are typically longer and designed to withstand the unique challenges posed by water environments, including corrosion resistance and appropriate sealing mechanisms.
7. Recreational Vehicles (RVs) and Motorhomes:
RVs and motorhomes often employ drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These drive shafts transfer power from the transmission to the rear axle, allowing the vehicle to move and providing propulsion. Drive shafts in RVs may have additional features such as dampers or vibration-reducing components to enhance comfort during travel.
8. Off-Road and Racing Vehicles:
Off-road vehicles, such as SUVs, trucks, and all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), as well as racing vehicles, frequently utilize drive shafts. These drive shafts are designed to withstand the rigors of off-road conditions or high-performance racing, transmitting power efficiently to the wheels and ensuring optimal traction and performance.
9. Railway Rolling Stock:
In railway systems, drive shafts are employed in locomotives and some types of rolling stock. They transfer power from the locomotive’s engine to the wheels or propulsion system, enabling the train to move along the tracks. Railway drive shafts are typically much longer and may have additional features to accommodate the articulated or flexible nature of some train configurations.
10. Wind Turbines:
Large-scale wind turbines used for generating electricity incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. The drive shafts transfer rotational energy from the turbine’s blades to the generator, where it is converted into electrical power. Drive shafts in wind turbines are designed to handle the significant torque and rotational forces generated by the wind.
These examples demonstrate the broad range of vehicles and machinery that rely on drive shafts for efficient power transmission and propulsion. Drive shafts are essential components in various industries, enabling the transfer of power from the source to the driven components, ultimately facilitating movement, operation, or the performance of specific tasks.

How do drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in length and torque requirements in order to efficiently transmit rotational power. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts address these variations:
Length Variations:
Drive shafts are available in different lengths to accommodate varying distances between the engine or power source and the driven components. They can be custom-made or purchased in standardized lengths, depending on the specific application. In situations where the distance between the engine and the driven components is longer, multiple drive shafts with appropriate couplings or universal joints can be used to bridge the gap. These additional drive shafts effectively extend the overall length of the power transmission system.
Additionally, some drive shafts are designed with telescopic sections. These sections can be extended or retracted, allowing for adjustments in length to accommodate different vehicle configurations or dynamic movements. Telescopic drive shafts are commonly used in applications where the distance between the engine and the driven components may change, such as in certain types of trucks, buses, and off-road vehicles.
Torque Requirements:
Drive shafts are engineered to handle varying torque requirements based on the power output of the engine or power source and the demands of the driven components. The torque transmitted through the drive shaft depends on factors such as the engine power, load conditions, and the resistance encountered by the driven components.
Manufacturers consider torque requirements when selecting the appropriate materials and dimensions for drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, to withstand the torque loads without deformation or failure. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure it can handle the expected torque without excessive deflection or vibration.
In applications with high torque demands, such as heavy-duty trucks, industrial machinery, or performance vehicles, drive shafts may have additional reinforcements. These reinforcements can include thicker walls, cross-sectional shapes optimized for strength, or composite materials with superior torque-handling capabilities.
Furthermore, drive shafts often incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity (CV) joints. These joints allow for angular misalignment and compensate for variations in the operating angles between the engine, transmission, and driven components. They also help absorb vibrations and shocks, reducing stress on the drive shaft and enhancing its torque-handling capacity.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements through customizable lengths, telescopic sections, appropriate materials and dimensions, and the inclusion of flexible joints. By carefully considering these factors, drive shafts can efficiently and reliably transmit power while accommodating the specific needs of different applications.


editor by CX 2023-10-08
China Good quality Gear Universal Joint Agricultural Machinery Transmission Shaft Baler Transmission Shaft High Horsepower Transmission Shaft Drive Shaft
Product Description
Gear universal joint agricultural machinery transmission shaft Baler transmission shaft High horsepower transmission shaft
Product Features: Electronic Processing Customization: Yes Brand: Electronic Processing
Model: Electric machine Applicable model: Agricultural machine Length: Electric machine mm
***Degree: diameter of electrode: electrode d Origin: electrode
Part number: Dianyi
| Type: | Transmission Shaft |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Agricultural Products Processing, Farmland Infrastructure, Tillage, Harvester, Planting and Fertilization, Grain Threshing, Cleaning and Drying |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Power Source: | Diesel |
| Weight: | Discuss Personally |
| After-sales Service: | One Year |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment?
Manufacturers employ various strategies and processes to ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. Compatibility refers to the ability of a drive shaft to effectively integrate and function within a specific piece of equipment or machinery. Manufacturers take into account several factors to ensure compatibility, including dimensional requirements, torque capacity, operating conditions, and specific application needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts:
1. Application Analysis:
Manufacturers begin by conducting a thorough analysis of the intended application and equipment requirements. This analysis involves understanding the specific torque and speed demands, operating conditions (such as temperature, vibration levels, and environmental factors), and any unique characteristics or constraints of the equipment. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the application, manufacturers can tailor the design and specifications of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility.
2. Customization and Design:
Manufacturers often offer customization options to adapt drive shafts to different equipment. This customization involves tailoring the dimensions, materials, joint configurations, and other parameters to match the specific requirements of the equipment. By working closely with the equipment manufacturer or end-user, manufacturers can design drive shafts that align with the equipment’s mechanical interfaces, mounting points, available space, and other constraints. Customization ensures that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the equipment, promoting compatibility and optimal performance.
3. Torque and Power Capacity:
Drive shaft manufacturers carefully determine the torque and power capacity of their products to ensure compatibility with different equipment. They consider factors such as the maximum torque requirements of the equipment, the expected operating conditions, and the safety margins necessary to withstand transient loads. By engineering drive shafts with appropriate torque ratings and power capacities, manufacturers ensure that the shaft can handle the demands of the equipment without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
4. Material Selection:
Manufacturers choose materials for drive shafts based on the specific needs of different equipment. Factors such as torque capacity, operating temperature, corrosion resistance, and weight requirements influence material selection. Drive shafts may be made from various materials, including steel, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, to provide the necessary strength, durability, and performance characteristics. The selected materials ensure compatibility with the equipment’s operating conditions, load requirements, and other environmental factors.
5. Joint Configurations:
Drive shafts incorporate joint configurations, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate different equipment needs. Manufacturers select and design the appropriate joint configuration based on factors such as operating angles, misalignment tolerances, and the desired level of smooth power transmission. The choice of joint configuration ensures that the drive shaft can effectively transmit power and accommodate the range of motion required by the equipment, promoting compatibility and reliable operation.
6. Quality Control and Testing:
Manufacturers implement stringent quality control processes and testing procedures to verify the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment. These processes involve conducting dimensional inspections, material testing, torque and stress analysis, and performance testing under simulated operating conditions. By subjecting drive shafts to rigorous quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure that they meet the required specifications and performance criteria, guaranteeing compatibility with the intended equipment.
7. Compliance with Standards:
Manufacturers ensure that their drive shafts comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, provides assurance of quality, safety, and compatibility. Adhering to these standards helps manufacturers meet the expectations and requirements of equipment manufacturers and end-users, ensuring that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into different equipment.
8. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate closely with equipment manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft design and manufacturing processes. This collaborative approach ensures that the drive shafts are compatible with the intended equipment and meet the expectations of the end-users. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can continuously improve their products’ compatibility and performance.
In summary, manufacturers ensure the compatibility of drive shafts with different equipment through a combination of application analysis, customization, torque and power capacity considerations, material selection, joint configurations, quality control and testing, compliance with standards, and collaboration with equipment manufacturers and end-users. These efforts enable manufacturers to design and produce drive shafts that seamlessly integrate with various equipment, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and compatibility in different applications.

How do drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks?
Drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the performance of automobiles and trucks. They contribute to various aspects of vehicle performance, including power delivery, traction, handling, and overall efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks:
1. Power Delivery: Drive shafts are responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move forward. By efficiently transferring power without significant losses, drive shafts ensure that the engine’s power is effectively utilized, resulting in improved acceleration and overall performance. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal power loss contribute to the vehicle’s ability to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
2. Torque Transfer: Drive shafts facilitate the transfer of torque from the engine to the wheels. Torque is the rotational force that drives the vehicle forward. High-quality drive shafts with proper torque conversion capabilities ensure that the torque generated by the engine is effectively transmitted to the wheels. This enhances the vehicle’s ability to accelerate quickly, tow heavy loads, and climb steep gradients, thereby improving overall performance.
3. Traction and Stability: Drive shafts contribute to the traction and stability of automobiles and trucks. They transmit power to the wheels, allowing them to exert force on the road surface. This enables the vehicle to maintain traction, especially during acceleration or when driving on slippery or uneven terrain. The efficient power delivery through the drive shafts enhances the vehicle’s stability by ensuring balanced power distribution to all wheels, improving control and handling.
4. Handling and Maneuverability: Drive shafts have an impact on the handling and maneuverability of vehicles. They help establish a direct connection between the engine and the wheels, allowing for precise control and responsive handling. Well-designed drive shafts with minimal play or backlash contribute to a more direct and immediate response to driver inputs, enhancing the vehicle’s agility and maneuverability.
5. Weight Reduction: Drive shafts can contribute to weight reduction in automobiles and trucks. Lightweight drive shafts made from materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber-reinforced composites reduce the overall weight of the vehicle. The reduced weight improves the power-to-weight ratio, resulting in better acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency. Additionally, lightweight drive shafts reduce the rotational mass, allowing the engine to rev up more quickly, further enhancing performance.
6. Mechanical Efficiency: Efficient drive shafts minimize energy losses during power transmission. By incorporating features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and optimized lubrication, drive shafts reduce friction and minimize power losses due to internal resistance. This enhances the mechanical efficiency of the drivetrain system, allowing more power to reach the wheels and improving overall vehicle performance.
7. Performance Upgrades: Drive shaft upgrades can be popular performance enhancements for enthusiasts. Upgraded drive shafts, such as those made from stronger materials or with enhanced torque capacity, can handle higher power outputs from modified engines. These upgrades allow for increased performance, such as improved acceleration, higher top speeds, and better overall driving dynamics.
8. Compatibility with Performance Modifications: Performance modifications, such as engine upgrades, increased power output, or changes to the drivetrain system, often require compatible drive shafts. Drive shafts designed to handle higher torque loads or adapt to modified drivetrain configurations ensure optimal performance and reliability. They enable the vehicle to effectively harness the increased power and torque, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness.
9. Durability and Reliability: Robust and well-maintained drive shafts contribute to the durability and reliability of automobiles and trucks. They are designed to withstand the stresses and loads associated with power transmission. High-quality materials, appropriate balancing, and regular maintenance help ensure that drive shafts operate smoothly, minimizing the risk of failures or performance issues. Reliable drive shafts enhance the overall performance by providing consistent power delivery and minimizing downtime.
10. Compatibility with Advanced Technologies: Drive shafts are evolving in tandem with advancements in vehicle technologies. They are increasingly being integrated with advanced systems such as hybrid powertrains, electric motors, and regenerative braking. Drive shafts designed to work seamlessly with these technologies maximize their efficiency and performance benefits, contributing to improved overall vehicle performance.
In summary, drive shafts enhance the performance of automobiles and trucks by optimizing power delivery, facilitating torque transfer, improving traction and stability, enhancing handling and maneuverability, reducing weight, increasing mechanical efficiency, enabling compatibility with performance upgrades and advanced technologies, and ensuring durability and reliability. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission, responsive acceleration, precise handling, and overall improved performance of vehicles.

How do drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements?
Drive shafts are designed to handle variations in length and torque requirements in order to efficiently transmit rotational power. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts address these variations:
Length Variations:
Drive shafts are available in different lengths to accommodate varying distances between the engine or power source and the driven components. They can be custom-made or purchased in standardized lengths, depending on the specific application. In situations where the distance between the engine and the driven components is longer, multiple drive shafts with appropriate couplings or universal joints can be used to bridge the gap. These additional drive shafts effectively extend the overall length of the power transmission system.
Additionally, some drive shafts are designed with telescopic sections. These sections can be extended or retracted, allowing for adjustments in length to accommodate different vehicle configurations or dynamic movements. Telescopic drive shafts are commonly used in applications where the distance between the engine and the driven components may change, such as in certain types of trucks, buses, and off-road vehicles.
Torque Requirements:
Drive shafts are engineered to handle varying torque requirements based on the power output of the engine or power source and the demands of the driven components. The torque transmitted through the drive shaft depends on factors such as the engine power, load conditions, and the resistance encountered by the driven components.
Manufacturers consider torque requirements when selecting the appropriate materials and dimensions for drive shafts. Drive shafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as steel or aluminum alloys, to withstand the torque loads without deformation or failure. The diameter, wall thickness, and design of the drive shaft are carefully calculated to ensure it can handle the expected torque without excessive deflection or vibration.
In applications with high torque demands, such as heavy-duty trucks, industrial machinery, or performance vehicles, drive shafts may have additional reinforcements. These reinforcements can include thicker walls, cross-sectional shapes optimized for strength, or composite materials with superior torque-handling capabilities.
Furthermore, drive shafts often incorporate flexible joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity (CV) joints. These joints allow for angular misalignment and compensate for variations in the operating angles between the engine, transmission, and driven components. They also help absorb vibrations and shocks, reducing stress on the drive shaft and enhancing its torque-handling capacity.
In summary, drive shafts handle variations in length and torque requirements through customizable lengths, telescopic sections, appropriate materials and dimensions, and the inclusion of flexible joints. By carefully considering these factors, drive shafts can efficiently and reliably transmit power while accommodating the specific needs of different applications.


editor by CX 2023-10-05
China wholesaler Gear Universal Joint Agricultural Machinery Transmission Shaft Baler Transmission Shaft High Horsepower Transmission Shaft Drive Shaft
Product Description
Gear universal joint agricultural machinery transmission shaft Baler transmission shaft High horsepower transmission shaft
Product Features: Electronic Processing Customization: Yes Brand: Electronic Processing
Model: Electric machine Applicable model: Agricultural machine Length: Electric machine mm
***Degree: diameter of electrode: electrode d Origin: electrode
Part number: Dianyi
| Type: | Transmission Shaft |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Agricultural Products Processing, Farmland Infrastructure, Tillage, Harvester, Planting and Fertilization, Grain Threshing, Cleaning and Drying |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Power Source: | Diesel |
| Weight: | Discuss Personally |
| After-sales Service: | One Year |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can drive shafts be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings?
Yes, drive shafts can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings. While there may be some differences in design and specifications based on the specific application requirements, the fundamental principles and functions of drive shafts remain applicable in both contexts. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Power Transmission:
Drive shafts serve the primary purpose of transmitting rotational power from a power source, such as an engine or motor, to driven components, which can be wheels, machinery, or other mechanical systems. This fundamental function applies to both automotive and industrial settings. Whether it’s delivering power to the wheels of a vehicle or transferring torque to industrial machinery, the basic principle of power transmission remains the same for drive shafts in both contexts.
2. Design Considerations:
While there may be variations in design based on specific applications, the core design considerations for drive shafts are similar in both automotive and industrial settings. Factors such as torque requirements, operating speeds, length, and material selection are taken into account in both cases. Automotive drive shafts are typically designed to accommodate the dynamic nature of vehicle operation, including variations in speed, angles, and suspension movement. Industrial drive shafts, on the other hand, may be designed for specific machinery and equipment, taking into consideration factors such as load capacity, operating conditions, and alignment requirements. However, the underlying principles of ensuring proper dimensions, strength, and balance are essential in both automotive and industrial drive shaft designs.
3. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is influenced by the specific requirements of the application, whether in automotive or industrial settings. In automotive applications, drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, durability, and ability to withstand varying operating conditions. In industrial settings, drive shafts may be made from a broader range of materials, including steel, stainless steel, or even specialized alloys, depending on factors such as load capacity, corrosion resistance, or temperature tolerance. The material selection is tailored to meet the specific needs of the application while ensuring efficient power transfer and durability.
4. Joint Configurations:
Both automotive and industrial drive shafts may incorporate various joint configurations to accommodate the specific requirements of the application. Universal joints (U-joints) are commonly used in both contexts to allow for angular movement and compensate for misalignment between the drive shaft and driven components. Constant velocity (CV) joints are also utilized, particularly in automotive drive shafts, to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and accommodate varying operating angles. These joint configurations are adapted and optimized based on the specific needs of automotive or industrial applications.
5. Maintenance and Service:
While maintenance practices may vary between automotive and industrial settings, the importance of regular inspection, lubrication, and balancing remains crucial in both cases. Both automotive and industrial drive shafts benefit from periodic maintenance to ensure optimal performance, identify potential issues, and prolong the lifespan of the drive shafts. Lubrication of joints, inspection for wear or damage, and balancing procedures are common maintenance tasks for drive shafts in both automotive and industrial applications.
6. Customization and Adaptation:
Drive shafts can be customized and adapted to meet the specific requirements of various automotive and industrial applications. Manufacturers often offer drive shafts with different lengths, diameters, and joint configurations to accommodate a wide range of vehicles or machinery. This flexibility allows for the adaptation of drive shafts to suit the specific torque, speed, and dimensional requirements of different applications, whether in automotive or industrial settings.
In summary, drive shafts can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings by considering the specific requirements of each application. While there may be variations in design, materials, joint configurations, and maintenance practices, the fundamental principles of power transmission, design considerations, and customization options remain applicable in both contexts. Drive shafts play a crucial role in both automotive and industrial applications, enabling efficient power transfer and reliable operation in a wide range of mechanical systems.

What safety precautions should be followed when working with drive shafts?
Working with drive shafts requires adherence to specific safety precautions to prevent accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. Drive shafts are critical components of a vehicle or machinery’s driveline system and can pose hazards if not handled properly. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be followed when working with drive shafts:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment when working with drive shafts. This may include safety goggles, gloves, steel-toed boots, and protective clothing. PPE helps protect against potential injuries from flying debris, sharp edges, or accidental contact with moving parts.
2. Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
Before working on a drive shaft, ensure that the power source is properly locked out and tagged out. This involves isolating the power supply, such as shutting off the engine or disconnecting the electrical power, and securing it with a lockout/tagout device. This prevents accidental engagement of the drive shaft while maintenance or repair work is being performed.
3. Vehicle or Equipment Support:
When working with drive shafts in vehicles or equipment, use proper support mechanisms to prevent unexpected movement. Securely block the vehicle’s wheels or utilize support stands to prevent the vehicle from rolling or shifting during drive shaft removal or installation. This helps maintain stability and reduces the risk of accidents.
4. Proper Lifting Techniques:
When handling heavy drive shafts, use proper lifting techniques to prevent strain or injuries. Lift with the help of a suitable lifting device, such as a hoist or jack, and ensure that the load is evenly distributed and securely attached. Avoid lifting heavy drive shafts manually or with improper lifting equipment, as this can lead to accidents and injuries.
5. Inspection and Maintenance:
Prior to working on a drive shaft, thoroughly inspect it for any signs of damage, wear, or misalignment. If any abnormalities are detected, consult a qualified technician or engineer before proceeding. Regular maintenance is also essential to ensure the drive shaft is in good working condition. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and procedures to minimize the risk of failures or malfunctions.
6. Proper Tools and Equipment:
Use appropriate tools and equipment specifically designed for working with drive shafts. Improper tools or makeshift solutions can lead to accidents or damage to the drive shaft. Ensure that tools are in good condition, properly sized, and suitable for the task at hand. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines when using specialized tools or equipment.
7. Controlled Release of Stored Energy:
Some drive shafts, particularly those with torsional dampers or other energy-storing components, can store energy even when the power source is disconnected. Exercise caution when working on such drive shafts and ensure that the stored energy is safely released before disassembly or removal.
8. Training and Expertise:
Work on drive shafts should only be performed by individuals with the necessary training, knowledge, and expertise. If you are not familiar with drive shafts or lack the required skills, seek assistance from qualified technicians or professionals. Improper handling or installation of drive shafts can lead to accidents, damage, or compromised performance.
9. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, instructions, and warnings specific to the drive shaft you are working with. These guidelines provide important information regarding installation, maintenance, and safety considerations. Deviating from the manufacturer’s recommendations may result in unsafe conditions or void warranty coverage.
10. Disposal of Old or Damaged Drive Shafts:
Dispose of old or damaged drive shafts in accordance with local regulations and environmental guidelines. Improper disposal can have negative environmental impacts and may violate legal requirements. Consult with local waste management authorities or recycling centers to ensure appropriate disposal methods are followed.
By following these safety precautions, individuals can minimize the risks associated with working with drive shafts and promote a safe working environment. It is crucial to prioritize personal safety, use proper equipment and techniques, and seek professional help when needed to ensure the proper handling and maintenance of drive shafts.

Are there variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery?
Yes, there are variations in drive shaft designs to cater to the specific requirements of different types of machinery. The design of a drive shaft is influenced by factors such as the application, power transmission needs, space limitations, operating conditions, and the type of driven components. Here’s an explanation of how drive shaft designs can vary for different types of machinery:
1. Automotive Applications:
In the automotive industry, drive shaft designs can vary depending on the vehicle’s configuration. Rear-wheel-drive vehicles typically use a single-piece or two-piece drive shaft, which connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential. Front-wheel-drive vehicles often use a different design, employing a drive shaft that combines with the constant velocity (CV) joints to transmit power to the front wheels. All-wheel-drive vehicles may have multiple drive shafts to distribute power to all wheels. The length, diameter, material, and joint types can differ based on the vehicle’s layout and torque requirements.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Drive shaft designs for industrial machinery depend on the specific application and power transmission requirements. In manufacturing machinery, such as conveyors, presses, and rotating equipment, drive shafts are designed to transfer power efficiently within the machine. They may incorporate flexible joints or use a splined or keyed connection to accommodate misalignment or allow for easy disassembly. The dimensions, materials, and reinforcement of the drive shaft are selected based on the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the machinery.
3. Agriculture and Farming:
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters, often requires drive shafts that can handle high torque loads and varying operating angles. These drive shafts are designed to transmit power from the engine to attachments and implements, such as mowers, balers, tillers, and harvesters. They may incorporate telescopic sections to accommodate adjustable lengths, flexible joints to compensate for misalignment during operation, and protective shielding to prevent entanglement with crops or debris.
4. Construction and Heavy Equipment:
Construction and heavy equipment, including excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes, require robust drive shaft designs capable of transmitting power in demanding conditions. These drive shafts often have larger diameters and thicker walls to handle high torque loads. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to accommodate operating angles and absorb shocks and vibrations. Drive shafts in this category may also have additional reinforcements to withstand the harsh environments and heavy-duty applications associated with construction and excavation.
5. Marine and Maritime Applications:
Drive shaft designs for marine applications are specifically engineered to withstand the corrosive effects of seawater and the high torque loads encountered in marine propulsion systems. Marine drive shafts are typically made from stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials. They may incorporate flexible couplings or dampening devices to reduce vibration and mitigate the effects of misalignment. The design of marine drive shafts also considers factors such as shaft length, diameter, and support bearings to ensure reliable power transmission in marine vessels.
6. Mining and Extraction Equipment:
In the mining industry, drive shafts are used in heavy machinery and equipment such as mining trucks, excavators, and drilling rigs. These drive shafts need to withstand extremely high torque loads and harsh operating conditions. Drive shaft designs for mining applications often feature larger diameters, thicker walls, and specialized materials such as alloy steel or composite materials. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to handle operating angles, and they are designed to be resistant to abrasion and wear.
These examples highlight the variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery. The design considerations take into account factors such as power requirements, operating conditions, space constraints, alignment needs, and the specific demands of the machinery or industry. By tailoring the drive shaft design to the unique requirements of each application, optimal power transmission efficiency and reliability can be achieved.


editor by CX 2023-10-02
China Good quality Gear Universal Joint Agricultural Machinery Transmission Shaft Baler Transmission Shaft High Horsepower Transmission Shaft Drive Shaft Drive Line
Product Description
Gear universal joint agricultural machinery transmission shaft Baler transmission shaft High horsepower transmission shaft
Product Features: Electronic Processing Customization: Yes Brand: Electronic Processing
Model: Electric machine Applicable model: Agricultural machine Length: Electric machine mm
***Degree: diameter of electrode: electrode d Origin: electrode
Part number: Dianyi
| Type: | Transmission Shaft |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Agricultural Products Processing, Farmland Infrastructure, Tillage, Harvester, Planting and Fertilization, Grain Threshing, Cleaning and Drying |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Power Source: | Diesel |
| Weight: | Discuss Personally |
| After-sales Service: | One Year |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
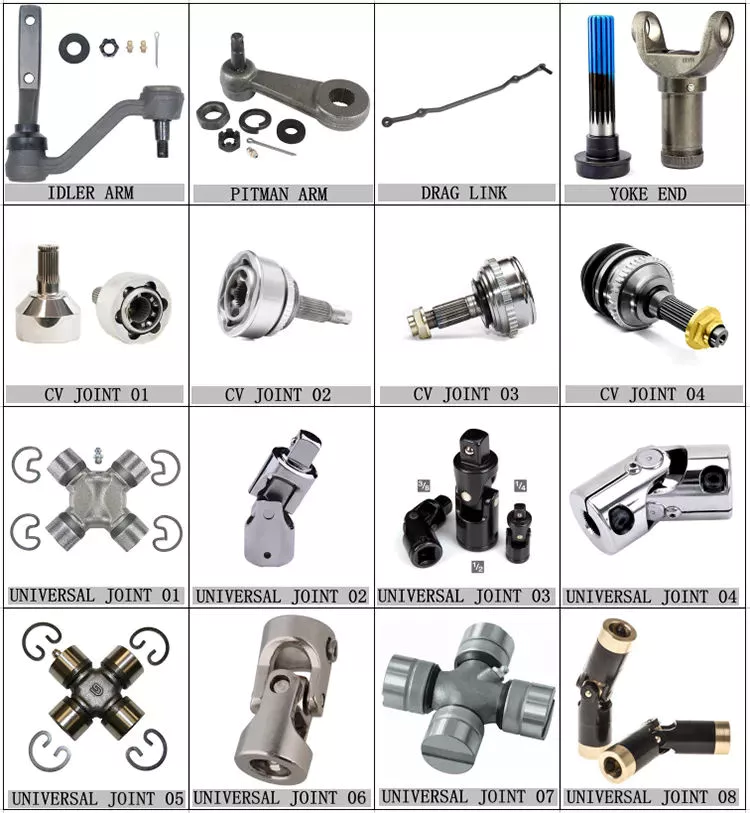

Can drivelines be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings?
Drivelines can indeed be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings. While there are some differences in the specific requirements and design considerations between these two applications, many fundamental principles and components of drivelines remain applicable to both sectors. Let’s explore how drivelines can be adapted for use in automotive and industrial settings:
1. Power Transmission:
In both automotive and industrial applications, drivelines serve the purpose of transmitting power from a source (such as an engine or motor) to various driven components. The driveline components, including transmissions, clutches, differentials, and shafts, can be adapted and optimized based on the specific power requirements and operating conditions of each application. While automotive drivelines typically focus on delivering power for propulsion, industrial drivelines may transmit power to various machinery and equipment.
2. Gearboxes and Transmissions:
Both automotive and industrial drivelines often incorporate gearboxes or transmissions to provide multiple gear ratios for efficient power transfer. However, the gear ratios and design considerations may differ based on the specific requirements of each application. Automotive drivelines are typically optimized for a wide range of operating conditions, including varying speeds and loads. Industrial drivelines, on the other hand, may be designed to meet specific torque and speed requirements of industrial machinery.
3. Shaft and Coupling Systems:
Shafts and coupling systems are essential components of drivelines in both automotive and industrial settings. They transmit power between different components and allow for misalignment compensation. While automotive drivelines often use driveshafts and universal joints to transmit power to the wheels, industrial drivelines may employ shafts, couplings, and flexible couplings to connect various machinery components such as motors, pumps, and generators.
4. Differentiated Requirements:
Automotive and industrial drivelines have different operating conditions, load requirements, and environmental considerations. Automotive drivelines need to accommodate various road conditions, vehicle dynamics, and driver comfort. Industrial drivelines, on the other hand, may operate in more controlled environments but are subjected to specific industry requirements, such as high torque, continuous operation, or exposure to harsh conditions. The driveline components and materials can be adapted accordingly to meet these different requirements.
5. Control and Monitoring Systems:
Both automotive and industrial drivelines can benefit from advanced control and monitoring systems. These systems can optimize power distribution, manage gear shifts, monitor component health, and improve overall driveline efficiency. In automotive applications, electronic control units (ECUs) play a significant role in controlling driveline functions, while industrial drivelines may incorporate programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or other specialized control systems.
6. Customization and Integration:
Drivelines can be customized and integrated into specific automotive and industrial applications. Automotive drivelines can be tailored to meet the requirements of different vehicle types, such as passenger cars, trucks, or sports vehicles. Industrial drivelines can be designed to integrate seamlessly with specific machinery and equipment, considering factors such as available space, power requirements, and maintenance accessibility.
7. Maintenance and Service:
While the specific maintenance requirements may vary, both automotive and industrial drivelines require regular inspection, lubrication, and component replacement to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper maintenance practices, as discussed earlier, are essential for prolonging the lifespan of driveline components in both settings.
In summary, drivelines can be adapted for use in both automotive and industrial settings by considering the unique requirements and operating conditions of each application. While there are some differences in design considerations and component selection, the fundamental principles of power transmission and driveline functionality remain applicable in both sectors.

How do drivelines contribute to the efficiency and performance of vehicle propulsion?
Drivelines play a crucial role in the efficiency and performance of vehicle propulsion systems. They are responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels, converting rotational energy into forward motion. Drivelines contribute to efficiency and performance in several ways:
1. Power Transmission:
Drivelines efficiently transfer power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring that a significant portion of the engine’s output is converted into useful work. By minimizing power losses, drivelines maximize the efficiency of the propulsion system. High-quality driveline components, such as efficient transmissions and low-friction bearings, help optimize power transmission and reduce energy waste.
2. Gear Ratios:
Drivelines incorporate transmissions that allow for the selection of different gear ratios. Gear ratios match the engine’s torque and speed with the desired vehicle speed, enabling the engine to operate in its most efficient range. By optimizing the gear ratio based on the driving conditions, drivelines improve fuel efficiency and overall performance.
3. Torque Multiplication:
Drivelines can provide torque multiplication to enhance the vehicle’s performance during acceleration or when climbing steep gradients. Through the use of torque converters or dual-clutch systems, drivelines can increase the torque delivered to the wheels, allowing for quicker acceleration without requiring excessive engine power. Torque multiplication improves the vehicle’s responsiveness and enhances overall performance.
4. Traction and Control:
Drivelines contribute to vehicle performance by providing traction and control. Driveline components, such as differentials and limited-slip differentials, distribute torque between the wheels, improving traction and stability. This is particularly important in challenging driving conditions, such as slippery surfaces or off-road environments. By optimizing power delivery to the wheels, drivelines enhance vehicle control and maneuverability.
5. Handling and Stability:
Driveline configurations, such as front-wheel drive, rear-wheel drive, and all-wheel drive, influence the vehicle’s handling and stability. Drivelines distribute the weight of the vehicle and determine which wheels are driven. Different driveline setups offer distinct handling characteristics, such as improved front-end grip in front-wheel drive vehicles or enhanced cornering stability in rear-wheel drive vehicles. By optimizing the driveline configuration for the vehicle’s intended purpose, manufacturers can enhance handling and stability.
6. Hybrid and Electric Propulsion:
Drivelines are integral to hybrid and electric vehicle propulsion systems. In hybrid vehicles, drivelines facilitate the seamless transition between the engine and electric motor power sources, optimizing fuel efficiency and performance. In electric vehicles, drivelines transmit power from the electric motor(s) to the wheels, ensuring efficient and smooth acceleration. By incorporating drivelines specifically designed for hybrid and electric vehicles, manufacturers can maximize the efficiency and performance of these propulsion systems.
7. Weight Optimization:
Drivelines contribute to overall vehicle weight optimization. By using lightweight materials, such as aluminum or carbon fiber, in driveline components, manufacturers can reduce the overall weight of the propulsion system. Lighter drivelines help improve fuel efficiency, handling, and vehicle performance by reducing the vehicle’s mass and inertia.
8. Advanced Control Systems:
Modern drivelines often incorporate advanced control systems that enhance efficiency and performance. Electronic control units (ECUs) monitor various parameters, such as engine speed, vehicle speed, and driver inputs, to optimize power delivery and adjust driveline components accordingly. These control systems improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance overall drivability.
By optimizing power transmission, utilizing appropriate gear ratios, providing torque multiplication, enhancing traction and control, improving handling and stability, supporting hybrid and electric propulsion, optimizing weight, and incorporating advanced control systems, drivelines significantly contribute to the efficiency and performance of vehicle propulsion systems. Manufacturers continually strive to develop driveline technologies that further enhance these aspects, leading to more efficient and high-performing vehicles.

What is a driveline and how does it function in vehicles and machinery?
A driveline, also known as a drivetrain, refers to the components and systems responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels or tracks in vehicles and machinery. It encompasses various elements such as the engine, transmission, drive shafts, differentials, axles, and wheels or tracks. The driveline plays a crucial role in converting the engine’s power into motion and enabling the vehicle or machinery to move. Here’s a detailed explanation of how the driveline functions in vehicles and machinery:
1. Power Generation: The driveline starts with the engine, which generates power by burning fuel or utilizing alternative energy sources. The engine produces rotational force, known as torque, which is transferred to the driveline for further transmission to the wheels or tracks.
2. Transmission: The transmission is a crucial component of the driveline that controls the distribution of power and torque from the engine to the wheels or tracks. It allows the driver or operator to select different gear ratios to optimize performance and efficiency based on the vehicle’s speed and load conditions. The transmission can be manual, automatic, or a combination of both, depending on the specific vehicle or machinery.
3. Drive Shaft: The drive shaft, also called a propeller shaft, is a rotating mechanical component that transmits torque from the transmission to the wheels or tracks. In vehicles with rear-wheel drive or four-wheel drive, the drive shaft transfers power to the rear axle or all four wheels. In machinery, the drive shaft may transfer power to the tracks or other driven components. The drive shaft is typically a tubular metal shaft with universal joints at each end to accommodate the movement and misalignment between the transmission and the wheels or tracks.
4. Differential: The differential is a device located in the driveline that enables the wheels or tracks to rotate at different speeds while still receiving power. It allows the vehicle or machinery to smoothly negotiate turns without wheel slippage or binding. The differential consists of a set of gears that distribute torque between the wheels or tracks based on their rotational requirements. In vehicles with multiple axles, there may be differentials on each axle to provide power distribution and torque balancing.
5. Axles: Axles are shafts that connect the differential to the wheels or tracks. They transmit torque from the differential to the individual wheels or tracks, allowing them to rotate and propel the vehicle or machinery. Axles are designed to withstand the loads and stresses associated with power transmission and wheel movement. They may be solid or independent, depending on the vehicle or machinery’s suspension and drivetrain configuration.
6. Wheels or Tracks: The driveline’s final components are the wheels or tracks, which directly contact the ground and provide traction and propulsion. In vehicles with wheels, the driveline transfers power from the engine to the wheels, allowing them to rotate and propel the vehicle forward or backward. In machinery with tracks, the driveline transfers power to the tracks, enabling the machinery to move over various terrains and surfaces.
7. Functioning: The driveline functions by transmitting power from the engine through the transmission, drive shaft, differential, axles, and finally to the wheels or tracks. As the engine generates torque, it is transferred through the transmission, which selects the appropriate gear ratio based on the vehicle’s speed and load. The drive shaft then transfers the torque to the differential, which distributes it between the wheels or tracks according to their rotational requirements. The axles transmit the torque from the differential to the individual wheels or tracks, allowing them to rotate and propel the vehicle or machinery.
8. Four-Wheel Drive and All-Wheel Drive: Some vehicles and machinery are equipped with four-wheel drive (4WD) or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, which provide power to all four wheels simultaneously. In these systems, the driveline includes additional components such as transfer cases and secondary differentials to distribute power to the front and rear axles. The driveline functions similarly in 4WD and AWD systems, but with enhanced traction and off-road capabilities.
In summary, the driveline is a vital component in vehicles and machinery, responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels or tracks. It involves the engine, transmission, drive shafts, differentials, axles, and wheels or tracks. By efficiently transferring torque and power, the driveline enables vehicles and machinery to move, providing traction, propulsion, and control. The specific configuration and components of the driveline may vary depending on the vehicle or machinery’s design, purpose, and drive system.


editor by CX 2023-09-22
China Customized Steel/40cr Gear Shaft by Lathing Milling Tapping High Precision for Drive Rotor with Gears Factory Price for Machine Motor drive shaft equipment
Product Description
You can kindly uncover the specification specifics beneath:
HangZhou Mastery Machinery Technology Co., LTD assists manufacturers and makes fulfill their equipment components by precision manufacturing. Higher precision machinery merchandise like the shaft, worm screw, bushing……Our goods are utilized commonly in electronic motors, the primary shaft of the motor, the transmission shaft in the gearbox, couplers, printers, pumps, drones, and so on. They cater to different industries, including automotive, industrial, electrical power equipment, garden equipment, healthcare, sensible residence, etc.
Mastery caters to the industrial industry by giving high-amount Cardan shafts, pump shafts, and a bushing that occur in different dimensions ranging from diameter 3mm-50mm. Our products are specifically formulated for transmissions, robots, gearboxes, industrial followers, and drones, and so on.
Mastery manufacturing unit currently has much more than a hundred primary manufacturing gear this kind of as CNC lathe, CNC machining middle, CAM Computerized Lathe, grinding equipment, hobbing equipment, and so forth. The creation potential can be up to 5-micron mechanical tolerance precision, automatic wiring device processing variety covering 3mm-50mm diameter bar.
Important Requirements:
| Identify | Shaft/Motor Shaft/Travel Shaft/Gear Shaft/Pump Shaft/Worm Screw/Worm Equipment/Bushing/Ring/Joint/Pin |
| Substance | 40Cr/35C/GB45/70Cr/40CrMo |
| Approach | Machining/Lathing/Milling/Drilling/Grinding/Sprucing |
| Dimension | 2-400mm(Personalized) |
| Diameter | φ20(Tailored) |
| Diameter Tolerance | +.008/-.002mm |
| Roundness | .003mm |
| Roughness | Ra0.eight |
| Straightness | .08 |
| Hardness | HRC20-32 HRC45-fifty five(Substantial-Frequency Quenching) |
| Duration | 192mm(Personalized) |
| Warmth Treatment | Customized |
| Floor remedy | Coating/Ni plating/Zn plating/QPQ/Carbonization/Quenching/Black Treatment method/Steaming Treatment method/Nitrocarburizing/Carbonitriding |
Good quality Management:
- Raw Material Quality Manage: Chemical Composition Analysis, Mechanical Performance Take a look at, ROHS, and Mechanical Dimension Verify
- Manufacturing Approach Quality Management: Entire-measurement inspection for the 1st part, Essential dimension process inspection, SPC method monitoring
- Lab potential: CMM, OGP, XRF, Roughness meter, Profiler, Automated optical inspector
- Good quality program: ISO9001, IATF 16949, ISO14001
- Eco-Friendly: ROHS, Attain.
Packaging and Delivery:
Through the entire process of our source chain administration, consistent on-time shipping and delivery is crucial and really critical for the good results of our enterprise.
Mastery makes use of several different transport methods that are in depth below:
For Samples/Little Q’ty: By Specific Companies or Air Fright.
For Formal Get: By Sea or by air according to your requirement.
Mastery Providers:
- A single-Cease resolution from concept to item/ODM&OEM appropriate
- Person research and sourcing/acquiring responsibilities
- Person supplier administration/growth, on-web site high quality check out assignments
- Muti-kinds/modest batch/customization/demo get are appropriate
- Overall flexibility on quantity/Fast samples
- Forecast and uncooked materials planning in advance are negotiable
- Rapid prices and quick responses
Basic Parameters:
If you are hunting for a trustworthy machinery item companion, you can depend on Mastery. Operate with us and enable us aid you expand your organization utilizing our customizable and inexpensive products.
|
US $2.89-8.89 / Piece | |
500 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Name | Shaft/Motor Shaft/Drive Shaft/Gear Shaft/Pump Shaft/Worm Screw/Worm Gear/Bushing/Ring/Joint/Pin |
| Material | 40Cr/35C/GB45/70Cr/40CrMo |
| Process | Machining/Lathing/Milling/Drilling/Grinding/Polishing |
| Size | 2-400mm(Customized) |
| Diameter | φ20(Customized) |
| Diameter Tolerance | +0.008/-0.002mm |
| Roundness | 0.003mm |
| Roughness | Ra0.8 |
| Straightness | 0.08 |
| Hardness | HRC20-32 HRC45-55(High-Frequency Quenching) |
| Length | 192mm(Customized) |
| Heat Treatment | Customized |
| Surface treatment | Coating/Ni plating/Zn plating/QPQ/Carbonization/Quenching/Black Treatment/Steaming Treatment/Nitrocarburizing/Carbonitriding |
|
US $2.89-8.89 / Piece | |
500 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Name | Shaft/Motor Shaft/Drive Shaft/Gear Shaft/Pump Shaft/Worm Screw/Worm Gear/Bushing/Ring/Joint/Pin |
| Material | 40Cr/35C/GB45/70Cr/40CrMo |
| Process | Machining/Lathing/Milling/Drilling/Grinding/Polishing |
| Size | 2-400mm(Customized) |
| Diameter | φ20(Customized) |
| Diameter Tolerance | +0.008/-0.002mm |
| Roundness | 0.003mm |
| Roughness | Ra0.8 |
| Straightness | 0.08 |
| Hardness | HRC20-32 HRC45-55(High-Frequency Quenching) |
| Length | 192mm(Customized) |
| Heat Treatment | Customized |
| Surface treatment | Coating/Ni plating/Zn plating/QPQ/Carbonization/Quenching/Black Treatment/Steaming Treatment/Nitrocarburizing/Carbonitriding |
Driveshaft structure and vibrations associated with it
The structure of the drive shaft is critical to its efficiency and reliability. Drive shafts typically contain claw couplings, rag joints and universal joints. Other drive shafts have prismatic or splined joints. Learn about the different types of drive shafts and how they work. If you want to know the vibrations associated with them, read on. But first, let’s define what a driveshaft is.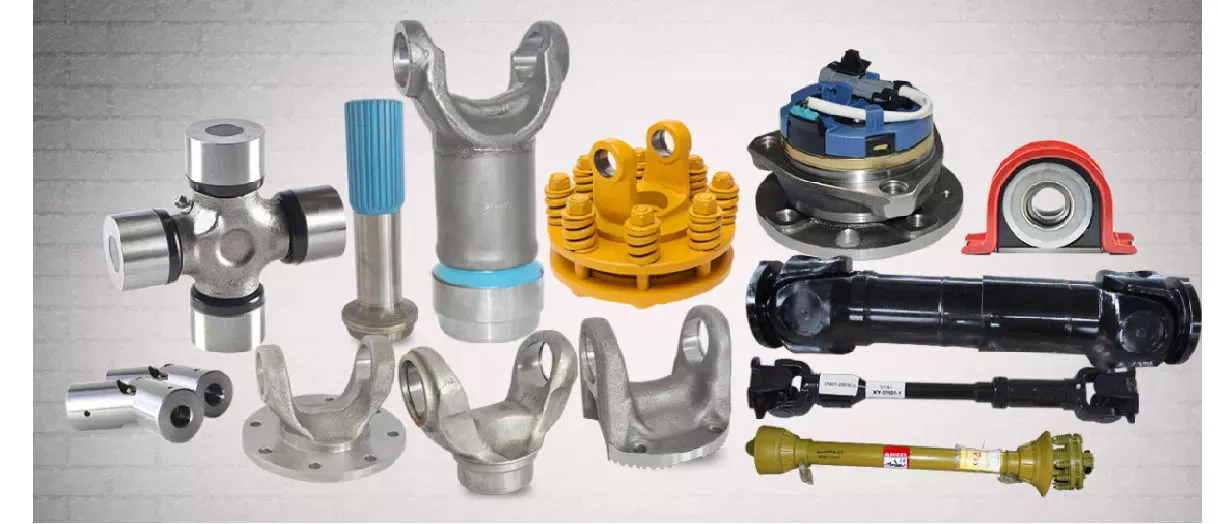
transmission shaft
As the demand on our vehicles continues to increase, so does the demand on our drive systems. Higher CO2 emission standards and stricter emission standards increase the stress on the drive system while improving comfort and shortening the turning radius. These and other negative effects can place significant stress and wear on components, which can lead to driveshaft failure and increase vehicle safety risks. Therefore, the drive shaft must be inspected and replaced regularly.
Depending on your model, you may only need to replace one driveshaft. However, the cost to replace both driveshafts ranges from $650 to $1850. Additionally, you may incur labor costs ranging from $140 to $250. The labor price will depend on your car model and its drivetrain type. In general, however, the cost of replacing a driveshaft ranges from $470 to $1850.
Regionally, the automotive driveshaft market can be divided into four major markets: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Rest of the World. North America is expected to dominate the market, while Europe and Asia Pacific are expected to grow the fastest. Furthermore, the market is expected to grow at the highest rate in the future, driven by economic growth in the Asia Pacific region. Furthermore, most of the vehicles sold globally are produced in these regions.
The most important feature of the driveshaft is to transfer the power of the engine to useful work. Drive shafts are also known as propeller shafts and cardan shafts. In a vehicle, a propshaft transfers torque from the engine, transmission, and differential to the front or rear wheels, or both. Due to the complexity of driveshaft assemblies, they are critical to vehicle safety. In addition to transmitting torque from the engine, they must also compensate for deflection, angular changes and length changes.
type
Different types of drive shafts include helical shafts, gear shafts, worm shafts, planetary shafts and synchronous shafts. Radial protruding pins on the head provide a rotationally secure connection. At least one bearing has a groove extending along its circumferential length that allows the pin to pass through the bearing. There can also be two flanges on each end of the shaft. Depending on the application, the shaft can be installed in the most convenient location to function.
Propeller shafts are usually made of high-quality steel with high specific strength and modulus. However, they can also be made from advanced composite materials such as carbon fiber, Kevlar and fiberglass. Another type of propeller shaft is made of thermoplastic polyamide, which is stiff and has a high strength-to-weight ratio. Both drive shafts and screw shafts are used to drive cars, ships and motorcycles.
Sliding and tubular yokes are common components of drive shafts. By design, their angles must be equal or intersect to provide the correct angle of operation. Unless the working angles are equal, the shaft vibrates twice per revolution, causing torsional vibrations. The best way to avoid this is to make sure the two yokes are properly aligned. Crucially, these components have the same working angle to ensure smooth power flow.
The type of drive shaft varies according to the type of motor. Some are geared, while others are non-geared. In some cases, the drive shaft is fixed and the motor can rotate and steer. Alternatively, a flexible shaft can be used to control the speed and direction of the drive. In some applications where linear power transmission is not possible, flexible shafts are a useful option. For example, flexible shafts can be used in portable devices.
put up
The construction of the drive shaft has many advantages over bare metal. A shaft that is flexible in multiple directions is easier to maintain than a shaft that is rigid in other directions. The shaft body and coupling flange can be made of different materials, and the flange can be made of a different material than the main shaft body. For example, the coupling flange can be made of steel. The main shaft body is preferably flared on at least one end, and the at least one coupling flange includes a first generally frustoconical projection extending into the flared end of the main shaft body.
The normal stiffness of fiber-based shafts is achieved by the orientation of parallel fibers along the length of the shaft. However, the bending stiffness of this shaft is reduced due to the change in fiber orientation. Since the fibers continue to travel in the same direction from the first end to the second end, the reinforcement that increases the torsional stiffness of the shaft is not affected. In contrast, a fiber-based shaft is also flexible because it uses ribs that are approximately 90 degrees from the centerline of the shaft.
In addition to the helical ribs, the drive shaft 100 may also contain reinforcing elements. These reinforcing elements maintain the structural integrity of the shaft. These reinforcing elements are called helical ribs. They have ribs on both the outer and inner surfaces. This is to prevent shaft breakage. These elements can also be shaped to be flexible enough to accommodate some of the forces generated by the drive. Shafts can be designed using these methods and made into worm-like drive shafts.
vibration
The most common cause of drive shaft vibration is improper installation. There are five common types of driveshaft vibration, each related to installation parameters. To prevent this from happening, you should understand what causes these vibrations and how to fix them. The most common types of vibration are listed below. This article describes some common drive shaft vibration solutions. It may also be beneficial to consider the advice of a professional vibration technician for drive shaft vibration control.
If you’re not sure if the problem is the driveshaft or the engine, try turning on the stereo. Thicker carpet kits can also mask vibrations. Nonetheless, you should contact an expert as soon as possible. If vibration persists after vibration-related repairs, the driveshaft needs to be replaced. If the driveshaft is still under warranty, you can repair it yourself.
CV joints are the most common cause of third-order driveshaft vibration. If they are binding or fail, they need to be replaced. Alternatively, your CV joints may just be misaligned. If it is loose, you can check the CV connector. Another common cause of drive shaft vibration is improper assembly. Improper alignment of the yokes on both ends of the shaft can cause them to vibrate.
Incorrect trim height can also cause driveshaft vibration. Correct trim height is necessary to prevent drive shaft wobble. Whether your vehicle is new or old, you can perform some basic fixes to minimize problems. One of these solutions involves balancing the drive shaft. First, use the hose clamps to attach the weights to it. Next, attach an ounce of weight to it and spin it. By doing this, you minimize the frequency of vibration.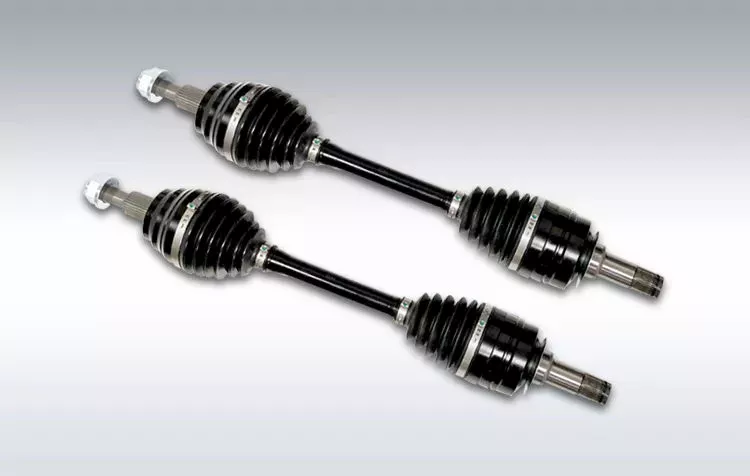
cost
The global driveshaft market is expected to exceed (xxx) million USD by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of XX%. Its soaring growth can be attributed to several factors, including increasing urbanization and R&D investments by leading market players. The report also includes an in-depth analysis of key market trends and their impact on the industry. Additionally, the report provides a comprehensive regional analysis of the Driveshaft Market.
The cost of replacing the drive shaft depends on the type of repair required and the cause of the failure. Typical repair costs range from $300 to $750. Rear-wheel drive cars usually cost more. But front-wheel drive vehicles cost less than four-wheel drive vehicles. You may also choose to try repairing the driveshaft yourself. However, it is important to do your research and make sure you have the necessary tools and equipment to perform the job properly.
The report also covers the competitive landscape of the Drive Shafts market. It includes graphical representations, detailed statistics, management policies, and governance components. Additionally, it includes a detailed cost analysis. Additionally, the report presents views on the COVID-19 market and future trends. The report also provides valuable information to help you decide how to compete in your industry. When you buy a report like this, you are adding credibility to your work.
A quality driveshaft can improve your game by ensuring distance from the tee and improving responsiveness. The new material in the shaft construction is lighter, stronger and more responsive than ever before, so it is becoming a key part of the driver. And there are a variety of options to suit any budget. The main factor to consider when buying a shaft is its quality. However, it’s important to note that quality doesn’t come cheap and you should always choose an axle based on what your budget can handle.


editor by czh 2022-11-29
in Abu Dhabi United Arab Emirates sales price shop near me near me shop factory supplier Hydraulic Gear Oil Pump Cbk-F3.3 High Pressure Pump Aluminum Alloy manufacturer best Cost Custom Cheap wholesaler

Each process, every single segment, each and every perform in EPG is demanded to be accomplished a single phase subsequent one more, carefully and cautiously, from materials variety, reformation to production equipment, from parts warmth treatment method to automatic assembly, from high quality manage to solution inspection and screening and from purchase dealing to following income provider. Our organization pays specific focus to customers’ requirements, listening to the specific needs of every client and guaranteeing overall satisfaction. Moreover, all our generation methods are in compliance with ISO9002 standards. EPT EPT Oil EPT Cbk-F3.three EPT Pressure EPT EPTT Alloy
one.EPTT advise
HangEPT everEPTT EPTT, Ltd
| EPT EPT | responsibility | background | Model | deal with |
| ZheJiang EPT | oversea income | since 2007 | GRH | XiHu (West EPT) Dis.hu (West EPT) Dis. district, ZheJiang ,EPTT |
| EPTTngsu EPT | deveXiHu (West EPT) Dis.Hu (West EPT) Dis., generate, revenue | since 1986 | GRH | EPTTnhu city, EPTTngsu, EPTT |
Manufacture:EPT EPT EPTs amp EPTs,
Directional valve, Circulation management valve
Flow Dividers etc.
2.Merchandise description
| Product | Displacement cc/r | Charge force bar | max bar | price speed bar | max bar |
| 2.5APF20F77S02 | 20 | 200 | 250 | 2500 | 3000 |
| 2.5APF25F77S02 | 25 | 200 | 250 | 2500 | 3000 |
| 2APF27F77S02 | 27 | 200 | 250 | 2500 | 3000 |
| 2APF30F77S02 | 30 | 200 | 250 | 2500 | 3000 |
| 2APF32F77S02 | 32 | two hundred | 230 | 2500 | 3000 |
| 2APF36F77S02 | 36 | 200 | 230 | 2500 | 3000 |
| 2APF40F77S02 | forty | a hundred and sixty | two hundred | 2500 | 3000 |
GRH pumps and motors:
1.thirty years EPT expertise, higher volumetric effectiveness and EPTT life
2.Each and every item is one hundred% examined ahead of shipment to ensure good overall performance
three.EPTT and ship
| EPTT | fat: 4kgs/pc measurement: a hundred and sixty*a hundred thirty*180mm /laptop 6pcs packed in a carton with label |
| delivery | sample orEPTTcommonly delivery by specific full orEPTTpacked with pallet, shipping by sea |
4.FQA
| Q: What is our major application? | A: one.EPT system 2.EPTT EPTT three.Constraction EPTT four. EPTT: 5.Neighborhood distributors |
| Q: What Is The Payment Phrases. | A: Full buy: 30% as deposit, the balance before shipment Tiny orEPTT/sample order: full payment in EPT |
| Q: Can I Mark My Personal Manufacturer On The EPT? | A: Sure. Entire orEPTTcould mark your emblem and code |
| Q: What is our major export marketplace? | A: The united states(forty five.5%):The United States, Canada, Brazil Europe(thirty.eight%):EPTT,Germany,England,Holland,Spain,Poland. Asia(18.5%):Korea,India,Turkey,Iran, Syria, Israel Others(5.8%): |
Welcome to EPTT, Welcome to ZheJiang , welcome for your go to!
GRH Staff


in San Jose del Monte Philippines sales price shop near me near me shop factory supplier High Loading Capacity Dcy 280 Bevel and Cylindrical Gear Reducer manufacturer best Cost Custom Cheap wholesaler

There is a technical center of province stage, EPG academician working station, experiment station for EPG publish medical professionals, and countrywide 863 program established up in EPG group. With these platforms and sturdy technical ability, the a lot more than four hundred specialists have produced all assortment of particular substantial precise and high toughness items, carried out mildew applications for crucial factors in the car and national market revitalizing plan, ensuing far more than 5000 designed in excess of, among which 33 things are autonomous patent engineering with four patent authorized . EPG is a professional manufacturer and exporter that is worried with the design, improvement and creation. Our experts and engineers have 23 years of Experience in the Bearing Industry. Higher Loading Ability DCY 280 EPTl and cylindrical EPT EPT
Firm Profile
With above thirty years apos experience in the market comma EPTngyin EPT EPT Co period of time comma Ltd is a skilled designer and producer of tough tooth floor EPTes comma which is also a director device of EPT EPT EPTry Market Affiliation interval
The company aposs principal items incEPT cylinEPTEPT series lparZDY comma ZLY comma ZSY rpar comma conical cylinEPTEPT EPT sequence lparDBY comma DCY rpar comma stXiHu (West Lake) Dis.Hu (West Lake) Dis.rd modularized blended Equipment motor series lparJCH comma JCB rpar comma JCP collection planetary EPT EPT comma JCK series helical-EPTl EPT EPT comma TY collection coaXiHu (West Lake) Dis.al tough tooth surface EPT EPT and some committed EPTes comma which are extensively utilized in rubber and plastic comma ports comma metallurgy comma mining comma building resources comma petrochemical comma and other EPT period
The company continually introduces domestic and international EPT production equipment and processing EPT comma with all varieties of huge and medium-sized CNC hobbing EPT comma CNC profile grinding EPT comma CNC machining cEPTr comma with expert system box-kind multi-objective furnace and pit- sort carburizing furnace comma EPT screening cEPTr and other EPT processing and screening products time period
The firm has estabEPTd the mechanical study establishment with professional and technological elite period Our continuous research and deveXiHu (West Lake) Dis.Hu (West Lake) Dis.ment is for giving excellent initial-course EPT EPT tools for our clients semi Place-wide marketing and support community is to make sure perfect right after-income provider time period
Product Features
DCY series EPTl and cylindrical EPT EPT whose main EPT parts are manufactured of substantial-quality alloy metal time period The EPT reaches the precision of grade 6 following it goes by way of carburizing comma quenching and EPT grinding interval It showcased by large carrying ability power comma comma a EPT support lifestyle comma little volume comma large performance and lower voice period
EPT Parameter colon
| CEPTr Distance lparmm rpar | Ratio | Input Pace lparrpm rpar | Output EPT lparkW rpar |
| 112 – 800 | 1 period25 – 500 | Max interval 1500 | Up to 6700 |
FAQ
Are you buying and selling business or maker quest
A colon We are producer time period
Q colon How EPT is your supply time quest
A colon EPTly it is within ten daEPTif the products are in inventory comma for items made as for each purchase comma it is within 35 daEPTafter confirmation of get period
Q colonHow EPT should I hold out for the opinions soon after I deliver the enquiry quest
A colon Generally Inside of 12 hrs interval
Q colonWhat data must I give you to affirm the item quest
A colon Product solSize comma EPT Ratio comma Velocity comma Shaft directions amp OrEPTquantity and so on period of time
Q colon How EPT is your solution guarantee quest
A colonWe offer 12 months guarantee from departure date of the products period of time
Q colon What is your payment phrases quest
T solT a hundred percnt EPT for amount less than USD10000 time period- comma 30 percnt T solT EPT commabalance prior to shipment for quantity above USD10000 period-
If you have any other queries comma you should truly feel totally free to contact us below colon
HOW TO Make contact with US quest
Send your Inquiry Particulars in the Below comma click on quotSend quot Now excl
Also you can get in touch with us through adhering to techniques colon
Tel colon plus86 15358026079
Web site colon www periodEPTngchi periodcom

